Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Uda, Toshiaki*; Hayashi, Daisuke*; Emori, Minoru*; Kimura, Shun
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(1), p.11 - 20, 2024/06
no abstracts in English
 F
FKatsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Suzuki, Ryo*; Sato, Naoto*; Oda, Ryoya*; Motoyama, Shingo*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Nakashima, Mamoru*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 36(8), p.3697 - 3704, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)A perovskite-type oxynitride BaFeO F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO
F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
Imatomi, Daisuke*; Ishikawa, Ryosuke*; Nakata, Akira*; Ito, Tatsuya; Han, K.*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*
Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 45(1), p.3 - 17, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Chemistry, Physical)Phase equilibria in the Mn-Zn binary system were experimentally determined by chemical composition examination, crystal structure determination, and thermal analysis. Major changes were detected for the  ,
,  , and
, and  phases. The
phases. The  -B2 single-phase region could not be confirmed in the studied system because a disordered body-centered cubic structure, which is identical to the
-B2 single-phase region could not be confirmed in the studied system because a disordered body-centered cubic structure, which is identical to the  Mn phase, was confirmed in a quenched sample from the previously proposed region of
Mn phase, was confirmed in a quenched sample from the previously proposed region of  phase. The
phase. The  phase has been controversial whether the phase is separated into
phase has been controversial whether the phase is separated into  ,
, 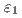 , and
, and 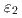 phases or not. By studying a diffusion couple and several alloy compositions, it was established that the
phases or not. By studying a diffusion couple and several alloy compositions, it was established that the  ,
, 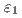 , and
, and 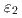 phases are not separate and comprise a single
phases are not separate and comprise a single  phase. Furthermore, the
phase. Furthermore, the  phase is not present in the Zn-rich region of the system because the corresponding invariant reactions were not detected via thermal analysis.
phase is not present in the Zn-rich region of the system because the corresponding invariant reactions were not detected via thermal analysis.
Mori, Hideki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(6), p.063605_1 - 063605_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The introduction of obstacles (e.g., precipitates) for controlling dislocation motion in molecular structures is a prevalent method for designing the mechanical strength of metals. Owing to the nanoscale size of the dislocation core ( 1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the
1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the 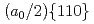 edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Kanazawa, Ryosuke*; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Lobzenko, I.; Tsuru, Tomohito; Koyama, Masanori*; Mori, Hideki*
Scripta Materialia, 207, p.114268_1 - 114268_4, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:80.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)This study reports grain boundary (GB) energy calculations for 46 symmetric-tilt GBs in  -iron using molecular mechanics based on an artificial neural network (ANN) potential and compares the results with calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT), the embedded atom method (EAM), and the modified EAM (MEAM). The results by the ANN potential are in excellent agreement with those of the DFT (5% on average), while the EAM and MEAM significantly differ from the DFT results (about 27% on average). In a uniaxial tensile calculation of GB, the ANN potential reproduced the brittle fracture tendency of the GB observed in the DFT while the EAM and MEAM mistakenly showed ductile behaviors. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the ANN potential in calculating grain boundaries of iron, which is in high demand in modern industry.
-iron using molecular mechanics based on an artificial neural network (ANN) potential and compares the results with calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT), the embedded atom method (EAM), and the modified EAM (MEAM). The results by the ANN potential are in excellent agreement with those of the DFT (5% on average), while the EAM and MEAM significantly differ from the DFT results (about 27% on average). In a uniaxial tensile calculation of GB, the ANN potential reproduced the brittle fracture tendency of the GB observed in the DFT while the EAM and MEAM mistakenly showed ductile behaviors. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the ANN potential in calculating grain boundaries of iron, which is in high demand in modern industry.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear) Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear) F from
F from  O
O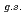 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 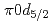 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O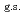 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 glass up to 10 GPa
glass up to 10 GPaUrakawa, Satoru*; Inoue, Toru*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Kohara, Shinji*; Wakabayashi, Daisuke*; Sato, Tomoko*; Funamori, Nobumasa*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Minerals (Internet), 10(1), p.84_1 - 84_13, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.04(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The structure of hydrous amorphous SiO is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO
is fundamental to investigate the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of oxide glasses and magma. The hydrous SiO glass with 13 wt.% D
glass with 13 wt.% D O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO
O was synthesized under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions and its structure was investigated by small angle X-ray scattering, X-ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction experiments at pressures of up to 10 GPa and room temperature. This hydrous glass is separated into a SiO rich major phase and a D
rich major phase and a D O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO
O rich minor phase. Medium-range order of the hydrous glass shrinks compared to the anhydrous SiO glass due to disruption of SiO
glass due to disruption of SiO linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D
linkage by formation of Si-OD deuterioxyl, while the pressure response is similar. Most of D O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO
O molecules are in the small domains and hardly penetrate into SiO major phase.
major phase.
