Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
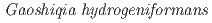 sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formationUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 75(6), p.006802_1 - 006802_11, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Masuki, Yuma*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Umemura, Ayako*; Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Minami, Masayo*; Niwa, Masakazu; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Lacustrine deposits have 30-fold higher As abundance than the average crustal deposit. Arsenic is mostly concentrated as discrete horizons deposited in spring and autumn. As-rich layers contain FeAsS, AsS, and As S
S but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
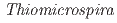 sp. strain V2501 isolated from 250 m below the ground level in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan
sp. strain V2501 isolated from 250 m below the ground level in Horonobe, Hokkaido, JapanUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
Microbiology Resource Announcements (Internet), 13(11), p.e00108-24_1 - e00108-24_4, 2024/11
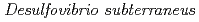 sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium isolated from a deep siliceous mudstone formation
sp. nov., a mesophilic sulfate-reducing deltaproteobacterium isolated from a deep siliceous mudstone formationUeno, Akio*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Kiyama, Tamotsu*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Tamaki, Hideyuki*; Naganuma, Takeshi*; et al.
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 71(2), p.004683_1 - 004683_10, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.24(Microbiology)A novel mesophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium, designated strain HN2 , was isolated from groundwater sampled from the subsurface Miocene Wakkanai Formation located in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan. The cells were Gram-negative rods, with motility conferred by a single polar flagellum. The isolate expressed desulfoviridin, but no catalase or oxidase activities was detected. Strain HN2
, was isolated from groundwater sampled from the subsurface Miocene Wakkanai Formation located in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan. The cells were Gram-negative rods, with motility conferred by a single polar flagellum. The isolate expressed desulfoviridin, but no catalase or oxidase activities was detected. Strain HN2 grew in a temperature range of 5-43
grew in a temperature range of 5-43  C (optimum, 35
C (optimum, 35  C) and in a pH range of 6.5-7.5 (optimum, pH 7.0-7.3). It used sulfate, thiosulfate, dimethyl sulfoxide, anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate, Fe
C) and in a pH range of 6.5-7.5 (optimum, pH 7.0-7.3). It used sulfate, thiosulfate, dimethyl sulfoxide, anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate, Fe , and manganese oxide as electron acceptors, but not elemental sulfur, nitrite, or nitrate. The bacterium showed very weak growth with sulfite as the electron acceptor. The strain fermented pyruvate and cysteine in the absence of sulfate, but not malate or succinate. The bacterium did not require NaCl, but tolerated up to 4% NaCl (w/v). Strain HN2
, and manganese oxide as electron acceptors, but not elemental sulfur, nitrite, or nitrate. The bacterium showed very weak growth with sulfite as the electron acceptor. The strain fermented pyruvate and cysteine in the absence of sulfate, but not malate or succinate. The bacterium did not require NaCl, but tolerated up to 4% NaCl (w/v). Strain HN2 did not require vitamins. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 56.66 mol%. A 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that the closest recognized relative of strain HN2
did not require vitamins. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 56.66 mol%. A 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that the closest recognized relative of strain HN2 is
is 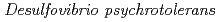 JS1
JS1 (97.0% similarity). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) value between strain HN2
(97.0% similarity). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) value between strain HN2 and D.
and D. 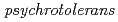 JS1
JS1 was 79.8%. Based on the phenotypic and molecular genetic evidence, the isolate is assigned to the new species
was 79.8%. Based on the phenotypic and molecular genetic evidence, the isolate is assigned to the new species 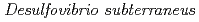 sp. nov. The type strain is HN2
sp. nov. The type strain is HN2 (=DSM 101010
(=DSM 101010 =NBRC 112213
=NBRC 112213 ).
).
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Takano, Masao*; Sano, Naomi; Tani, Yukinori*; Ochiai, Shinya*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Niwa, Masakazu; Kawakami, Shinichi*
Sedimentology, 66(6), p.2490 - 2510, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:51.64(Geology)Micro-X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanning spectroscopy of marine and lake sedimentary sequences can provide detailed paleoenvironmental records available through element intensities proxy data. However, problems for effects of interstitial pore water on the micro-XRF intensities have been pointed out so far because of direct measurement on the split wet sediment surfaces. In this study, new methods for the XRF corrections were developed by being considered with the micro-X-ray scanning spectroscopy.
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Ikeda, Hisashi*; Shibata, Kenji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Takuma*; Tani, Yukinori*; Takano, Masao*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Tanaka, Atsushi*; Naito, Sayuri*; et al.
Global and Planetary Change, 164, p.11 - 26, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:40.88(Geography, Physical)Paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate changes in Siberia were reconstructed by continuous, high-resolution records of chemical compositions from a sediment core retrieved from the Buguldeika Saddle, Lake Baikal, dating back to the last 33 cal. ka BP. The Holocene climate followed by a shift at ca. 6.5 cal. ka BP toward warm and dry, suggesting that the climate system transition from the glacial to interglacial state occurred. In the last glacial period, the deposition of carbonate mud from the Primorsky Range was associated with Heinrich events (H3 and H1) and the Selenga River inflow was caused by meltwater of mountain glaciers in the Khamar-Daban Range. The anoxic bottom-water during Allerod-Younger Dryas was probably a result of weakened ventilation associated with reduced Selenga River inflow and microbial decomposition of organic matters from the Primorsky Range. The rapid decline in precipitation during the early Holocene may have been a response to the 8.2 ka cooling event.
