Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Endo, Yukihiro*; Fukaya, Yuki; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Takayama, Akari*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Hasegawa, Shuji*
Carbon, 157, p.857 - 862, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:76.39(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Hyodo, Toshio*; Wada, Ken*; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Kimura, Masao*; Toge, Nobukazu*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki*; Kawasuso, Atsuo*; Iida, Shimpei*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 791(1), p.012003_1 - 012003_8, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:74.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Yuki; Matsuda, Iwao*; Feng, B.*; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Shamoto, Shinichi
2D Materials (Internet), 3(3), p.035019_1 - 035019_7, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:82.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 (110)(1
(110)(1 2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)
2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)Mochizuki, Izumi*; Ariga, Hiroko*; Fukaya, Yuki; Wada, Ken*; Maekawa, Masaki*; Kawasuso, Atsuo*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Asakura, Kiyotaka*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(9), p.451 - 456, 2016/09
no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Yuki; Entani, Shiro; Sakai, Seiji; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Carbon, 103, p.1 - 4, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:59.26(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 (110)-(1
(110)-(1 2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)
2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)Mochizuki, Izumi*; Ariga, Hiroko*; Fukaya, Yuki; Wada, Ken*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Asakura, Kiyotaka*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18(10), p.7085 - 7092, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:62.79(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Okano, Yoshinobu*; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.73 - 76, 2015/11
The radiation effect on GaAs p-i-n solar cells with quantum dot (QD) in the i-layer was investigated. In a previous work, we particularly noted the degradation of fill-factor (FF) for the QD cells. In this work, to clarify the reason of the FF degradation in QD cells, generation current due to low-energy proton irradiation, which we call ion beam induced current (IBIC), was observed to characterize behavior of the generated minority carrier by the protons in the depletion region where QDs are located. The energy of protons was adjusted to damage the depletion region, and decrease of generation current was measured during the proton irradiation. The results suggest that the serious degradation of FF is caused by a decrease of the carrier collection efficiency in the depletion region due to proton damage.
Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Wada, Ken*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Ichimiya, Ayahiko*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Applied Physics Express, 7(5), p.056601_1 - 056601_4, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.05(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 505, p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.08(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Hyodo, Toshio*; Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Wada, Ken*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Ichimiya, Ayahiko*; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 505(1), p.012001_1 - 012001_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:93.91(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Yuki; Mochizuki, Izumi*; Maekawa, Masaki; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Physical Review B, 88(20), p.205413_1 - 205413_4, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:90.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ge-
Ge- Ga positron source
Ga positron sourceMaekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 308, p.9 - 14, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kawasuso, Atsuo; Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Mochizuki, Izumi; Zhang, H.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 443(1), p.012084_1 - 012084_4, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.26(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Spin-polarized positrons are useful in studying spintronics materials. We are producing positron sources for highly polarized positrons and are developing polarized positron beams using those sources. We investigated some ferromagnets and found that their electron momentum distributions exhibit field-reversal asymmetry. We also found a strong current-induced spin accumulation on Pt surfaces.
Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Mochizuki, Izumi; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 443(1), p.012068_1 - 012068_6, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:97(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
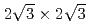 -B surface studied by reflection high-energy positron diffraction
-B surface studied by reflection high-energy positron diffractionFukaya, Yuki; Mochizuki, Izumi; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Physical Review B, 86(3), p.035423_1 - 035423_5, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Mochizuki, Izumi; Fukaya, Yuki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yaji, Koichiro*; Harasawa, Ayumi*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Wada, Ken*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Physical Review B, 85(24), p.245438_1 - 245438_6, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.1(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The atomic configuration and electronic band structure of Pt-induced nanowires on a Ge(001) surface are investigated using scanning tunneling microscopy, reflection high-energy positron diffraction, and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. A previously proposed theoretical model, composed of Ge dimers on the top layer and buried Pt arrays in the second and fourth layers, is found to be the fundamental structure of the observed nanowires. At low temperatures (
 80 K), each Ge dimer is alternately tilted in the surface normal direction (asymmetric), causing a p(
80 K), each Ge dimer is alternately tilted in the surface normal direction (asymmetric), causing a p(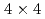 ) periodicity. At high temperatures (
) periodicity. At high temperatures (
 110 K), each Ge dimer is flat with respect to the horizontal axis (symmetric), giving rise to p (
110 K), each Ge dimer is flat with respect to the horizontal axis (symmetric), giving rise to p (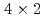 ) periodicity. Upon the above phase transition, the electronic band dispersion related to the Ge dimers in the deeper energy region shifts to the Fermi level.
