Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
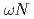 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear)Togo, Yoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Amano, Yuki; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Terada, Yasuko*; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 191, p.165 - 186, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:76.66(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Iodine distribution, speciation, and isotope ratio ( I/
I/ I) in both rock and groundwater phases were determined to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shale. It was suggested that I
I) in both rock and groundwater phases were determined to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shale. It was suggested that I is released to the ground water during the progress of the maturation of organic matter. Dissociated I
is released to the ground water during the progress of the maturation of organic matter. Dissociated I could move toward the surface because of the upward water flow driven by the compaction during burial diagenetic process. Thus, iodine rich brine is created by integration of iodine released from underlying formations. Because of low affinity of I
could move toward the surface because of the upward water flow driven by the compaction during burial diagenetic process. Thus, iodine rich brine is created by integration of iodine released from underlying formations. Because of low affinity of I to solid phase, released I
to solid phase, released I remains in solution phase, and the concentration of the iodine in the solution has been possibly increasing during sedimentation history.
remains in solution phase, and the concentration of the iodine in the solution has been possibly increasing during sedimentation history.
Seki, Miharu*; Oikawa, Junichi*; Taguchi, Taro*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Sakamoto, Kazunori*; Amachi, Seigo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 47(1), p.390 - 397, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:74.04(Engineering, Environmental)The laccase released by microorganisms oxidizes iodide to molecular iodine or hypoiodous acid, both of which are easily incorporated into natural soil organic matter.
Sugihara, Kenta; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Ogawa, Takemitsu; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2012/07
Numerical simulation code, based on multi-phase thermohydraulics, has been being developed with a goal of a control and prediction for the laser cutting process. A thermohydraulic numerical simulation of the laser steel cutting was carried out to confirm an assist gas and sweep velocity effect to the cutting performance. The performance was evaluated, based on temperature profile and cutting front formation. Simulation results were as follows. If there was no effect of dross ejection by assist gas, a laser light was absorbed into molten steel stagnated in the kerf. Therefore, there was less laser heat input to a solid surface directly. Then, heat transport to the back side of steel plate got delayed. In the case of faster sweep velocity, delay of heat conduction and failure cut were confirmed at behind the cut starting position of the steel plate. Failure cut at the position was observed in our experiments. From these results, it was concluded that the thermohydraulics in the kerf takes important role for not only dross ejection but also promotion of heat input at solid surface.
Suzuki, Toshiyuki; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Kamoshida, Shigeo
JAEA-Testing 2007-001, 58 Pages, 2007/03
As a part of safety research of light water reactors (LWR), fuel behavior during a reactivity-initiated accident (RIA) has being studied in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) using irradiated fuels in commercial reactors. During a past decade, RIA-simulating experiments in the NSRR showed that cladding failures at higher burnup occurred at lower enthalpy values than those would be expected. It was supposed that this type of the fuel failure may be influenced by an initial temperature of cladding since the failure occurs before the temperature escalation of the cladding due to the power burst. In order to verify the influence of the cladding temperature before the onset of power escalation during an RIA, we developed B-I type (the 1st type to simulate BWR operation condition) high pressure water capsule. This manual describes a series of working procedures from receiving the capsule to transporting it after experiment and a procedure in case of an emergency in order to perform the RIA-simulating experiments using the B-I type capsule safely and smoothly.
Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Okawara, Masami; Suzuki, Toshiyuki; Shibata, Isao; Fuketa, Toyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-028, 47 Pages, 2007/03
As a part of Advanced LWR Fuel Performance and Safety Research Program, irradiation experiments are conducted with high burnup uranium dioxide fuel and uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor. When an irradiation capsule is transferred and loaded to the reactor core, a capsule loader is used. The previous capsule loader, however, could not have enough shielding capability against neutron flux from high burnup MOX fuel. In order to fulfill the requirement and to handle a new high pressure water capsule, accordingly, a type-B capsule loader was developed.
