Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ashikawa, Naoko*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Hayashi, Takao; Ueda, Yoshio*; Muroga, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 438, p.S664 - S667, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, W concentrations of dusts at P-8 section and hydrogen isotope retentions in dusts are analyzed. Compositions of C including W material dusts were observed in JT-60U. For an enhanced resolution of the XPS measurement to analyze quantitatively the composition of the dust flakes, the new analysis using XPS with indium foil was done and showed that the dust flakes contains about less than 1% of tungsten in carbon. Compositions of tungsten-carbon mixed dusts at different poloidal positions are reported. Produced areas of dust including W is estimated on the outer doom wing by IMPGYRO code. Relative intensities at low temperature regions were smaller than bulk divertor target, which may be caused by the high baking/operation temperature. Amounts of retained Hydrogen/Deuterium in dust particles depend on internal defects and carbon composition of dusts.
Garin, P.*; Diegele, E.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ibarra, A.*; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; M slang, A.*; Muroga, Takeo*; Nishitani, Takeo; Poitevin, Y.*; et al.
slang, A.*; Muroga, Takeo*; Nishitani, Takeo; Poitevin, Y.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.611 - 614, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:85.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper summarizes the proposals and findings of the IFMIF Specification Working Group established to update the Users requirements and top level specifications for the Facility. Special attention is given to the different roadmaps of fusion path way towards power plants, of materials R&D and of facilities and their interactions. The materials development and validation activities on structural materials, blanket functional materials and non-metallic materials are analyzed and specific objectives and requirements to be implemented in IFMIF are proposed. Emphasis is made in additional potential validation activities that can be developed in IFMIF for ITER TBM qualification as well as for DEMO-oriented mock-up testing.
Tanaka, Teruya*; Sato, Satoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Ochiai, Kentaro; Murata, Isao*; Takakura, Kosuke; Sato, Fuminobu*; Kada, Wataru*; Iida, Toshiyuki*; Konno, Chikara; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(2), p.681 - 686, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Irradiation experiments of 14 MeV neutrons have been performed on a Li block assembly of 46  51
51  51 cm
51 cm with a 5 cm thick V-alloy layer inside to examine the accuracy of neutronics calculations for the Li/V-alloy blanket design. Foils of Nb, Ni, In and Au for reaction rate measurements of
with a 5 cm thick V-alloy layer inside to examine the accuracy of neutronics calculations for the Li/V-alloy blanket design. Foils of Nb, Ni, In and Au for reaction rate measurements of  Nb(n,2n)
Nb(n,2n)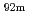 Nb,
Nb,  Ni(n,p)
Ni(n,p) Co,
Co,  In(n,n')
In(n,n')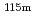 In,
In,  Au(n,
Au(n, )
)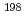 Au reactions and
Au reactions and  Li enriched (
Li enriched ( Li: 95.5%) and
Li: 95.5%) and  Li enriched (
Li enriched ( Li: 99.9%) Li
Li: 99.9%) Li CO
CO pellets for tritium production rate measurements were installed in the assembly. Results of the measurements were compared with those of calculations with MCNP5, JENDL-3.3 and JENDL/D-99. The comparisons for the reaction rates in the Nb, Ni and In foils indicate that measurements and calculations of the fast neutron transport are consistent almost within 10%. In the comparison for the reaction rates in the Au foils, the underestimation of 15% was found at a surface of the V-alloy layer. There is a possibility that this is due to the elastic scattering cross section of V around 4 keV as previously reported. The comparisons for tritium production rates in the
pellets for tritium production rate measurements were installed in the assembly. Results of the measurements were compared with those of calculations with MCNP5, JENDL-3.3 and JENDL/D-99. The comparisons for the reaction rates in the Nb, Ni and In foils indicate that measurements and calculations of the fast neutron transport are consistent almost within 10%. In the comparison for the reaction rates in the Au foils, the underestimation of 15% was found at a surface of the V-alloy layer. There is a possibility that this is due to the elastic scattering cross section of V around 4 keV as previously reported. The comparisons for tritium production rates in the  Li enriched and
Li enriched and  Li enriched Li
Li enriched Li CO
CO pellets indicate that calculated rates were larger than results of the measurements by 2-8% and 1-4%, respectively.
pellets indicate that calculated rates were larger than results of the measurements by 2-8% and 1-4%, respectively.
Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji*; Sugiura, Hirokazu*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Matsushita, Izuru*; Muroga, Takeo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 85(7-9), p.1102 - 1105, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper reports a measurement technique for surface waves on a liquid lithium jet for a Li target of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility. The characteristic of the waves was successfully clarified by a contact-type liquid level detector. As a result, it was found that the wave distributions in the all jet velocity range up to 15 m/s were conformed each other in normalized form and Rayleigh distribution which is one of popular model to show irregular water wave.
Sugiura, Hirokazu*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Niwa, Yuta*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Matsushita, Izuru*; Muroga, Takeo*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(7-11), p.1803 - 1807, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)To develop a diagnostics system in view of its application on International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) liquid lithium (Li) target, velocity measurements on a liquid Li flow were performed in a Li circulation loop at Osaka University with a test section having a contraction nozzle 1/2.5 scale of IFMIF and producing a flat plane jet of 70 mm width and 10 mm thickness. Based on the Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) technique, a local Li flow velocity distribution was measured by tracking brightness intensity patterns of surface waves generated on the flow. Measured surface velocity showed good agreement with a surface velocity obtained in previous water experiments, and had an insignificant effect at an area corresponding to a deuteron beam irradiation area on the IFMIF target.
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Sugiura, Hirokazu*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Matsushita, Izuru*; Muroga, Takeo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(7-11), p.1086 - 1090, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)A liquid lithium(Li) target of International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is formed as flat plane free-surface flow by a nozzle and flows at high speed around 15 m/s. This paper focuses on flatness of the liquid Li target. A Li flow experiment was conducted in Osaka University Li Loop with a test section which was 1/2.5 scaled model of IFMIF. A thickness of the Li flow was measured and obtained by a contact method which was developed for the measurement. Analytical study on Kelvin wake and numerical calculation on wakes near side walls of the flow channel were also conducted and compared with the experimental results. As the results, positions of wake crest obtained from both of the experiment and numerical calculation assuming contact angle 140 agreed well with an iso-phase line of the analytical model. Generation of the wake are likely depends on wettability between Li and a structural material which is 304SS in the present study.
agreed well with an iso-phase line of the analytical model. Generation of the wake are likely depends on wettability between Li and a structural material which is 304SS in the present study.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Agostini, P.*; Ara, Kuniaki; Cevolani, S.*; Chida, Teruo*; Ciotti, M.*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Garin, P.*; Gessii, A.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.1007 - 1014, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the latest design of liquid lithium target system in IFMIF. Design requirement of the Li target is to provide a stable Li jet with a speed of 20 m/s to handle an averaged heat flux of 1 GW/m . A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
. A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
Shikama, Tatsuo*; Knitter, R.*; Konys, J.*; Muroga, Takeo*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; M slang, A.*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Nagata, Shinji*
slang, A.*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Nagata, Shinji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.976 - 982, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:90.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Functional materials should play an important role not only in ITER but also in fusion machines beyond ITER, though it is occasionally claimed that future fusion plants should have much more simple structures and they should be free from auxiliary systems such as diagnostics. Studies on test blanket modules (TBM) clearly show the importance of functional materials there. The paper will review the present status of studies and developments of functional ceramics for nuclear fusion applications, with a perspective on their application in electric-power generating fusion power plant, namely DEMO.
Wakai, Eiichi; Muroga, Takeo*; Hasegawa, Akira*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(9), p.571 - 582, 2008/09
no abstracts in English
Li, Z.*; Tanaka, Teruya*; Muroga, Takeo*; Sato, Satoshi; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Science and Technology, 52(4), p.817 - 820, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Seki, Masahiro; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Norimatsu, Takayoshi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mori, Masahiro; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Genshiryoku Handobukku, p.906 - 1029, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Hiroo*; Kanemura, Takuji*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Matsushita, Izuru*; Muroga, Takeo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2483 - 2489, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lithium flow experiments were conducted for International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) at Osaka University. In the experiment, Li plane jet of 10 mm in depth and 70 mm in width formed by a two contractions nozzle was tested in the velocity range of less than 15 m/s. In the present report, Li surface measurement by pattern projection method was tested. This is a three dimensional image measurement, where stripe patterns are projected onto the flow surface without touching it. The projected patterns were observed to be deformed according to the surface up- and- down. Three-dimensional surface shape could be obtained by analyzing the deformed patterns. By the method, shapes of wave pattern called surface wakes were successfully measured. The surface wakes were observed to be formed from the nozzle edge. It was found that the nozzle edge was damaged and became serrated after lithium flowing of 1,300 hours at this moment.
