Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamashita, Susumu; Kondo, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Monji, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.740 - 761, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To confirm the validity of the thermal-hydraulics design tool based on the Ansys Fluent, we used a detailed computational fluid dynamics code named JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER) for the thermal-hydraulics around the beam window (BW) of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS). The Fluent uses the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) model and can quickly calculate the turbulent flow around the BW as a BW design tool. At first, we compared the results of JUPITER with the experimental results using a mock-up BW system in water to confirm the validity of JUPITER. As a result, we confirmed that numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Thus, we showed that JUPITER could be used as a benchmark code. We also performed a benchmark simulation for the Fluent calculation using validated JUPITER to show the applicability of JUPITER as an alternative of experiments. As a result, the mean values around the BW agreed with each other, e.g., the mean velocity profile for stream and horizontal directions. Therefore, we confirmed that JUPITER showed a good performance in validating the thermal-hydraulics design tool as a fluid dynamics solver. Moreover, Fluent has enough accuracy as a thermal-hydraulics design tool for the ADS.
Tobita, Daiki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Yamashita, Susumu; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Sugawara, Takanori
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
Kato, Yuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Ryotaro*; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2015/05
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 1(4), p.TEP0025_1 - TEP0025_11, 2014/08
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2014/07
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-21) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/07
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Dai-62-Kai Riron Oyo Rikigaku Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2013/03
no abstracts in English
Hirabayashi, Masaru; Monji, Hideaki*; Sagawa, Hiroshi*
Jikken Rikigaku, 12(4), p.391 - 397, 2012/12
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/12
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-25-Kai Keisan Rikigaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.693 - 695, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Masaaki; Takita, Hiroki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 78(792), p.1462 - 1465, 2012/08
Water experiment and numerical simulation under thermal interaction conditions between fluid and structure were conducted for a T-junction piping system. In the experiment, temperatures at 2 mm from the wall in fluid, on the wall and at 3 mm inside from the wall in structure along a vertical trace line were measured simultaneously. Numerical results indicated that the fluid temperature distribution near the wall was much affected by the thermal interaction with the structure and that fluid-structure thermal interaction was necessarily considered for thermal fatigue estimation in the thermal striping phenomena.
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/07
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference 2012 (APPEEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2012/03
Tanaka, Masaaki; Takita, Hiroki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Dai-16-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.223 - 224, 2011/06
Water experiment and numerical simulation under thermal interaction conditions between fluid and structure were conducted for a T-junction piping system (T-pipe) consisting of a rectangular duct for main stream and a circular pipe for branch stream. Numerical results were compared with the experimental results and indicated that the fluid-structure thermal interaction was necessarily considered for thermal fatigue estimation in the thermal striping phenomena because fluid temperature distribution near the wall was much affected by the thermal interaction.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Kurokawa, Koji*; Takita, Hiroki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 77(776), p.969 - 973, 2011/04
Numerical simulations for a T-pipe consisting of a rectangular duct for main stream and a circular pipe for branch stream were performed to investigate relation between large-scale eddy structure formation in the mixing area and temperature fluctuation generation on the wall. Moreover, the numerical simulation to investigate thermal interaction between fluid and structure were conducted. Experimental results of temperatures at 2 mm from the wall in fluid, on the wall and at 3 mm inside from the wall in structure were compared with those of the numerical results. The numerical results indicate that the fluid-structure thermal interaction is necessarily considered for thermal fatigue estimation in the thermal striping phenomena.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Monji, Hideaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(9), p.790 - 801, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:86.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)Numerical simulation of thermal striping phenomena in a T-junction piping system (JAEA WATLON experiment) was conducted by using the numerical simulation code "MUGTHES", which has been developed at JAEA. MUGTHES employs the large eddy simulation (LES) approach and standard Smagorinsky model as a turbulence eddy viscosity model with the model coefficient of 0.14 (=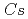 ). Numerical results were validated by comparisons with the experimental results of velocity and temperature. Applicability of MUGTHES to the thermal striping phenomena in the T-pipe was confirmed and the characteristic large-scale hairpin vortex structure which dominates thermal mixing and may cause high-cycle thermal fatigue was revealed.
). Numerical results were validated by comparisons with the experimental results of velocity and temperature. Applicability of MUGTHES to the thermal striping phenomena in the T-pipe was confirmed and the characteristic large-scale hairpin vortex structure which dominates thermal mixing and may cause high-cycle thermal fatigue was revealed.
Ito, Kei; Sakai, Takaaki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Xu, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(9), p.771 - 778, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A gas entrainment (GE) prediction method has been developed to establish design criteria for the large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor (JSFR) systems. In this paper, the evaluation accuracy of gas core lengths is improved by introducing the surface tension effects into the prototype GE prediction method. For the improvement, the mechanical balance between gravitational, centrifugal, and surface tension forces is considered. The improved GE prediction method is validated by analyzing the gas core lengths observed in simple experiments. Results show that the analytical gas core lengths calculated by the improved GE prediction method become shorter in comparison to the prototype GE prediction method, and are in good agreement with the experimental data. In addition, the experimental data under different temperature and surfactant concentration conditions are reproduced by the improved GE prediction method.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Kurokawa, Koji*; Takita, Hiroki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Dai-15-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.221 - 224, 2010/06
Numerical simulations for a T-pipe consisting of a rectangular duct for main stream and a circular pipe for branch stream were performed to investigate relation between large-scale eddy structure formation in the mixing area and temperature fluctuation generation on the wall. Water experiment and numerical simulation in the T-pipe to investigate fluid-structure thermal interaction were conducted. The numerical results indicate that the fluid-structure thermal interaction is necessarily considered for thermal fatigue estimation in the thermal striping phenomena.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Kurokawa, Koji*; Takita, Hiroki*; Monji, Hideaki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 76(763), p.463 - 465, 2010/03
In this study, a simplified T-junction piping system consisting of a rectangular duct for main stream and a circular pipe for branch stream was used as the test section in the water experiment. Time series of instantaneous two-dimensional velocity fields were obtained by PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) in the mixing area. And fluid temperature fluctuations at several positions at 2 mm inside from the wall were also measured by thermo-couples. Focusing on the frequency characteristics, formation of eddy structure in the mixing area and mutual relation between the temperature fluctuation generation and the flow structure were discussed.
Monji, Hideaki*; Shinozaki, Tatsuya*; Kamide, Hideki; Sakai, Takaaki
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 132(1), p.012901_1 - 012901_8, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:64.98(Engineering, Mechanical)This paper deals with characteristics of surface vortex in a cylindrical vessel. One of the characteristics is a gas core length which is important to estimate the onset condition of the gas entrainment but influenced easily by the experimental condition. In the experiment using water, the effects of the water temperature, water level and the surface tension on the gas core length were investigated. The onset condition of the gas entrainment is sometimes estimated by using the Burgers vortex model but the real flow in the vessel is different from the model. The velocity fields were measured by PIV and the velocity gradient of the downward flow was discussed. The proper flow conditions for the Burgers vortex model are a high water level and a high flow rate.