Murao, Hiroyuki; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Okawara, Masami; Shibata, Isao
JAEA-Technology 2006-062, 32 Pages, 2007/02
In NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor) experiments, test fuels are inserted in the especial capsule and the capsule will be inserted into the experimental tube which is located in the center of reactor core. In NSRR, there are 17 types of atmospheric pressure capsule, and one of them Type X-IV atmospheric pressure capsule has been produced 6 times under authorization of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). Application for the 7th time of authorization was submitted to the MEXT in June 2006. On this application, standard which is used to design was changed to The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) S NC1-2005 from the Notification 501 of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). The JSME S NC1-2005 introduced the service condition in addition to the reactor condition which has been used in the Notification 501. In this application, stress limits were calculated based on the service condition. The JSME S NC1-2005 requires estimation of combined stress for Class1 support structures, which was unnecessary in the Notification 501. In this application, combined stresses were calculated and confirmed not to exceed the stress limits.
 I by Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) and its application on earth and environmental sciences
I by Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) and its application on earth and environmental sciencesSuzuki, Takashi; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*
Radioisotopes, 54, p.51 - 53, 2005/00
no abstracts in English
Murao, Hiroyuki; Yachi, Shigeyasu; Ota, Kazunori; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Takehiko; Terakado, Yoshibumi
UTNL-R-0435, p.15_1 - 15_9, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Murao, Hiroyuki; Yachi, Shigeyasu; Ota, Kazunori; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Takehiko; Terakado, Yoshibumi
JAERI-Tech 2003-094, 41 Pages, 2004/01
Prior to actual runs in the shaped pulse and in the combined pulse operations, the online simulation and the offline simulation must be performed to examine safety and appropriation. Actual reactor power of the NSRR can be simulated practically, but a slight difference canbe observed between the present simulation results and the actual operation during the NSRR start-up phase and power controled operation. Regulating rod worth and fuel temperature feedback reactivity were re-evaluated and installed into the simulators. As a result, the accuracy of the simulator was remarkably improved. So that the application and safety of the shaped pulse and combined pulse operation were improved.
 Sb
Sb
Okane, Tetsuo; Fujimori, Shinichi; Mamiya, Kazutoshi; Okamoto, Jun; Muramatsu, Yasuji; Fujimori, Atsushi; Nagamoto, Yasuyuki*; Koyanagi, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(28), p.S2197 - S2200, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.64(Physics, Condensed Matter)The filled skutterudite compounds 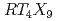 (
( = alkaline earth, rare earth, actinide;
= alkaline earth, rare earth, actinide;  = Fe, Ru, Os;
= Fe, Ru, Os; 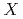 = pnictogen: P, As, Sb) exhibit a variety of physical properties such as superconductivity, magnetic ordering, heavy-Fermion behavior, and metal-insulator transition. Among them, YbFe
= pnictogen: P, As, Sb) exhibit a variety of physical properties such as superconductivity, magnetic ordering, heavy-Fermion behavior, and metal-insulator transition. Among them, YbFe Sb
Sb shows a heavy-Fermion or intermediate-valence behavior in the magnetic, electrical transport, and thermal properties, which might be associated with a valence instability of Yb atom. In this study, the electronic structure of YbFe
shows a heavy-Fermion or intermediate-valence behavior in the magnetic, electrical transport, and thermal properties, which might be associated with a valence instability of Yb atom. In this study, the electronic structure of YbFe Sb
Sb have been investigated by the high-resolution photoemission spectroscopy, using He discharge lamp and synchrotron radiation as an excitation sources. The bulk and surface components of the Yb
have been investigated by the high-resolution photoemission spectroscopy, using He discharge lamp and synchrotron radiation as an excitation sources. The bulk and surface components of the Yb signal is clearly divided in the spectra. The relation of the energy position between them is anomalous compared to that of the conventional mixed-valent Yb compounds.
signal is clearly divided in the spectra. The relation of the energy position between them is anomalous compared to that of the conventional mixed-valent Yb compounds.
Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Udagawa, Yutaka
no journal, ,
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has performed a great number of pulse irradiation experiments of light water reactor fuel rods using the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor to study fuel behavior under reactivity initiated accident (RIA) conditions. With experiences of measurement of very fast transient under strong irradiation conditions, unique instrumentation techniques have been developed. Remote-control techniques, for oxide removal from the cladding surface and spot-welding of thermocouple wires to the cladding surface, enable the measurement of cladding temperature evolution during boiling transitions at the surface of a high burnup fuel rod. Water column velocimeter can measure the movement of coolant water at fuel failure and enables evaluation of generated mechanical energy. With these techniques, a great deal of data has been obtained and the results have been reflected in safety evaluation guidelines for RIA in some other countries as well as in Japan.