Kanemura, Takuji*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Matsushita, Izuru*; Muroga, Takeo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2550 - 2557, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)For a study on characteristics of lithium target flow of International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), experiments were carried out by using a lithium loop at Osaka University. In the experiment, fluctuations of a free surface of the horizontal flow were directly measured by using an electro-contact probe acquiring condition of contact/non-contact of the probe with the flow surface as voltage data. Vertical location of the probe tip was set by 0.1 mm step. Horizontal location of the probe was 175 mm downstream from the nozzle exit, corresponding to the footprint of deuteron beam in the IFMIF case. It was found that the maximum amplitude of the surface wave, including rarely arising ones, was 2.2 mm at the center of the flow channel with width of 70 mm at the maximum flow velocity of 15 m/s. The average thickness of the flow was found to be 10.13 mm.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Horiike, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Nakamura, Hiroo; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Matsushita, Izuru*; Ida, Mizuho; Ara, Kuniaki; Muroga, Takeo*; Matsui, Hideki*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Li, Z.*; Tanaka, Teruya*; Muroga, Takeo*; Sato, Satoshi; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(23-24), p.2893 - 2897, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ito, Kazuhiro*; Ito, Taro*; Kukita, Yutaka*; Koterazawa, Hiroyuki*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hideo; Nakamura, Hiroo; et al.
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2006/07
Waves on a liquid-lithium jet flow, simulating a proposed high-energy beam target design, have been measured using an optical technique based on specular reflection of a single laser beam on the jet surface. The streamwise and spanwise fluctuations of the local free-surface slope were least-square fitted with a sinusoidal curve to makeup the signals lost due to the constriction in the optical arrangement. The waveform was estimated with an assumption that wave phase speed can be calculated using the dispersion relation for linear capillary gravity waves. The direction of propagation on the jet surface was also evaluated so that the wave amplitudes, calculated by integral of slope angle signal, agree consistently in streamwise and spanwise direction. These measurements and analyses show that the waves at the measurement location for a jet velocity of 1.2 m/s can best be represented by oblique waves with an inclination of 0.32 rad, a wavelength of 4.2 mm and a wave amplitude of about 0.06 mm.
Ito, Kazuhiro*; Ito, Taro*; Kukita, Yutaka*; Koterazawa, Hiroyuki*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hideo; Nakamura, Hiroo; et al.
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Arata*; Muroga, Takeo*; Takeuchi, Takao*; Nishitani, Takeo; Morioka, Atsuhiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1675 - 1681, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor plant, a neutral beam injector (NBI) will be operated for a long time, and it will allow neutron streaming from NBI ports to outside of the plasma vacuum vessel. It requires the superconducting magnet to develop nuclear technology to produce stable magnetic field and to reduce activation of the magnet components. In this report, the back ground of the necessity and the contents of the nuclear technology of the superconducting magnets for fusion application are discussed and some typical investigation results are presented, which are the neutron irradiation effect on Nb Sn wire, the development of low activation superconducting wire, and the design concept to reduce nuclear heating and nuclear transformation by streaming. In addition, recent activities in high energy particle physics are introduced and potential ripple effect of the technology of the superconducting magnets is described briefly.
Sn wire, the development of low activation superconducting wire, and the design concept to reduce nuclear heating and nuclear transformation by streaming. In addition, recent activities in high energy particle physics are introduced and potential ripple effect of the technology of the superconducting magnets is described briefly.
Enoeda, Mikio; Akiba, Masato; Tanaka, Satoru*; Shimizu, Akihiko*; Hasegawa, Akira*; Konishi, Satoshi*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Koyama, Akira*; Sagara, Akio*; Muroga, Takeo*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.415 - 424, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:96.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English