Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tomita, Takuro*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Minami, Yasuo*; Takei, Ryota*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Eyama, Tsuyoshi*; Takayoshi, Shodai*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Morita, Toshimasa; et al.
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 9(2), p.137 - 142, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.94(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Femtosecond laser ablation processes on platinum, gold, and tungsten were observed by the single shot pump and probe reflective imaging using a soft X-ray laser probe. To avoid the timing error due to the jitter, we adopted a posteriori correction technique by simultaneous measurement of timing between the pump and probe pulses for every single shot, using a soft X-ray streak camera. A clear difference was found in the temporal behavior of the dynamical response of the soft X-ray reflectivity depending on the irradiated laser fluence in these three materials. On the other hand, the narrow dark rings were found in Pt and W, while an additional bright ring was found outside the dark disk in Au. Our result gives the experimental data comparable with various numerical simulations.
Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Morita, Toshimasa; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kageyama, Kei*; Nagatomo, Hideo*; Nishihara, Katsunobu; Sagisaka, Akito; Kotaki, Hideyuki; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 745, p.150 - 163, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:95.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)Morita, Toshimasa
Physics of Plasmas, 21(5), p.053104_1 - 053104_8, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Ion acceleration by using a laser pulse irradiating a disk target which includes hydrogen and carbon is examined using three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. It is shown that over 200 MeV protons can be generated by using a 620 TW, 5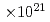 W/cm
W/cm laser pulse. In a polyethylene (CH
laser pulse. In a polyethylene (CH ) target, protons and carbon ions separate and form two layers by radiation pressure acceleration. A strong Coulomb explosion in this situation and Coulomb repulsion of each layer generates high energy protons. A doped target, low density hydrogen within a carbon disk, becomes a double layer target which is comprised of a thin and low density hydrogen disk on the surface of a high-
) target, protons and carbon ions separate and form two layers by radiation pressure acceleration. A strong Coulomb explosion in this situation and Coulomb repulsion of each layer generates high energy protons. A doped target, low density hydrogen within a carbon disk, becomes a double layer target which is comprised of a thin and low density hydrogen disk on the surface of a high- atom layer. This then generates a quasi-monoenergetic proton beam.
atom layer. This then generates a quasi-monoenergetic proton beam.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; Morita, Toshimasa; Sasaki, Akira; Terakawa, Kota*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2012; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.147, p.117 - 120, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We have developed the femto-second laser pump and soft X-ray laser probe system in order to observe the dynamical processes of the femto-second laser ablation. By using this system, we succeed to obtain the temporal evolution of the soft X-ray reflectivity from the laser induced Pt surface. The results lead that the rate of decrease in the reflectivity of the probe beam has a non-linear relation with the pump laser fluence.
Morita, Toshimasa
Physics of Plasmas, 20(9), p.093107_1 - 093107_10, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.37(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The ion acceleration by a hundred TW laser pulse irradiating a double-layer target is examined using three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. For a sufficiently high ion charge-to-mass ratio in the first layer of the target, a strongly inhomogeneous expansion of the first layer occurs due to its Coulomb explosion and the onset of the radiation pressure dominant acceleration regime. The time-varying electric potential of the inhomogeneously expanding ion cloud efficiently accelerates protons. Using the optimum material for the first layer and the optimum laser pulse incidence angle one can obtain a high-energy quasimonoenergetic proton beam.
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Kando, Masaki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(2), p.024501_1 - 024501_6, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.17(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It is shown analytically and by three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations that higher energy protons are obtained by using material with a high charge-to-mass ratio in the first layer of a double-layer target, because a strong Coulomb explosion occurs in such a material. As a result, the protons keep accelerating for a longer time. Using the optimal conditions for the target, it is shown that high energy and high quality protons can be generated.
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Kando, Masaki
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.94 - 96, 2011/03
no abstracts in English
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
AIP Conference Proceedings 1153, p.103 - 112, 2009/07
In proton acceleration by a laser pulse obliquely incident on a double layer target, it is shown by PIC simulations that the energy spread of the generated protons can be reduced by irradiating the laser pulse on to the off-center position of the target. This provides a way to control the proton energy spectrum. The high energy protons are found to come from an area shifted from the initial target center towards the propagation direction of the laser pulse. We show that the high energy protons with much smaller energy spread can be obtained by appropriately adjusting the size and position of the second proton layer.
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
Physics of Plasmas, 16(3), p.033111_1 - 033111_7, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We investigate proton acceleration by a laser pulse obliquely incident on a double layer target via 3D PIC simulations. It is found that the proton beam energy spread changes by the laser irradiation position and it reaches a minimum at certain position. This provides a way to control the proton energy spectrum. We show that by appropriately adjusting the size and position of the second proton layer that high energy protons with much smaller energy spread can be obtained.