Kawashima, Kazuhito; Suzuki, Toshiyuki; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Taguchi, Yuji
no journal, ,
For the aging management of reactor pool in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the inspection of pool lining, which is made of Aluminum, was decided to be an important item. Therefore, we develop a device which is controlled remotely and measures the thickness of the pool lining by non-destructive method using ultrasonic wave.
Taguchi, Yuji; Kawashima, Kazuhito; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Awa, Yasuaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawashima, Kazuhito; Taguchi, Yuji; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Suzuki, Toshiyuki; Okawara, Masami
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akiyama, Yoshiya; Kawashima, Kazuhito; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Murao, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimamoto, Yoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Amano, Yuki; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
Study of migration of iodine in the subsurface environment is important for natural analogue of HLW. The vertical distribution of iodine concentration, the type of iodine, and isotope were analyzed for the sample of groundwater and sedimentary rocks of the Horonobe area. The results showed that iodine ion were existed in the groundwater, and the mixed iodine with organic and inorganic type were existed in the rock samples.
 I/
I/ I analysis
I analysis  I/
I/ I
IShimamoto, Yoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Amano, Yuki; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
We determined iodine distribution, speciation, and isotope ratio ( I/
I/ I), to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shales, using core and groundwater samples collected at JAEA Horonobe underground research center. Iodine in core samples dramatically decreased near the boundary between Wk and Kt Formations. Iodine exists as I
I), to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shales, using core and groundwater samples collected at JAEA Horonobe underground research center. Iodine in core samples dramatically decreased near the boundary between Wk and Kt Formations. Iodine exists as I in groundwater, while that in shales is a mixture of organic and inorganic I. Iodine isotope ratio (
in groundwater, while that in shales is a mixture of organic and inorganic I. Iodine isotope ratio ( I/
I/ I) is slightly higher in siliceous shale compared with that of groundwater. According to these results, migration of iodine in this area can be expected as follows; (1) iodine accumulated as organic iodine in siliceous sediment. (2) Iodine was released from Wk Formation during diagenetic process as I
I) is slightly higher in siliceous shale compared with that of groundwater. According to these results, migration of iodine in this area can be expected as follows; (1) iodine accumulated as organic iodine in siliceous sediment. (2) Iodine was released from Wk Formation during diagenetic process as I to form iodine-rich groundwater. (3) Iodine-rich groundwater was distributed to Wk and Kt Formations due to the compaction of the layers. (4) Both iodine and chlorine were diluted by freshwater from the surface.
to form iodine-rich groundwater. (3) Iodine-rich groundwater was distributed to Wk and Kt Formations due to the compaction of the layers. (4) Both iodine and chlorine were diluted by freshwater from the surface.
Togo, Yoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Amano, Yuki; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
To understand behavior of iodine in shallow and deep underground is essential because radioactive wastes, which contain high levels of radioiodine, are planned to be stored in underground nuclear-waste repository. We determined iodine distribution, speciation, and isotope ratio ( I/
I/ I), to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shales, using core and groundwater samples collected at JAEA Horonobe underground research center. Iodine exists as I- in groundwater, while that in shales is a mixture of organic and inorganic I.
I), to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shales, using core and groundwater samples collected at JAEA Horonobe underground research center. Iodine exists as I- in groundwater, while that in shales is a mixture of organic and inorganic I.
Sugihara, Kenta; Ogawa, Takemitsu; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
no journal, ,
A thermohydraulic numerical simulation of the laser steel cutting was carried out to confirm an assist gas and sweep velocity effect to the cutting performance. The performance was evaluated, based on temperature profile and cutting front formation. Simulation results were as follows. If there was no effect of dross ejection by assist gas, a laser light was absorbed into molten steel stagnated in the kerf. Therefore, there was less laser heat input to a solid surface directly. Then, heat transport to the back side of steel plate got delayed. In the case of faster sweep velocity, delay of heat conduction and failure cut were confirmed at behind the cut starting position of the steel plate. Failure cut at the position was observed in our experiments. From these results, it was concluded that the thermohydraulics in the kerf takes important role for not only dross ejection but also promotion of heat input at solid surface.