 F and comparison of the structure among perovskite-type oxyfluorides
F and comparison of the structure among perovskite-type oxyfluoridesKatsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Suzuki, Ryo*; Sato, Naoto*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Nakashima, Mamoru*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 279, p.120919_1 - 120919_8, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.06(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Katsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Seramikkusu, 54(9), p.629 - 632, 2019/09
Crystal structure analysis of ABO perovskite-type oxyfluoride were performed by using high-energy synchrotron X-ray measurement. The effect of tolerance factor appeared in the local structure. The average structure of perovskite-type oxyfluoride found to be a cubic structure in the traditional crystal structure analysis.
perovskite-type oxyfluoride were performed by using high-energy synchrotron X-ray measurement. The effect of tolerance factor appeared in the local structure. The average structure of perovskite-type oxyfluoride found to be a cubic structure in the traditional crystal structure analysis.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.46(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 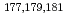 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
Mori, Masanobu*; Sagara, Katsuya*; Arai, Kaori*; Nakatani, Nobutake*; Ohira, Shinichi*; Toda, Kei*; Itabashi, Hideyuki*; Kozaki, Daisuke*; Sugo, Yumi; Watanabe, Shigeki; et al.
Journal of Chromatography A, 1431, p.131 - 137, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.10(Biochemical Research Methods)Takeda, Takeshi; Onuki, Akira*; Kanamori, Daisuke*; Otsu, Iwao
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2016, p.7481793_1 - 7481793_15, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.49(Nuclear Science & Technology) -type oxide PbZnO
-type oxide PbZnO
Mori, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Kie*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 54(23), p.11405 - 11410, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:82.11(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Tamada, Taro; Shinmi, Daisuke*; Ikeda, Masahiro*; Yonezawa, Yasushi*; Kataoka, Shiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Mori, Eiji*; Motoki, Kazuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.17936_1 - 17936_12, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:59.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The fully human monoclonal antibody KMTR2 acts as a strong direct agonist for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2), which is capable of inducing apoptotic cell death without cross-linking. To investigate the mechanism of direct agonistic activity induced by KMTR2, the crystal structure of the extracellular region of TRAIL-R2 and a Fab fragment derived from KMTR2 (KMTR2-Fab) was determined to 2.1  resolution. Two KMTR2-Fabs assembled with the complementarity-determining region 2 of the light chain via two-fold crystallographic symmetry, suggesting that the KMTR2-Fab assembly tended to enhance TRAIL-R2 oligomerization. A single mutation at Asn53 to Arg located at the two-fold interface in the KMTR2 resulted in a loss of its apoptotic activity, although it retained its antigen-binding activity. These results indicate that the strong agonistic activity, such as apoptotic signaling and tumor regression, induced by KMTR2 is attributed to TRAIL-R2 superoligomerization induced by the interdimerization of KMTR2.
resolution. Two KMTR2-Fabs assembled with the complementarity-determining region 2 of the light chain via two-fold crystallographic symmetry, suggesting that the KMTR2-Fab assembly tended to enhance TRAIL-R2 oligomerization. A single mutation at Asn53 to Arg located at the two-fold interface in the KMTR2 resulted in a loss of its apoptotic activity, although it retained its antigen-binding activity. These results indicate that the strong agonistic activity, such as apoptotic signaling and tumor regression, induced by KMTR2 is attributed to TRAIL-R2 superoligomerization induced by the interdimerization of KMTR2.
 as the origin of volume collapse
as the origin of volume collapseYu, R.*; Hojo, Hajime*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Mizokawa, Takashi*; Oka, Kengo*; Kim, H.*; Machida, Akihiko; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(39), p.12719 - 12728, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:72.17(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yamaji, Tatsuya*; Koizumi, Yasuo; Yamazaki, Kohei*; Otake, Hiroyasu*; Hasegawa, Koji*; Onuki, Akira*; Kanamori, Daisuke*
Konsoryu Shimpojiumu 2015 Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2015/08
Experiments of condensing counter-current two-phase flow in a vertical pipe were performed. This study was intended to examine water accumulation in the up-flow side of steam generator U-tubes of a PWR during the reflux cooling stage of a small break LOCA. It has been apprehended that the water accumulation may result in temporary core liquid level depression. The inner diameter and the length of a test flow channel used in the experiments were 18 mm and 4 m, respectively. The experiments were performed by using steam and water at 0.1 MPa. Two kinds of experiments were conducted; visualization experiments by using a transparent test section and quantitative water accumulation evaluation experiments by using a brass test section. Even if water on the inner surface of the test pipe could not flow downward at the lower portion of the test pipe, a part of water became to flow downward at the upper portion of the test pipe since steam velocity decreased because of condensation. Thus, two-phase mixture level was formed in the upper portion of the test pipe, which resulted in the water accumulation in the pipe. The model to predict the water accumulation was proposed. It predicted the water accumulation reasonably well.
 thin films
thin filmsIshigami, Keisuke*; Yoshimatsu, Kohei*; Toyota, Daisuke*; Takizawa, Masaru*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Shibata, Goro*; Harano, Takayuki*; Takahashi, Yukio*; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Verma, V. K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 92(6), p.064402_1 - 064402_5, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:83.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C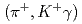 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 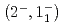 was measured to be
was measured to be 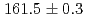 (stat)
(stat)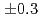 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 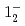 and
and 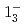 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 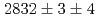 , keV and
, keV and 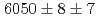 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.