Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sheikh, Md. A. R.*; Son, E.*; Kamiyama, Motoki*; Morioka, Toru*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.623 - 633, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:84.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)During core-disruptive accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors, the sedimentation behavior of fragmented debris is crucial for in-vessel retention. The height of the beds formed may influence both the cooling of the bed and the neutronic characteristics. To develop an experimental database of bed formation behavior, a series of experiments using simulant materials, namely, Al O
O , ZrO
, ZrO , and stainless steel, were performed under gravity-driven discharge of solid particles from a nozzle into a quiescent cylindrical water pool. The bed height was measured for particles of different size, density, and sphericity, and an injection nozzle with varying diameter, injection velocity, and injection height. From these experiments, an empirical correlation was established to predict the bed height for both homogeneous and mixed particles for the different properties. This correlation reproduces reasonably well the experimental trend in bed height.
, and stainless steel, were performed under gravity-driven discharge of solid particles from a nozzle into a quiescent cylindrical water pool. The bed height was measured for particles of different size, density, and sphericity, and an injection nozzle with varying diameter, injection velocity, and injection height. From these experiments, an empirical correlation was established to predict the bed height for both homogeneous and mixed particles for the different properties. This correlation reproduces reasonably well the experimental trend in bed height.
Shamsuzzaman, M.*; Horie, Tatsuro*; Fuke, Fusata*; Kamiyama, Motoki*; Morioka, Toru*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Tagami, Hirotaka; Suzuki, Toru*; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 111, p.474 - 486, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:86.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sheikh, M. A. R.*; Son, E.*; Kamiyama, Motoki*; Morioka, Toru*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/11
During the material relocation phase of core disruptive accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors, the sedimentation behavior of fragmented debris leading to the formation of debris beds is crucial for in-vessel retention by debris bed cooling. In this study, a series of experiments using simulant materials was performed to develop an experimental database of bed formation behavior by gravity driven discharge of solid particles from a nozzle into a quiescent cylindrical water pool. The bed height as well as the bed shape was measured. Three types of spherical and non-spherical particles, namely Al O
O , ZrO
, ZrO and stainless steel with different size were employed to study the effect of key experimental parameter on debris bed mound shape. Based on the experimental results, an empirical correlation as experimental database was proposed to predict the particle bed height. The proposed correlation reasonably reproduces the experimental trend of the bed height variation on the crucial factors. This result demonstrates a wide applicability of the proposed empirical model to predict the bed height in terms of all crucial factors with reasonable accuracy.
and stainless steel with different size were employed to study the effect of key experimental parameter on debris bed mound shape. Based on the experimental results, an empirical correlation as experimental database was proposed to predict the particle bed height. The proposed correlation reasonably reproduces the experimental trend of the bed height variation on the crucial factors. This result demonstrates a wide applicability of the proposed empirical model to predict the bed height in terms of all crucial factors with reasonable accuracy.
Sheikh, M. A. R.*; Son, E.*; Kamiyama, Motoki*; Morioka, Toru*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru
Proceedings of 11th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-11) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2016/10
This paper reports an experimental evaluation on debris bed formation characteristics in core-disruptive accidents cogitating the heterogeneous mixture of particles. In the present study, to appraise the characteristics, a series of experiments was accomplished by gravity driven discharge of solid binary mixtures of particles as simulant debris from a nozzle into a quiescent water pool in isothermal condition at room temperature. Currently, two types of spherical particles, namely Alumina and stainless steel with different diameter are employed to study the effect of key experimental parameters on bed mound shape. In experimental investigation both convex and concave mound shapes were perceived based on the effect of particle size and nozzle diameter. The present outcomes could be useful to validate numerical models and simulation codes of particulate debris sedimentation.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.60(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.60(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
 n eigenmodes in reversed shear plasmas in JT-60U negative-ion-based neutral beam injection discharges
n eigenmodes in reversed shear plasmas in JT-60U negative-ion-based neutral beam injection dischargesTakechi, Manabu; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Ishikawa, Masao; Cheng, C. Z.*; Shinohara, Koji; Ozeki, Takahisa; Kusama, Yoshinori; Takeji, Satoru*; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 12(8), p.082509_1 - 082509_7, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:71.67(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Rapid frequency sweeping modes observed in reversed magnetic shear (RS) plasmas on the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute Tokamak 60 Upgrade (JT-60U) have been identified as Reversed-Shear-induced Alfv n Eigenmodes (RSAEs), which are ideal MHD Alfv
n Eigenmodes (RSAEs), which are ideal MHD Alfv n eigenmodes (AEs) localized to the region of minimum safety factor,
n eigenmodes (AEs) localized to the region of minimum safety factor,  , and are excited by negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The chirping and subsequent saturation of the mode frequency are consistent with theoretical predictions for the transition from RSAEs to Toroidal Alfv
, and are excited by negative-ion-based neutral beam injection. The chirping and subsequent saturation of the mode frequency are consistent with theoretical predictions for the transition from RSAEs to Toroidal Alfv n eigenmodes (TAEs). The previously observed rapid frequency sweeping modes in ion cyclotron wave heated plasmas in JT-60U can also be similarly explained. The observed AE amplitude is largest during the transition from RSAEs to TAEs, and fast ion loss is observed when the AE amplitude is largest at this transition. It is preferable to operate outside the transition range of
n eigenmodes (TAEs). The previously observed rapid frequency sweeping modes in ion cyclotron wave heated plasmas in JT-60U can also be similarly explained. The observed AE amplitude is largest during the transition from RSAEs to TAEs, and fast ion loss is observed when the AE amplitude is largest at this transition. It is preferable to operate outside the transition range of 
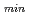 , e.g., 2.4
, e.g., 2.4 

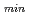
 2.7 for the n = 1 AE to avoid substantial fast ion loss in RS plasmas.
