Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Anraku, Sohtaro; Matsubara, Isamu*; Morimoto, Kazuya*; Sato, Tsutomu*
Nendo Kagaku, 55(2), p.17 - 30, 2017/00
Anionic radionuclides are important for the long-term safety assessment of Japanese transuranic (TRU) waste disposal facilities. Degradation of cementitious materials used to construct the TRU waste disposal facilities, however, can produce a hyperalkaline leachate and so it is necessary to understand the reaction mechanisms that will control the behavior and fate of anionic radionuclides under these hyperalkaline conditions. An excellent natural analogue site to study relevant reaction mechanisms is provided in Oman where hyperalkaline spring waters (pH  11) from serpentinized peridotites discharge into moderately alkaline rivers. Aragonite was found in all secondary mineral samples, with accessory minerals of calcite, layered double hydroxide (LDH) and brucite. LDH was observed at the high Al concentration springs and brucite at the low Al concentration springs. Calcite was only found close to the springs. Distal calcite formation was inhibited due to high Mg concentrations in the river water. The spatial distribution of minerals therefore implicates the importance of the mixing ratio of spring to river water and the relative chemical compositions of the spring and river waters. Supporting mixing model calculations could successfully reproduce the precipitation of aragonite and LDH. The observed decrease in Ca concentration could be explained by aragonite precipitation. pH exerted a strong control on the precipitation of LDH and so too, therefore, on Al concentration. In the mixing water experiments containing up to 40% river water, LDH and brucite were both oversaturated, but brucite was not always identified by XRD. The possible inhibition of brucite by LDH precipitation was an unexpected result.
11) from serpentinized peridotites discharge into moderately alkaline rivers. Aragonite was found in all secondary mineral samples, with accessory minerals of calcite, layered double hydroxide (LDH) and brucite. LDH was observed at the high Al concentration springs and brucite at the low Al concentration springs. Calcite was only found close to the springs. Distal calcite formation was inhibited due to high Mg concentrations in the river water. The spatial distribution of minerals therefore implicates the importance of the mixing ratio of spring to river water and the relative chemical compositions of the spring and river waters. Supporting mixing model calculations could successfully reproduce the precipitation of aragonite and LDH. The observed decrease in Ca concentration could be explained by aragonite precipitation. pH exerted a strong control on the precipitation of LDH and so too, therefore, on Al concentration. In the mixing water experiments containing up to 40% river water, LDH and brucite were both oversaturated, but brucite was not always identified by XRD. The possible inhibition of brucite by LDH precipitation was an unexpected result.
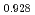 Am
Am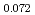 )O
)O at high temperatures
at high temperaturesMatsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1296 - 1302, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:63.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)The oxygen potentials of (Pu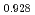 Am
Am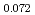 )O
)O were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

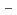
 ,Am
,Am )O
)O (x=0.03, 0.07)
(x=0.03, 0.07)Matsumoto, Taku*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
Development of minor actinide (MA) bearing MOX fuels has been advanced to reduce high level waste. In the development of such new type fuels, it is important to understand physical properties. The thermal conductivity is one of the important properties for development of the fuels, and effect of PuO and AmO
and AmO content on thermal conductivity was investigated. A few thermal conductivity of PuO
content on thermal conductivity was investigated. A few thermal conductivity of PuO were reported previously, which differ widely in the measured data. The data of Am-containing MOX were also measured, but the effect of Am was unclear because of low Am content. In the present work, thermal conductivity of (Pu,Am)O
were reported previously, which differ widely in the measured data. The data of Am-containing MOX were also measured, but the effect of Am was unclear because of low Am content. In the present work, thermal conductivity of (Pu,Am)O was measured, and the effect of Am content was evaluated to contribute to analyze thermal conductivity of MA-bearing oxide fuels.
was measured, and the effect of Am content was evaluated to contribute to analyze thermal conductivity of MA-bearing oxide fuels.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
The diffusion couples of (U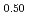 Pu
Pu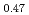 Am
Am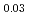 )O
)O and UO
and UO were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of
were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of  G
G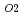 that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
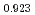 Am
Am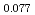 )O
)O
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Hirohisa*; Yokoyama, Shingo*; Watanabe, Yujiro*; Morimoto, Kazuya*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Hatta, Tamao*
no journal, ,
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
O/M ratio dependence of inter-diffusion coefficient of U and Pu at 1873 K was evaluated from MOX and UO diffusion couple. The diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, GB and bulk diffusions were not clearly observed for O/M = 1.96.
diffusion couple. The diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, GB and bulk diffusions were not clearly observed for O/M = 1.96.