Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Furuno, Akiko; Omori, Ryuta*; Tateoka, Hisanori*; Minakawa, Yuya*; Kurihara, Toshiyuki; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Tomita, Yutaka
Pure and Applied Geophysics, 14 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) Okinawa radionuclide monitoring station (JPP37) is located on a hill facing the East China Sea at the center of the main island of Okinawa. It occasionally detects Cs-137, although no nuclear facilities are located on the island. This study focused on the detection of Cs-137 at JPP37 and examined the ratio of simultaneous detections at nearby stations of the International Monitoring System (IMS) of the CTBTO and the relationship with Asian dust from inland East Asia. The detection of Cs-137 in JPP37 from 2020 to 2023, which motivated this study, was high in spring. Among the nine IMS radionuclide stations in East Asia, the detections in Beijing, Lanzhou, and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, were also high in spring. This suggested a high association with the detection of Asian dust in East Asia. Thus, we confirmed the detection of Cs-137 at nine nearby IMS stations when Asian dust was observed at any of the sites in Japan. In addition, we observed that the detection rates were high in Takasaki, Beijing, Lanzhou, and Ulaanbaatar. It can be inferred that the Cs-137 observed mainly in spring at the IMS particulate radionuclide stations in the East Asian region around Japan were likely to pick up the effects of global fallout conveyed by Asian dust. Thereafter, we conducted a preliminary source estimation analysis for Asian dust arrival near Japan. Atmospheric dispersion simulations explained the detection of Cs-137 at nearby IMS particulate radionuclide stations, assuming that Cs-137 was emitted from the desert, the source of the Asian dust.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)Kanamura, Shohei*; Takahashi, Yuya*; Omori, Takashi*; Nohira, Toshiyuki*; Sakamura, Yoshiharu*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Denki Kagaku, 88(3), p.289 - 290, 2020/09
no abstracts in English
 F from
F from  O
O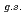 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 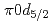 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O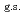 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
 -ray beams
-ray beamsHajima, Ryoichi; Sawamura, Masaru; Nagai, Ryoji; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Angell, C.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.79 - 83, 2015/09
Generation of energy-tunable narrow-bandwidth  -rays via Laser Compton Scattering (LCS) is of great interest for scientific studies and applications of MeV photons which interact with nuclei. We are developing technologies relevant to generation of high-brightness LCS
-rays via Laser Compton Scattering (LCS) is of great interest for scientific studies and applications of MeV photons which interact with nuclei. We are developing technologies relevant to generation of high-brightness LCS  -ray beams. One of the promising applications of such
-ray beams. One of the promising applications of such  -rays is the nondestructive detection and assay of nuclides which are necessary for nuclear security and safeguards. We summarize R-and-D status of LCS
-rays is the nondestructive detection and assay of nuclides which are necessary for nuclear security and safeguards. We summarize R-and-D status of LCS  -ray sources and overview future applications.
-ray sources and overview future applications.
Nagai, Ryoji; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Akagi, Tomoya*; Kosuge, Atsushi*; Honda, Yosuke*; Araki, Sakae*; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*; Urakawa, Junji*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1328 - 1330, 2015/09
Accelerator and laser technologies required for laser Compton scattering (LCS) photon source based on an energy-recovery linac (ERL) have been developed at the Compact ERL (cERL) facility. A high-flux, energy tunable, and monochromatic photon source such as the ERL-based LCS photon source is necessary for nondestructive assay of nuclear materials. For the demonstration of the ERL-based LCS photon generation, a laser enhancement cavity was installed at the recirculation loop of the cERL. The electron beam energy, the laser wavelength, and the collision angle are 20 MeV, 1064 nm, and 18  , respectively. The calculated maximum energy of the LCS photons is about 7 keV. A silicon drift detector (SDD) with active area of 17 mm
, respectively. The calculated maximum energy of the LCS photons is about 7 keV. A silicon drift detector (SDD) with active area of 17 mm placed 16.6 m from the collision point was used for observation of the LCS photons. As a result of the measurement, the flux on the detector, central energy, and energy width of the LCS photons were obtained as 1200/s, 6.91 keV, and 81 eV, respectively.
placed 16.6 m from the collision point was used for observation of the LCS photons. As a result of the measurement, the flux on the detector, central energy, and energy width of the LCS photons were obtained as 1200/s, 6.91 keV, and 81 eV, respectively.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C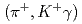 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 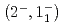 was measured to be
was measured to be 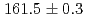 (stat)
(stat)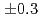 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 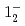 and
and 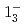 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 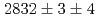 , keV and
, keV and 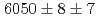 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Nagai, Ryoji; Hajima, Ryoichi; Mori, Michiaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Akagi, Tomoya*; Araki, Sakae*; Honda, Yosuke*; Kosuge, Atsushi*; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*; Urakawa, Junji*
Proceedings of 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '15) (Internet), p.1607 - 1609, 2015/06
Accelerator and laser technologies required for laser Compton scattering (LCS) photon source based on an energy-recovery linac (ERL) have been developed at the Compact ERL (cERL) facility. A high-flux, energy tunable, and monochromatic photon source such as the ERL-based LCS photon source is necessary for nondestructive assay of nuclear materials. For the demonstration of the ERL-based LCS photon generation, a laser enhancement cavity was installed at the recirculation loop of the cERL. The electron beam energy, the laser wavelength, and the collision angle are 20 MeV, 1064 nm, and 18 deg., respectively. The calculated maximum energy of the LCS photons is about 7 keV. A silicon drift detector (SDD) with active area of 17 mm placed 16.6 m from the collision point was used for observation of the LCS photons. As a result of the measurement, the flux on the detector, central energy, and energy width of the LCS photons were obtained as 1200 /s, 6.91 keV, and 81 eV, respectively.
placed 16.6 m from the collision point was used for observation of the LCS photons. As a result of the measurement, the flux on the detector, central energy, and energy width of the LCS photons were obtained as 1200 /s, 6.91 keV, and 81 eV, respectively.
