Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 studied by means of NMR/NQR techniques
studied by means of NMR/NQR techniquesSakai, Hironori; Kurita, Nobuyuki*; Miclea, C. F.*; Movshovich, R.*; Lee, H.-O.*; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA059_1 - SA059_3, 2011/07
The effect of dilute La substitution in Ce La
La RhIn
RhIn (0
(0 x
x 0.07) has been investigated microscopically by nuclear magnetic/quadrupole resonance (NMR/NQR). By the dilute La substitutions, the 4
0.07) has been investigated microscopically by nuclear magnetic/quadrupole resonance (NMR/NQR). By the dilute La substitutions, the 4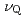 lines for In(1) sites are found to be undisturbed and to have a reasonably narrow width, even in the ordered AF state. These 4
lines for In(1) sites are found to be undisturbed and to have a reasonably narrow width, even in the ordered AF state. These 4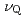 positions in the La-substituted CeRhIn
positions in the La-substituted CeRhIn indicate a decrease of the internal field on In(1) sites, due to the reduction of hyperfine couplings by La substitutions. The spin-lattice relaxation rates (
indicate a decrease of the internal field on In(1) sites, due to the reduction of hyperfine couplings by La substitutions. The spin-lattice relaxation rates (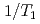 ) using these 4
) using these 4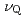 lines at high temperatures can be understood by the reduction of exchange energy and effective moments. On the other hand,
lines at high temperatures can be understood by the reduction of exchange energy and effective moments. On the other hand, 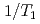 in the AF ordered state can be explained by a gapped Fermi surface and spin fluctuations of uncompensated localized Ce moments near the La ions.
in the AF ordered state can be explained by a gapped Fermi surface and spin fluctuations of uncompensated localized Ce moments near the La ions.
Bauer, E. D.*; Yang, Y.-F.*; Capan, C.*; Urbano, R. R.*; Miclea, C. F.*; Sakai, Hironori; Ronning, F.*; Graf, M. J.*; Balatsky, A. V.*; Movshovich, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(17), p.6857 - 6861, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here, we report a manifestation of electronic inhomogeneity in a strongly correlated  -electron system, using CeCoIn
-electron system, using CeCoIn as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.
as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.