Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperature
-nonyl N,N-dimethylammonio)-propyl sulfate, present in isotropic solutions above its upper critical solution temperatureTanji, Tamao*; Kusunoki, Yuto*; Nakagawa, Taichi; Takase, Tsugiko*; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hinze, W. L.*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Langmuir, 41(21), p.13184 - 13191, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Fuain Kemikaru, 54(5), p.53 - 60, 2025/05
no abstracts in English
Hirata, Yoshinobu*; Kaneko, Fumitoshi*; Radulescu, A.*; Nishizu, Takahisa*; Katsuno, Nakako*; Imaizumi, Teppei*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
Journal of Applied Glycoscience, 72(1), p.7201102_1 - 7201102_9, 2025/02
A simultaneous measurement system of SANS/FTIR-ATR was applied to record multiple structural changes in potato starch during retrogradation. In the SANS patterns, the shoulder-like peak becomes more pronounced with time. The peak intensity, Imax, which represents the amount of orderly arranged double helical structures, increased over time, showing that starch reassembled orderly on the nanoscale upon retrogradation. In the FTIR-ATR spectra, the increase of the ratio of absorptions at 1042 cm and 1016 cm
and 1016 cm , indicating the amount of short-range ordered structure in starch increased during retrogradation. The time to obtain half of the equilibrium value for
, indicating the amount of short-range ordered structure in starch increased during retrogradation. The time to obtain half of the equilibrium value for 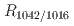 was larger than that for Imax. Changes in the short-range ordered structure of starch were observed to converge prior to changes in the nanostructure. These results indicate that the double-helix structures are initially formed by amylopectin side chains, and then these double-helical structures are arranged orderly.
was larger than that for Imax. Changes in the short-range ordered structure of starch were observed to converge prior to changes in the nanostructure. These results indicate that the double-helix structures are initially formed by amylopectin side chains, and then these double-helical structures are arranged orderly.
 capture and release at high pressures on a unique large-pore mesoporous carbon
capture and release at high pressures on a unique large-pore mesoporous carbonSzab , L.*; Inoue, Mizuki*; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumoto, Yusuke*; Nge, T. T.*; Ismail, E.*; Ichinose, Izumi*; Yamada, Tatsuhiko*
, L.*; Inoue, Mizuki*; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumoto, Yusuke*; Nge, T. T.*; Ismail, E.*; Ichinose, Izumi*; Yamada, Tatsuhiko*
ChemSusChem, p.e202402034_1 - e202402034_13, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Here, we developed a large-pore mesoporous carbon with pore sizes centered around 20-30 nm using a templated technical lignin. During the soft-templating process, unique cylindrical supramolecular assemblies form from the copolymer template, distinct from other systems reported thus far. This peculiar nanostructuring takes place due to the presence of polyethylene glycol (PEG) segments on both the Pluronic template and the PEG- grafted lignin derivative (glycol lignin). A large increase in CO uptake occurs on the resulting large-pore mesoporous carbon at 270 K close to the saturation pressure, owing to capillary condensation.
uptake occurs on the resulting large-pore mesoporous carbon at 270 K close to the saturation pressure, owing to capillary condensation.
Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Yamada, Masako*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Microscopic structures in liquid-liquid extraction, such as structuration between extractants or extracted complexes in bulk organic phases and at interfaces, can influence macroscopic phenomena, such as the distribution behavior of solutes, including extraction efficiency, selectivity, and phase separation of the organic phase. In this study, we correlated the macroscopic behavior of the extraction of Zr(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions with microscopic structural information in order to understand at the molecular level the key factors contributing to the higher metal ion extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system comprising fluorous phosphate (TFP) in perfluorohexane as compared to the analogous organic extraction system comprising organic phosphate (THP) in n-hexane. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, neutron reflectometry, and small-angle neutron scattering revealed the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion, the accumulation of extractant molecules at the interface, and the structuration of extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase, respectively. In the fluorous extraction system, extractant aggregates with were formed after contact with nitric acid. In contrast, in the organic extraction system, only extractant dimers were formed. We speculate that differences in the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion and the structuration of the extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase contribute to the high Zr(IV) extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system. In particular, the size of the aggregates hardly changed with increasing Zr(IV) concentration in the fluorous phase, which may be closely related to the absence of phase splitting in the fluorous extraction system.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okumura, Masahiko; Ueda, Yuki; Saito, Takumi*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yomogida, Takumi; Sazaki, Gen*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 7, p.128_1 - 128_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kumada, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Iwase, Hiroki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 57(Part 3), p.728 - 733, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Guerinoni, E.*; Giusti, F.*; Dourdain, S.*; Dufr che, J.-F.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ueda, Yuki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
che, J.-F.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ueda, Yuki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Zemb, T.*; Pellet-Rostaing, S.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 403, p.124820_1 - 124820_11, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Nakanishi, Yohei*; Shibata, Motoki*; Sawada, Satoshi*; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Mita, Kazuki*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Takenaka, Mikihito*
Polymer, 306, p.127209_1 - 127209_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.19(Polymer Science)Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Hamon, 34(2), p.50 - 53, 2024/05
Spin-contrast-variation (SCV) small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) enabled us to determine structure of nano-ice crystals that were generated in rapidly frozen sugar solution. In the frozen glucose solution, we found that the nano-ice crystals formed a planar structure with a radius larger than several tens of nanometers and a thickness of 2-3 nm, which was close to the critical nucleation size of ice crystals in supercooled water. This result suggests that the glucose molecules were preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then blocked the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Yamada, Masako*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.60(Chemistry, Physical)Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Daisuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Torikai, Naoya*; Amino, Naoya*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(21), p.8797 - 8802, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)We elucidated the entanglement of polybutadiene and silane coupling agent (SCA) molecules bound to Si substrates using spin-contrast-variation (SCV) neutron reflectivity (NR). In an annealed integral blend film of polybutadiene and SCA, a SCA layer generated on the Si substrate was composed of 70 vol. percent SCA molecules extended perpendicularly from the silicon substrate and entangled with 30 vol. percent polybutadiene molecules. By contrast, in an SCA-precoated polybutadiene film, the SCA-precoated layer is composed of densely packed SCA molecules forming crystal-like structure, and thus did not become entangled with the postcoated polybutadiene molecules. This poor entanglement resulted in poor binding between polybutadiene and Si substrate.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Shibayama, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Nanoscale, 16(19), p.9400 - 9405, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:70.50(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A tough carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMF)/ zirconium (Zr) hydrogel was obtained by freeze cross-linking method. The hydrogel was prepared by adding HCl solution containing Zr to frozen CMF and thawing it. The hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for fluoride. This simple gelation method provides useful insight for developing hydrogel-metal complexes.
 -phenylmaleimide
-phenylmaleimideYamazaki, Shun*; Kaneko, Naoya*; Kato, Atsuya*; Watanabe, Kohei*; Aoki, Daisuke*; Taniguchi, Tatsuo*; Karatsu, Takashi*; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okura, Koki*; et al.
Polymer, 298, p.126846_1 - 126846_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:74.19(Polymer Science) He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical)Kumada, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Oba, Yojiro; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Sekine, Yurina; Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1776 - 1783, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:97.57(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The combination of the existing position-sensitive photomultiplier and the  He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
Tsuji, Hayato*; Nakahata, Masaki*; Hishida, Mafumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inoue, Takeru*; Egawa, Yasunobu*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(49), p.11235 - 11241, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.28(Chemistry, Physical)Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Polymer Science)Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.