Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Iga, Fumitoshi*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(6), p.064705_1 - 064705_5, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shamoto, Shinichi; Ito, Takashi; Onishi, Hiroaki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(5), p.054429_1 - 054429_9, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:64.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear and magnetic structure and full magnon dispersions of yttrium iron garnet Y Fe
Fe O
O have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of
have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of  -integrated dynamical spin susceptibility
-integrated dynamical spin susceptibility  "(
"( ) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the
) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the  "(
"( ) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
Igarashi, Masayasu*; Matsumoto, Tomohiro*; Yagihashi, Fujio*; Yamashita, Hiroshi*; Ohara, Takashi; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Shimada, Shigeru*
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.140_1 - 140_8, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:68.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(1), p.120 - 127, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:96.13(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) planes of Na
planes of Na CoO
CoO
 yH
yH O
OMoyoshi, Taketo*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Solid State Sciences, 12(5), p.656 - 659, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) CoO
CoO

 D
D O; Neutron scattering
O; Neutron scatteringMoyoshi, Taketo*; Yasui, Yukio*; Soda, Minoru*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(7), p.074705_1 - 074705_6, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron scattering investigations on single crystal Na CoO
CoO y(D
y(D O) have been carried out. Strong 2-D diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordered state of D
O) have been carried out. Strong 2-D diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordered state of D O molecules are observed. Significant scattering has been also observed for phonons originating from the vibrations of the short-range ordered D
O molecules are observed. Significant scattering has been also observed for phonons originating from the vibrations of the short-range ordered D O molecules. No firm evidence for the magnetic fluctuations has been found for the hydrated superconducting component Na
O molecules. No firm evidence for the magnetic fluctuations has been found for the hydrated superconducting component Na CoO
CoO y(D
y(D O), while the very weak intensity modulation observed in the scans along (1/2,1/2,l) suggests the existence of the antiferromagnetic fluctuations in the non-hydrated parts of the sample.
O), while the very weak intensity modulation observed in the scans along (1/2,1/2,l) suggests the existence of the antiferromagnetic fluctuations in the non-hydrated parts of the sample.
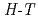 phase diagrams of Kagom
phase diagrams of Kagom staircase compound Co
staircase compound Co V
V O
O
Yasui, Yukio*; Kobayashi, Yusuke*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Soda, Minoru*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
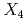 (
(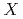 = Al, Ga)
= Al, Ga)Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Ai*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Munakata, Koji*; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
no journal, ,
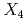 (
(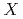 = Al, Ga)
= Al, Ga)Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Ai*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Munakata, Koji*; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kaneko, Koji; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Kuroda, Tetsuya*; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Oikawa, Kenichi; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*
no journal, ,
Kaneko, Koji; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Oikawa, Kenichi; Tamura, Itaru; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Nakao, Akiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Kuroda, Tetsuya*; Kaneko, Koji; Tamura, Itaru; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ohara, Takashi; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Kuroda, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nakao, Akiko*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Moriyama, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Mo
Mo O
O under magnetic fields
under magnetic fieldsKajimoto, Ryoichi; Iida, Kazuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Matsuda, Masaaki*; Ye, F.*; Mizuno, Yusuke*; Katsufuji, Takuro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Matsuda, Masaaki; Ishii, Yoshinobu; Nagai, Satoshi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Kito, Hijiri*; Igawa, Naoki; Soda, Minoru*; Yasui, Yukio*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
no journal, ,
Two examples of neutron scattering investigations on the magnetic ordering process in frustrated spin system coupled to lattice and charge degrees of freedom are presented, in both cases leading to a short-ranged magnetic ground state. (1) In LuFe O
O the Fe ions are arranged to form hexagonal double layers along the rhombohedral unique axis. Detailed investigation of the ordering process revealed a magnetic ground state with short-range order along the stacking direction. (2) YBaCo
the Fe ions are arranged to form hexagonal double layers along the rhombohedral unique axis. Detailed investigation of the ordering process revealed a magnetic ground state with short-range order along the stacking direction. (2) YBaCo O
O has a structure with alternating stacking of a kagome-like and triangular lattice formed of CoO
has a structure with alternating stacking of a kagome-like and triangular lattice formed of CoO tetrahedra. Although the Co moments do not exhibit a long range ordering down to 10K, strong diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordering of the moments on the kagome-like and triangular lattices are observed.
tetrahedra. Although the Co moments do not exhibit a long range ordering down to 10K, strong diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordering of the moments on the kagome-like and triangular lattices are observed.
Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Hara, Yoshiaki*
no journal, ,
 O molecules of deuterated Na
O molecules of deuterated Na xCoO
xCoO ; Neutron scattering
; Neutron scatteringMoyoshi, Taketo*; Yasui, Yukio*; Soda, Minoru*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu SbO
SbO with distorted honeycomb structure
with distorted honeycomb structureMiura, Yoko*; Yasui, Yukio*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
Magnetic excitation spectra of Na Cu
Cu SbO
SbO with the distorted honeycomb lattice structure have been investigated by means of neutron inelastic scattering. The observed dispersion of the magnetic excitation can be well understood in the framework of singlet-triplet excitation of quasi-one dimensional bond alternating system running in b-axis direction.
with the distorted honeycomb lattice structure have been investigated by means of neutron inelastic scattering. The observed dispersion of the magnetic excitation can be well understood in the framework of singlet-triplet excitation of quasi-one dimensional bond alternating system running in b-axis direction.