2.7 for the n = 1 AE to avoid substantial fast ion loss in RS plasmas.
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Sugie, Tatsuo; Hatae, Takaki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Kusama, Yoshinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Isayama, Akihiko; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.482 - 511, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The diagnostic system of JT-60U (JT-60upgrade) is composed of about 50 individual diagnostic devices. Recently, the detailed radial profile measurements of plasma parameters have been improved, so that the internal structure of plasmas has been explored. The understanding of plasma confinement has been enhanced by density and temperature fluctuation measurements using a mm-wave reflectometer and electron cyclotron emission measurements respectively. In addition, the real-time control experiments of electron density, neutron yield, radiated power and electron temperature gradient have been carried out successfully by corresponding diagnostic devices. These measurements and the real time control contribute to improving plasma performance. Diagnostic devices for next generation fusion devices such as a CO2 laser interferometer/polarimeter and a CO2 laser collective Thomson scattering system have been developed.
Tobita, Kenji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Shinohara, Koji; Nishitani, Takeo; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kramer, G. J.*; Nemoto, Masahiro*; Kondoh, Takashi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.315 - 326, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Energetic particle experiments in JT-60U are summarized, mainly covering ripple loss and Alfven eigenmodes (AE modes). Significant loss was observed for 85 keV NBI ions and fusion-produced tritons increased when toroidal field ripple at the plasma surface, especially in reversed shear plasma. Measurement of hot spots on the first wall due to ripple loss confirmed agreement with code predictions, validating the modeling incorporated in an orbit-following Monte Carlo code. A variety of AE modes were destabilized in ICRF minority heating and negative-ion-based NBI (N-NBI) heating. Most of the observed modes are gap modes identified to be TAE, EAE and NAE. Interesting finding is pulsating modes accompanying frequency sweep, which were destabilized by N-NBI and sometimes induced a beam ion loss of up to 25%. Also presented are energetic particle issues in auxiliary heating with ICRF and N-NBI.
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ichige, Hisashi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kato, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of 19th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE), p.221 - 225, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
 n eigenmodes driven by Alf
n eigenmodes driven by Alf nic beam ions in JT-60U
nic beam ions in JT-60UShinohara, Koji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Takechi, Manabu; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Ishikawa, Masao*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Tobita, Kenji; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takeji, Satoru; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 41(5), p.603 - 612, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:90.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kramer, G. J.; Iwase, Makoto; Kusama, Yoshinori; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Nemoto, Masahiro; Nishitani, Takeo; Shinohara, Koji; Takeji, Satoru; Tobita, Kenji; Ozeki, Takahisa; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 40(7), p.1383 - 1396, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:77.45(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 n eigenmodes, burst modes and chirping modes in the Alfv
n eigenmodes, burst modes and chirping modes in the Alfv n frequency range driven by negative ion based neutral beam injection in JT-60U
n frequency range driven by negative ion based neutral beam injection in JT-60UKusama, Yoshinori; Kramer, G. J.; Kimura, Haruyuki; Saigusa, Mikio*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Shinohara, Koji; Kondoh, Takashi; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 39(11Y), p.1837 - 1843, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:87.05(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 n eigenmodes and their impact on plasma characteristics in JT-60U
n eigenmodes and their impact on plasma characteristics in JT-60UKusama, Yoshinori; Nazikian, R.*; Kramer, G. J.*; Kimura, Haruyuki; Saigusa, Mikio*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Fu, G. Y.*; Tobita, Kenji; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Fusion Energy 1998, 2, p.537 - 544, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
Kamiyama, Motoki*; Deguchi, Ryohei*; Morioka, Toru*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru
no journal, ,
In order to clarify sedimentation behavior of fuel debris during core disruptive accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors, fundamental experiments were carried out, where solid particles simulating fuel debris were injected into a water pool. Based on the experimental results, sedimentation behavior and bed formation of different particles in properties were characterized.