Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Narita, Hirokazu*; Nicolson, R. M.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ito, Fumiyuki*; Morisaku, Kazuko*; Goto, Midori*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Heller, W. T.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.69(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi; Aiba, Nobuyuki
Nuclear Fusion, 53(6), p.063024_1 - 063024_11, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.34(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A mechanism for fast magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied for understanding sawtooth collapse in tokamak discharges. Explosive growth of the tearing mode driven by electron inertia is analytically estimated by using an energy principle with a nonlinear displacement map. Decrease of the potential energy in the nonlinear regime (where the island width exceeds the electron skin depth) is found to be steeper than in the linear regime, resulting in accelerated reconnection. Release of free energy by such ideal fluid motion leads to unsteady and strong convective flow, which is not deterred by the small dissipation effects in high-temperature tokamak plasmas. Direct numerical simulation in slab geometry substantiates the theoretical prediction of the nonlinear growth.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 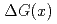 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:175 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 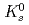 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*
no journal, ,
In collisionless regimes, magnetic reconnection may be accelerated by the mesoscopic effects which play the role of the singular perturbation to the ideal MHD model. Several authors have recently performed noncanonical Hamiltonian formulations of such extended MHD models, for which the dynamical systems approach is expected to provide further understandings of linear and nonlinear reconnection processes. This work focuses on the effect of electron inertia and develops the variational principle for a 2D fluid model including it. By introducing the displacement field of ideal plasma motion, the perturbation expansion around equilibrium state leads to a 2nd-order potential energy (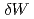 ). The linear growth rate of the reconnecting mode can be reproduced in the same manner as the MHD energy principle. Moreover, this approach is extended to the analysis of the early nonlinear phase of the reconnecting mode.
). The linear growth rate of the reconnecting mode can be reproduced in the same manner as the MHD energy principle. Moreover, this approach is extended to the analysis of the early nonlinear phase of the reconnecting mode.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*
no journal, ,
In mathematical models that describe multi-scale physics, a microscopic effect often acts as a singular perturbation of macroscopic governing equations; it brings a higher derivative term into the equations. Instead of directly solving such a multi-scale problem, it is mathematically convenient and physically informative to solve it with some approximation techniques such as the (renormalized) perturbation method and the asymptotic matching method. In this talk, we present another approach that utilizes the variational principle. This approach is basically applicable to multi-scale "Hamiltonian" systems in which the singular perturbation does not induce energy dissipation but modifies conservation laws. If successful, we can predict strongly nonlinear dynamics by this approach even when other perturbation techniques fail. As an application, we mainly argue the problem of magnetic reconnection in collisionless (i.e., dissipationless) plasma.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*
no journal, ,
Magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied by applying a technique that utilizes the variational principle. Following the fact that the model of collisionless plasma constitutes a Hamiltonian system, the corresponding variational principle is formulated, where the displacement field of the fluid elements is the dynamical variable to be varied. If the potential energy of this variational principle decreases with respect to some displacement field, such the fluid motion turns out to grow with the release of free energy. A rather simple fluid motion is enough to prove the occurrence of spontaneous magnetic reconnection which, moreover, accelerates in the nonlinear phase.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
A mechanism for fast magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied. Nonlinear growth of the tearing mode driven by electron inertia is analytically estimated by invoking the energy principle for the first time. Decrease of potential energy in the nonlinear regime(where the island width exceeds the electron skin depth) is found to be steeper than in the linear regime, resulting in acceleration of the reconnection. Release of free energy by such ideal fluid motion leads to unsteady and strong convective flow.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi; Aiba, Nobuyuki
no journal, ,
Magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied by applying a technique that utilizes variational principle. Following the fact that a model of collisionless (namely, dissipation less) plasma constitutes a Hamiltonian system, the corresponding variational principle is formulated, where the displacement field of fluid elements is the dynamic all variable to be varied. The effect of so-called "electron inertia" is a singular perturbation that modifies the topological invariant of plasma and, hence, allows magnetic reconnection to occur without any dissipation mechanism. If the potential energy of this variational principle decreases for some displacement field (under the modified topological constraint), such the fluid motion turns out to grow with the release of free energy. A rather simple fluid motion is enough to prove the occurrence of spontaneous magnetic reconnection. Decrease of potential energy in the nonlinear regime (where the magnetic island is larger than the width of boundary layer) is found to be steeper than in the linear regime, resulting in acceleration of the reconnection.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi; Aiba, Nobuyuki
no journal, ,
A mechanism for fast magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasma is studied for understanding sawtooth collapse in tokamak discharges. Nonlinear growth of the tearing mode driven by electron inertia is analytically estimated by invoking the energy principle for the first time. Decrease of potential energy in the nonlinear regime (where the island width exceeds the electron skin depth) is found to be steeper than in the linear regime, resulting in acceleration of there connection. Release of free energy by such ideal fluid motion leads to unsteady and strong convective flow, which theoretically corroborates the inertia-driven collapse model of the sawtooth crash.
Hirota, Makoto; Morrison, P. J.*; Ishii, Yasutomo; Yagi, Masatoshi; Aiba, Nobuyuki
no journal, ,
For the purpose of understanding physics of fast magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasmas, acceleration mechanism of the tearing instability is analyzed by taking a variational approach to a two-fluid model. This approach has recently shown that the electronindertia effect induces acceleration of the unstable growth in the nonlinear regime. In this talk, the electron temperature effect is further incorporated into the model, and its role in the acceleration mechanism is discussed.