Morita, Toshimasa; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Bulanov, S. V.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 51(2), p.024002_1 - 024002_18, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:9.62(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We investigate theoretically and with three dimensional particle-in-cell simulations high quality laser proton acceleration for the oblique incidence of a high intensity laser pulse on a double-layer target. The double-layer target is composed of a high-Z ion layer coated by a thin and narrow hydrogen patch. The highest proton energy gain is achieved at a certain incidence angle at which the fast proton maximum energy is much greater than the case of normal incidence. The fast protons form a tilted bunch which propagates at some angle with the respect to the normal of the target surface, as determined by the proton energy and the incidence angle.
Morita, Toshimasa; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Bulanov, S. V.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
AIP Conference Proceedings 1024, p.114 - 124, 2008/06
We investigate high quality laser proton acceleration with three dimensional particle-in-cell simulations for oblique incidence of the laser pulse on a double-layer target. The double-layer target is composed of a high-Z ion layer coated by a thin and narrow hydrogen patch. The highest proton energy gain is achieved at a certain incidence angle at which the fast proton maximum energy is much grater than the case of normal incidence. The fast protons form a tilted bunch which propagates at some angle with the respect to the normal of the target surface, as determined by the proton energy and the incidence angle.
Morita, Toshimasa; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Bulanov, S. V.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
Physical Review Letters, 100(14), p.145001_1 - 145001_4, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:80.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The laser-driven acceleration of high quality proton beams from a double-layer target, comprised of a high-Z ion layer and a thin disk of hydrogen, is investigated with three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations in the case of oblique incidence of a laser pulse. It is shown that the proton beam energy reaches its maximum at a certain incidence angle of the laser pulse, where it can be much greater than the energy at normal incidence. The proton beam propagates at some angle with respect to the target surface normal, as determined by the proton energy and the incidence angle.
Sagisaka, Akito; Utsumi, Takayuki*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Takai, Mamiko; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; et al.
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1281 - 1284, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Utsumi, Takayuki*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Takai, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kado, Masataka; et al.
Reza Enerugigaku Kenkyu Senta Heisei-17-Nendo Kyodo Kenkyu Seika Hokokusho (Heisei-17-Nen 4-Gatsu  Heisei-18-Nen 3-Gatsu), p.61 - 62, 2006/07
Heisei-18-Nen 3-Gatsu), p.61 - 62, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Takai, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Proceedings of RCNP-JAEA Workshop on Nuclear Photon Science "Hadron-nuclear physics probed by photon", p.195 - 200, 2006/00
High energy ions, electrons, and X-ray are generated from ultrashort pulse high-intensity laser-matter interactions. High-energy protons are observed with a thin-foil target irradiated with a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser at the peak intensity of  2.7
2.7 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . The maximum proton energy is
. The maximum proton energy is  900 keV.
900 keV.
Morita, Toshimasa
no journal, ,
Proton acceleration by using a 620TW, 18J laser pulse of peak intensity of 5 10
10 W/cm
W/cm irradiating a disk target is examined using three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. It is shown that protons are accelerated efficiently to high energy for a "light" material in the target. In addition, using the best conditions for the target, one can generate a proton beam with an energy of 200 MeV.
irradiating a disk target is examined using three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. It is shown that protons are accelerated efficiently to high energy for a "light" material in the target. In addition, using the best conditions for the target, one can generate a proton beam with an energy of 200 MeV.
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Koga, J. K.
no journal, ,
We study the conditions for generating higher energy protons with a lower power and energy laser. The simulations were performed with a 3D electromagnetic code, based on the PIC method. A laser pulse with a power of 620 TW, energy of 18J and peak intensity of 5 10
10 W/cm
W/cm , irradiates a disk target. The higher energy protons can be obtained by using a "light" material for the first layer. As a result of this, a strong Coulomb explosion occurs and movement of the first layer occurs by RPDA (Radiation Pressure Dominant Acceleration). By using a hydrogen disk target, we obtain a proton beam with an energy of 200 MeV and an energy spread of 2.3% by cutting the proton cloud.
, irradiates a disk target. The higher energy protons can be obtained by using a "light" material for the first layer. As a result of this, a strong Coulomb explosion occurs and movement of the first layer occurs by RPDA (Radiation Pressure Dominant Acceleration). By using a hydrogen disk target, we obtain a proton beam with an energy of 200 MeV and an energy spread of 2.3% by cutting the proton cloud.
Koga, J. K.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Morita, Toshimasa; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kageyama, Kei*; Nagatomo, Hideo*; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kotaki, Hideyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Sagisaka, Akito; Nakamura, Shu; Mori, Michiaki; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Hayashi, Yukio; Takai, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Morita, Toshimasa; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English