Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O)
O)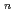 (
( = 1-7) clusters on semi-empirical PM6 potential energy surfaces
= 1-7) clusters on semi-empirical PM6 potential energy surfacesYoshikawa, Takehiro*; Motegi, Haruki*; Kakizaki, Akira*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics, 365(1-2), p.60 - 68, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.84(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations for the hydrogen-bonded glycine-(H O)
O)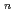 (
( = 1-7) clusters have been carried out using an on-the-fly direct dynamics technique at the semiempiricalPM6 level of theory. In the case of smaller clusters with
= 1-7) clusters have been carried out using an on-the-fly direct dynamics technique at the semiempiricalPM6 level of theory. In the case of smaller clusters with  = 1-3, the simulations show that the clusterstructure takes exclusively the hydrogen-bonded complex between a canonical neutral glycine and a water cluster moiety. In contrast, it was found that proton-exchange processes effectively occur between the COOH carboxylic group and water cluster moiety for
= 1-3, the simulations show that the clusterstructure takes exclusively the hydrogen-bonded complex between a canonical neutral glycine and a water cluster moiety. In contrast, it was found that proton-exchange processes effectively occur between the COOH carboxylic group and water cluster moiety for  = 4-6 clusters although the overall structures are the complex between a neutral glycine and water clusters. In the case of the
= 4-6 clusters although the overall structures are the complex between a neutral glycine and water clusters. In the case of the  = 7 cluster, glycine preferentially takes a zwitterionic form having NH
= 7 cluster, glycine preferentially takes a zwitterionic form having NH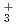 and COO
and COO functional groups.
functional groups.
 O)
O)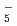 and (D
and (D O)
O)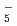
Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Motegi, Haruki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 482(4-6), p.195 - 200, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:28.06(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations have been performed for water anion clusters,(H O)
O)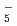 and (D
and (D O)
O)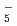 , on the basis of a semiempirical one-electron pseudopotential polarization model. Due to larger zero-point vibrational amplitudes for H atoms than that of D atoms, hydrogen-bond lengths in the (H
, on the basis of a semiempirical one-electron pseudopotential polarization model. Due to larger zero-point vibrational amplitudes for H atoms than that of D atoms, hydrogen-bond lengths in the (H O)
O)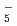 cluster are slightly larger than those in (D
cluster are slightly larger than those in (D O)
O)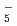 . The distribution of the vertical detachment energies for (H
. The distribution of the vertical detachment energies for (H O)
O)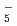 also show a broader feature than that for (D
also show a broader feature than that for (D O)
O)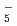 . The present simulations thus demonstrate the importance of nuclear quantum effects in water anion clusters.
. The present simulations thus demonstrate the importance of nuclear quantum effects in water anion clusters.
 SO
SO
 (H
(H O)
O)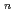 (
( =1-6) on semiempirical PM6 potential surfaces
=1-6) on semiempirical PM6 potential surfacesKakizaki, Akira*; Motegi, Haruki*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Molecular Structure; THEOCHEM, 901(1-3), p.1 - 8, 2009/05
Quantum path-integral molecular dynamics simulations for a series of sulfuric acid clusters, H SO
SO
 (H
(H O)
O)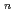 (
( =1-6), were performed using semiempirical PM6 method. It was found that the acid dissociation probability increases with an increase in the cluster size, and that so-called contact-ion-pair structures are dominant in the proton-dissociated clusters. The importance of nuclear quantum effects in the cluster structures and proton-transfer processes is demonstrated.
=1-6), were performed using semiempirical PM6 method. It was found that the acid dissociation probability increases with an increase in the cluster size, and that so-called contact-ion-pair structures are dominant in the proton-dissociated clusters. The importance of nuclear quantum effects in the cluster structures and proton-transfer processes is demonstrated.
Motegi, Haruki*; Kakizaki, Akira*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Taketsugu, Yuriko*; Taketsugu, Tetsuya*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics, 354(1-3), p.38 - 43, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:37.98(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations have been performed to understand the quantum helium solvation structures in the He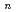 BeO cluster. Our simulations show that one helium atom is strongly bound to BeO to form HeBeO and that the first solvation shell around the HeBeO complex includes roughly 12-14 helium atoms. The present simulations implies that the HeBeO complex could be experimentally detected in large helium clusters using the HENDI technique.
BeO cluster. Our simulations show that one helium atom is strongly bound to BeO to form HeBeO and that the first solvation shell around the HeBeO complex includes roughly 12-14 helium atoms. The present simulations implies that the HeBeO complex could be experimentally detected in large helium clusters using the HENDI technique.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Yan, X.; Shimada, Takahiro*; Motegi, Haruki*; Kai, Satoru*; Otani, Akihito*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English