) periodicity. Upon the above phase transition, the electronic band dispersion related to the Ge dimers in the deeper energy region shifts to the Fermi level.
Mochizuki, Izumi; Fukaya, Yuki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 137, 2012/01
Defect-free quasi-one chain with the single atomic width is reconstructed on the Ge(001) surface by a Pt adsorption of sub-atomic layer. Recently, it has been reported that the atomic chain undergoes the Peierls transition about 80 K. But, the electronic property, the atomic arrangements and displacements in the phase transition are not yet elucidated. Using reflection high-energy positron diffraction (RHEPD), we have reported that the rocking curve in a one-beam condition matches the dynamical calculation assuming the Nano-Wire (NW) model suggested by Vanpoucke et al. However, they have also proposed several NW models with different Pt coverages and have argued that the phase transition derives from the change of the Pt coverage. In this study, we have tried to determine the atomic arrangement, the Pt coverage and the displacements in the phase transition by using RHEPD with a many-beam condition. The rocking curve shows a good agreement with the calculated curve assuming the NW model with the Pt coverage of 0.75 ML, while the curve does not agree with the curves from the Pt coverage of 0.8125 or 0.875 ML. In addition, the change of rocking curves in the phase transition shows that the structural phase transition is caused by the height difference of the topmost Ge dimer atoms making the p(4 4) structure.
4) structure.
 and 4
and 4 ferromagnets using polarized positrons
ferromagnets using polarized positronsKawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
Physical Review B, 85(2), p.024417_1 - 024417_6, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We measured the Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation (DBAR) spectra of 3 (Fe, Co and Ni) and 4
(Fe, Co and Ni) and 4 (Gd, Tb and Dy) ferromagnets under magnetic field by using spin-polarized positrons from a
(Gd, Tb and Dy) ferromagnets under magnetic field by using spin-polarized positrons from a  Ge-
Ge- Ga source. The results showed that the DBAR spectra of these metals have notable different magnetic field dependences. The differences among Fe, Co and Ni reflect that the upper minority spin bands of Fe and Co are nearly empty, while those of Ni are still mostly occupied. For the rare-earth metals, instead of the inner 4
Ga source. The results showed that the DBAR spectra of these metals have notable different magnetic field dependences. The differences among Fe, Co and Ni reflect that the upper minority spin bands of Fe and Co are nearly empty, while those of Ni are still mostly occupied. For the rare-earth metals, instead of the inner 4 electrons, 5d electrons that mediate the exchange interaction of the 4
electrons, 5d electrons that mediate the exchange interaction of the 4 electrons, are primarily responsible for magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra. Furthermore, magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra of Gd, Tb and Dy vanished above the Curie temperatures of the magnetic phase transition for these metals.
electrons, are primarily responsible for magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra. Furthermore, magnetic field effects on the DBAR spectra of Gd, Tb and Dy vanished above the Curie temperatures of the magnetic phase transition for these metals.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
Physical Review B, 83(10), p.100406_1 - 100406_4, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:69.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation (DBAR) spectra of Fe, Co, Ni and Gd polycrystals measured using spin-polarized positrons from a  Ge-
Ge- Ga source in magnetic fields exhibited clear asymmetry upon field reversal. The differential DBAR spectra between field-up and field-down conditions were qualitatively reproduced in calculations considering polarization of positrons and electrons. The magnitudes of the field-reversal asymmetry for the Fe, Co and Ni samples was approximately proportional to the effective magnetization. The magnetic field dependence of the DBAR spectrum for the Fe sample showed hysteresis that is similar to a magnetization curve. These results demonstrate that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy will be useful in studying magnetic substances.
Ga source in magnetic fields exhibited clear asymmetry upon field reversal. The differential DBAR spectra between field-up and field-down conditions were qualitatively reproduced in calculations considering polarization of positrons and electrons. The magnitudes of the field-reversal asymmetry for the Fe, Co and Ni samples was approximately proportional to the effective magnetization. The magnetic field dependence of the DBAR spectrum for the Fe sample showed hysteresis that is similar to a magnetization curve. These results demonstrate that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy will be useful in studying magnetic substances.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
no journal, ,
We review on-going two research projects (Study of surface low-dimensional materials using reflection high-energy positron diffraction(RHEPD), Application of spin-polarized positron beam for magnetic substances) in JAEA. As for the former project, we introduce the principle of RHEPD, the energy-loss process in positrons and the metal-insulator transition of Si(111)-In surface. As for the latter project, we report the production of 68-Ge positron source, its spin polarization and the trial positron annihilation measurements of some magnetic substances.