Murakami, Takuma; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mizuno, Takashi
Chikyu Kagaku, 50(4), p.299 - 317, 2016/12
Development of techniques for investigating the long-term migration of elements in deep underground is important with respect to safety assessment for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As one study of the migration of elements in deep underground, the distribution of REE, Th and U in sedimentary rock of Horonobe area in Hokkaido was investigated, and discussed whether the difference of hydrogeological structure and lithofacies influences on the distributions. As the results, it was considered that REE and Th were mainly retained in minerals originating from terrigenous clastic and secondary mineral occurred in early diagenesis, and their distributions were relatively homogenous in both the Koetoi and Wakkanai formations. Uranium was indicated to be maintained in the sedimentary rock until now after depositing in deep-sea sediment. It was considered that the U deposition was occurred by adsorption on organic matter and reductive precipitation with decomposition of organic matter. In addition, it was confirmed that the distributions of these elements were not influenced by the difference of hydrogeological and lithofacies.
Yamamoto, Hideaki; Yoshizawa, Michio; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Momose, Takumaro*; Tsujimura, Norio*; Kanai, Katsuta*; Cruz-Suarez, R.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 125(1-4), p.88 - 92, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The purpose of this paper is to discuss the results of the third intercomparison exercise of external radiation dosimetry organized under the Regional Cooperative Agreement (RCA) in the East Asia region of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Twenty five laboratories from 16 member states participated in the exercise. Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) arranged the standard irradiation of the participants' dosimeters. The results of the measurements of the irradiated dosimeters for the determination of external doses were satisfactory for all participants, demonstrating good performance in their external dosimetry.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Murakami, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Takai, Shizuka; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Takeda, Seiji
no journal, ,
In the intermediate depth disposal of radioactive waste, the monitoring boreholes are backfilled and sealed at the end of the monitoring period to prevent potential migration pathways for radioactive materials. However, the method to confirm whether the borehole is properly sealed has not been established, and there is a lack of scientific knowledge to determine the validity of borehole sealing. The aim of this study is to develop the confirmation method. Therefore, based on previous studies, experimental and analytical considerations were performed to identify the confirmation points of borehole sealing. In the former, laboratory experiments were performed to understand the swelling behavior and permeability of bentonite block in the borehole. These results indicated that the initial water content of the bentonite block could affect the internal structure after swelling. In the latter, groundwater flow analyses were performed for the hydrogeological structures with backfilled boreholes to understand the effect of backfill conditions on the borehole sealing. It was shown that the backfill conditions to prevent the formation of water pathways in the borehole were the grouting BDZ (Borehole Disturbed Zone), etc.
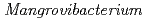 sp. strain Z1-71, isolated from the terrestrial subsurface environment and its co-cultivation within a methanogenic archaeon
sp. strain Z1-71, isolated from the terrestrial subsurface environment and its co-cultivation within a methanogenic archaeonUeno, Akio*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayakawa, Tsubasa*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Kokubu, Yoko; Hasebe, Noriko*; Murakami, Takuma; Miyata, Yoshiki*; Hasegawa, Hitoshi*; Nagao, Seiya*; Kawakami, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Ueno, Akio*; Tamaki, Hideyuki*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Kiyama, Tamotsu*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Abe, Takeyasu; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Murakami, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Takeda, Seiji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mizuno, Takashi; Nanjo, Isao; Yamamoto, Nobuyuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Murakami, Takuma
no journal, ,
This study aimed to understand the hydrochemical evolution process at Horonobe area, northern Hokkaido Japan, based on chemical tracers. In this study, existing data was used for the estimation. As the result, it is revealed that the resolution of gas hydrate and the diffusion of porewater from upper strata to lower strata is important factor of hydrochemical evolution.
Murakami, Takuma; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Kokami, Takayuki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Uezu, Yasuhiro; Tobita, Kazunori; Yamaguchi, Takenori; Momose, Takumaro; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Furuta, Sadaaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
JAEA was established on October 1st, 2005 by integrating the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. In these institutes, there were a several radiation control methods or original radiation control levels. After establishing JAEA, in order to make a harmonization of radiation control methods and levels, applications of these are investigated under actual situations.
Ueno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Itayama, Yui*; Murakami, Takuma*; Fujita, Natsuko; Kagami, Saya; Kida, Fukuka; Ochiai, Shinya*; Niwa, Masakazu; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*
no journal, ,
Lake Baikal in southeast Siberia is the most sensitive area on Earth which has been responded to changes in solar insolation. In this poster presentation, we report the results of paleoenvironment analyses of the 140 kyrs records after reestablishing the sediment chronology.
Ikeda, Hisashi*; Shibata, Kenji; Murakami, Takuma; Kokubu, Yoko; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Takuma; Mizuno, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English