 -rays with energies of 1.17 and 1.33 MeV by a flat Si crystal
-rays with energies of 1.17 and 1.33 MeV by a flat Si crystalMatsuba, Shunya*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Nagai, Ryoji; Sawamura, Masaru; Angell, C.; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Hajima, Ryoichi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(5), p.052203_1 - 052203_5, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.82(Physics, Applied)Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Toshito, Toshiyuki*; Komori, Masataka*; Morishita, Yuki*; Okumura, Satoshi*; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Saito, Yuichi; Kawachi, Naoki; Fujimaki, Shu
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 29(3), p.268 - 275, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:66.08(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging) promoter on Pt electro-catalyst
promoter on Pt electro-catalystFugane, Keisuke*; Mori, Toshiyuki*; Yan, P.*; Masuda, Takuya*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ye, F.*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Auchterlonie, G.*; Drennan, J.*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7(4), p.2698 - 2707, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:64.85(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)no abstracts in English
 -ray nondestructive assay by laser Compton scattered source
-ray nondestructive assay by laser Compton scattered sourceHajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Nagai, Ryoji; Mori, Michiaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Angell, C.; Seya, Michio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 7 Pages, 2015/01
no abstracts in English
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Nagai, Ryoji; Hajima, Ryoichi; Mori, Michiaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Akagi, Tomoya*; Kosuge, Atsushi*; Honda, Yosuke*; Urakawa, Junji*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1328 - 1331, 2014/10
A high intensity  -ray source from the laser Compton scattering (LCS) by an electron beam in an energy-recovery linac (ERL) is a key technology for a nondestructive assay system to identify nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate accelerator and laser technologies required for a LCS photon generation, a LCS photon source is under construction at the Compact ERL (cERL). The LCS photon source consists of a mode-locked fiber laser and a laser enhancement cavity. A beamline and an experimental hatch are also under construction. The commissioning of the LCS photon source will be started in February 2015 and LCS photon generation is scheduled in March 2015.
-ray source from the laser Compton scattering (LCS) by an electron beam in an energy-recovery linac (ERL) is a key technology for a nondestructive assay system to identify nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate accelerator and laser technologies required for a LCS photon generation, a LCS photon source is under construction at the Compact ERL (cERL). The LCS photon source consists of a mode-locked fiber laser and a laser enhancement cavity. A beamline and an experimental hatch are also under construction. The commissioning of the LCS photon source will be started in February 2015 and LCS photon generation is scheduled in March 2015.
Nagai, Ryoji; Hajima, Ryoichi; Mori, Michiaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Akagi, Tomoya*; Kosuge, Atsushi*; Honda, Yosuke*; Urakawa, Junji*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.839 - 842, 2014/10
In order to demonstrate accelerator and laser technologies required for a laser Compton scattering (LCS) photon generation, a LCS photon source is under construction at the Compact ERL (cERL). We considered the flux monitors for the adjustment LCS photon source. A thin scintillator detector and a silicon drift detector are employed as flux monitors and are installed at the upstream part of the LCS beamline. The background signal level due to the bremsstrahlung of the electron beam was measured by a CsI(pure) scintillator. In the result of the measurement, the background signal is acceptable level for the flux monitors.
Nagai, Ryoji; Hajima, Ryoichi; Mori, Michiaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Akagi, Tomoya*; Honda, Yosuke*; Kosuge, Atsushi*; Urakawa, Junji*
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.1940 - 1942, 2014/07
In order to demonstrate required accelerator and laser technologies for a high intensity  -ray source from the laser Compton scattering (LCS), an LCS photon source and the peripheral equipment are under construction at the Compact ERL (cERL) at High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK). The LCS photon source by an electron beam in the energy-recovery linac (ERL) is a key technology for a nondestructive assay system to identify nuclear species. The LCS photon source and the peripheral equipment consist of a mode-locked fiber laser, laser enhancement cavity, beamline, and experimental hatch. The commissioning of the LCS photon source will be started in February 2015.
-ray source from the laser Compton scattering (LCS), an LCS photon source and the peripheral equipment are under construction at the Compact ERL (cERL) at High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK). The LCS photon source by an electron beam in the energy-recovery linac (ERL) is a key technology for a nondestructive assay system to identify nuclear species. The LCS photon source and the peripheral equipment consist of a mode-locked fiber laser, laser enhancement cavity, beamline, and experimental hatch. The commissioning of the LCS photon source will be started in February 2015.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
JAEA-Testing 2014-001, 29 Pages, 2014/05
The penetration tests with solution containing radioactive nuclides were experimented to understand basic data for floor and wall materials of Fukushima Daiichi reactor buildings. The solution prepared from irradiated fuels was used as solution containing radioactive nuclides. The solution was applied to surface of epoxy paint, dried concrete and mortar used as specimens. Dose-rate profiles of direction of depth were given by radiation measurement and grinding of the specimens. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for epoxy paint specimens were not clearly observed and the penetration depths would be within 0.4 mm. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for dried concrete specimens proceeded. The penetration rates were substantially decreased when 16 days have elapsed from start. The dose rates of penetrated dried concrete specimens were reduced to background by grinding-2.0 mm.  -ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
-ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.