Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tajikara, Masayoshi*; Yasue, Kenichi; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Tanaka, Norifumi*; Morita, Yoshimune*; Sugai, Toshihiko
Chirigaku Hyoron, 84(2), p.118 - 130, 2011/03
Many papers reported that Quaternary climate and sea-level fluctuations have controlled riverbed elevation in the river basins in the northeastern Japan. However, in the southwestern Japan, such climatic-controlled riverbed fluctuations have not been reported, except a few reports based on uncertain chronological data. In this research, we investigated fluvial terraces along the Tokigawa river that flows through the low relief mountainous areas, and examined whether riverbed fluctuations similar to these in rivers in the northeastern Japan occurred in the river basin. We mapped fluvial terraces based on air photo analysis, and inferred the age and climate at the time of formation of these terraces based on  C dating, tephra analysis, and pollen analysis. Based on results of these analyses, we concluded that the fluvial terraces in the river basin have been formed in consequence of the riverbed fluctuation linked to the climate change.
C dating, tephra analysis, and pollen analysis. Based on results of these analyses, we concluded that the fluvial terraces in the river basin have been formed in consequence of the riverbed fluctuation linked to the climate change.
Morita, Yoshimune*; Kamiya, Chiho*; Sasaki, Toshinori*; Miyagi, Toyohiko*; Sugai, Toshihiko; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Fujiwara, Osamu*
Kikan Chirigaku, 62(4), p.195 - 210, 2010/12
It is assumed that the variation of temperature and the precipitation with the climate change may affect geological environment such as the subsurface water flow. Therefore, as well as global climate change from the past to the present, investigation technology to grasp local climate change is indispensable. A palynological study was carried out using the sediment core taken from the Okute Basin, located in the northeast of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. As a result, it was appeared that in a interglacial epoch, there was much precipitation around this area, and that in a glacial epoch, became colder and more arid, compared with Kinki region in the same latitude. This shows that the modern analog method with pollen data from the sediment of the inland basin is effective technique to estimate a local climate change.
Morita, Yoshimune*; Kamiya, Chiho*; Sasaki, Toshinori*; Miyagi, Toyohiko*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Fujiwara, Osamu*; Moriya, Toshifumi*
Kikan Chirigaku, 58(3), p.123 - 139, 2006/00
A palynological study was carried out using the 25.3 m long sediment core taken from Okute basin, Mizunami city, central Japan. Sediments of this core were accumilated for more than ca. 300,000 years. From the results of pollen analysis, the sediments are devided into 15 pollen assemblages zones. These changes show a repetition of five warm and four cool stages. Each stage corresponds to MIS 9 to 1. Consequently, a temperature of MIS 5 was higher than those of MIS 7 and 9. A temperature of MIS 9 was not so high.
Tajikara, Masayoshi; Yasue, Kenichi; Yanagida, Makoto*; Sugai, Toshihiko; Morita, Yoshimune*; Furusawa, Akira*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tajikara, Masayoshi; Takada, Keita*; Furusawa, Akira*; Morita, Yoshimune*; Sugai, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
We investigated fluvial terraces along the Kaburakawa River, in order to clarify the model of fluvial terrace development. Based on air photo analysis, fluvial terraces in the study area were classified into four categories (Q1-Q4). Existing papers reported that Q3 was formed in Marin Oxygen Isotope Stage (MIS) 2. In this study, we found a fragment of tree which is identified as 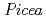 or
or 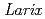 . This fact indicates that Q3 was formed in relatively cold age. Q2 is distributed at higher level than Q3. We found Iizuna-Kamitaru Tephra (Iz-Kt) at the lowermost part of aeolian deposits or uppermost part of overbank deposits in some outcrops of Q2 deposits. Since Iz-Kt is believed to fall at boundary of MIS 5 and 6, we concluded that Q2 deposits was accumulated in MIS 6 and that Q2 was incised in MIS 5.
. This fact indicates that Q3 was formed in relatively cold age. Q2 is distributed at higher level than Q3. We found Iizuna-Kamitaru Tephra (Iz-Kt) at the lowermost part of aeolian deposits or uppermost part of overbank deposits in some outcrops of Q2 deposits. Since Iz-Kt is believed to fall at boundary of MIS 5 and 6, we concluded that Q2 deposits was accumulated in MIS 6 and that Q2 was incised in MIS 5.
Tajikara, Masayoshi; Yasue, Kenichi; Sugiyama, Shinji*; Takada, Keita*; Kato, Takayuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko; Morita, Yoshimune*; Furusawa, Akira*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English