Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Mori, Tetsuya; Ohgama, Kazuya; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 209(7), p.1008 - 1023, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, the sodium radioactivity of  Na and
Na and  Na in the primary system measured in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated, and the reliability of measurements and calculations was examined. The calculated-to-experiment (C/E) values and their uncertainties for
Na in the primary system measured in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated, and the reliability of measurements and calculations was examined. The calculated-to-experiment (C/E) values and their uncertainties for  Na and
Na and  Na radioactivities were 0.97-1.07 and 8.1%-11.0% and 1.03-1.16 and 23.3%-24.1%, respectively, using JENDL-4.0 nuclear data library. The
Na radioactivities were 0.97-1.07 and 8.1%-11.0% and 1.03-1.16 and 23.3%-24.1%, respectively, using JENDL-4.0 nuclear data library. The  Na radioactivity calculated with ENDF/B-VIII.0 was larger by 40% than those calculated with JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.3 due to the
Na radioactivity calculated with ENDF/B-VIII.0 was larger by 40% than those calculated with JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.3 due to the  Na(n,2n) cross-section discrepancy. The importance of the
Na(n,2n) cross-section discrepancy. The importance of the  Na neutron capture effect was also confirmed herein for the accurate evaluation of the
Na neutron capture effect was also confirmed herein for the accurate evaluation of the  Na radioactivity. The experimental data was judged to be useful for validating the calculation method for improving the reliability of the future designs of sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Na radioactivity. The experimental data was judged to be useful for validating the calculation method for improving the reliability of the future designs of sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Mori, Tetsuya; Naganuma, Masayuki; Oki, Shigeo
Nuclear Technology, 209(4), p.532 - 548, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper deals with a conceptual study on a plutonium (Pu) and minor actinide (MA) burning fast reactor core for the distant future phaseout of a fast-reactor fuel cycle after it is commercialized and used for a long time. This burning core aims to reduce the Pu and MA inventories contained in the fuel cycle through multiple recycling. A key point for the core design is the degradation of Pu and MA during multiple recycling. This degradation affects the core feasibility by increasing the sodium void reactivity and decreasing the absolute value of the Doppler constant. A feasible core concept was found by incorporating the following three factors to improve the reactivity coefficients: core flattening, fuel burnup reduction, and the use of silicon carbide (SiC) in the cladding and wrapper tubes. Notably, softening the neutron spectrum using the SiC structural material not only improved the reactivity coefficients but also indirectly mitigated the degradation of Pu and MA. Consequently, the designed core allowed for multiple recycling to continue until the Pu and MA reduced significantly, particularly by about 99% in a phaseout scenario starting from a fast-reactor fleet of 30-GWe nuclear power capacity. Fast reactors were found to have the potential to become self-contained energy systems that can minimize the inventories of Pu they produced themselves, as well as long-lived MA. Fast reactors can be among the important options for environmental burden reduction in the future.
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 =1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
=1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O in transverse magnetic fields
in transverse magnetic fieldsOkutani, Akira*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Kimura, Shojiro*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Kida, Takanori*; Mori, Michiyasu; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Kindo, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(4), p.044704_1 - 044704_9, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Omori, Yasutaka*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sanada, Tetsuya*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Ono, Koji*; Furukawa, Masahide*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 40(3), p.R99 - R140, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:77.11(Environmental Sciences)UNSCEAR and the Nuclear Safety Research Association report the annual effective doses from cosmic rays, terrestrial radiation, inhalation and ingestion from natural sources. In this study, radiation doses from natural radiation sources in Japan were reviewed with the latest knowledge and data. Total annual effective dose from cosmic-ray exposure can be evaluated as 0.29 mSv. The annual effective dose from external exposure to terrestrial radiation for Japanese population can be evaluated as 0.33 mSv using the data of nationwide survey by the National Institute of Radiological Sciences. The Japan Chemical Analysis Center (JCAC) performed the nationwide radon survey using a unified method for radon measurements in indoor, outdoor and workplace. The annual effective dose for radon inhalation was estimated using a current dose conversion factor, and the values were estimated to be 0.50 mSv. The annual effective dose from thoron was reported as 0.09 mSv by UNSCEAR and then the annual effective dose from inhalation can be described as 0.59 mSv. According to the report of large scale survey of foodstuff by JCAC, the effective dose from main radionuclides due to dietary intake can be evaluated to be 0.99 mSv. Finally, Japanese population dose from natural radiation can be assessed as 2.2 mSv which is near to the world average value of 2.4 mSv.
 Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy
scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopyFujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Kamada, Kei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hosaka, Masahito*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 13(8), p.085505_1 - 085505_4, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.01(Physics, Applied)To clarify the existence of cation vacancies in Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y
(Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y Al
Al O
O , the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg
, the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.56(Physics, Nuclear)Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Koji; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-010, 46 Pages, 2020/07
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2020. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2020 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Parker, J. D.*; Harada, Masahide; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.102 - 107, 2020/05
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-006, 66 Pages, 2019/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 4th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-010, 46 Pages, 2019/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2019. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2019 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-015, 89 Pages, 2019/03
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-020, 46 Pages, 2019/01
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2018. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2018 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 13(12), p.e0208909_1 - e0208909_12, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.05(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Imaging of  Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).
Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).  Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV
Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV  rays, and was produced in the
rays, and was produced in the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction with a
Tc reaction with a  Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the
Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the  Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of
Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of  Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three
Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three  rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing
rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing  -ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy
-ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy  -ray emitters such as
-ray emitters such as  Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
 and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCA
and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCALens, L.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 106(12), p.949 - 962, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Online gas-solid adsorption studies with single atom quantities of Hg, Tl, and Pb on SiO and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO
and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO
or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO
surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 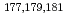 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
Taninaka, Hiroshi; Takegoshi, Atsushi; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Mori, Tetsuya; Usami, Shin
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 101(Part C), p.329 - 337, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present paper describes the evaluation of the power reactivity loss data obtained in the Japanese prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. The most recent analysis on the power reactivity loss measurement (Takano, et al., 2008) is updated considering the following findings: (a) in-core temperature distribution effect, (b) crystalline binding effect, (c) logarithmic averaging of the fuel temperature, (d) localized fuel thermal elongation effect, (e) updated Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library, JENDL-4.0, and (f) refined corrections on the measured value. The influences of the updates are quantitatively identified and the most precise and probable C/E value is derived together with a thorough uncertainty evaluation. As a result, it is revealed that the analysis overestimates the measurement by 4.6% for the measurement uncertainty of 2.0%. The discrepancy is reduced to as small as 1.1% when the core bowing effect is considered, which implies the importance of the core bowing effect in the calculation of the power reactivity loss.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.