Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

 generation; The Role of NO
generation; The Role of NO
 in the crevice corrosion repassivation of type 316L stainless steel
in the crevice corrosion repassivation of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sugawara, Yu*; Muto, Izumi*; Hara, Nobuyoshi*
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 166(10), p.C250 - C260, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:13.00(Electrochemistry)The role of NO
 in the repassivation of crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steel was investigated. In crevice corrosion tests, the solution was changed from 1 M NaCl to NaCl-NaNO
in the repassivation of crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steel was investigated. In crevice corrosion tests, the solution was changed from 1 M NaCl to NaCl-NaNO . NO
. NO
 led to complete repassivation. Repassivation of the crevice corrosion was found to take place in two steps. In the first step, the estimated current density inside the crevice gradually decreased from ca. 5 mA cm
led to complete repassivation. Repassivation of the crevice corrosion was found to take place in two steps. In the first step, the estimated current density inside the crevice gradually decreased from ca. 5 mA cm to ca. 5
to ca. 5  A cm
A cm . After that, the current density suddenly decreased to less than 0.1
. After that, the current density suddenly decreased to less than 0.1  A cm
A cm . From the potentiodynamic polarization in acidic solutions simulated inside the crevice (pH 0.2) and in situ observations of the crevice corrosion morphology, the first step was thought to be generated by the suppression of active dissolution by NO
. From the potentiodynamic polarization in acidic solutions simulated inside the crevice (pH 0.2) and in situ observations of the crevice corrosion morphology, the first step was thought to be generated by the suppression of active dissolution by NO
 . It would appear that the generation of NH
. It would appear that the generation of NH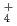 results in a pH increase and the further suppression of active dissolution, and then repassivation occurs.
results in a pH increase and the further suppression of active dissolution, and then repassivation occurs.
Otsubo, Takashi*; Oya, Susumu*; Goto, Jun*; ; Muto, Suguru*; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Sekine, Toshiaki
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.206 - 207, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; ; ; Muto, Suguru*; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 120-121(1-4), p.695 - 699, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 Cs following the decay of
Cs following the decay of  Xe atoms implanted in metals
Xe atoms implanted in metals; ; ; ; ; ; Muto, Suguru*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Osa, Akihiko; Sekine, Toshiaki; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 239(2), p.251 - 255, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 Cs
Cs; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; Muto, Suguru*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Physical Review B, 58(17), p.11313 - 11321, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Okazaki, Koki*; Naito, Susumu*; Nakayama, Kunihiko*; Makino, Shunichiro*; Shigeyama, Musashi*; Kuwako, Akira*; Izumi, Mikio*; Ito, Jun*; Okada, Hisashi*; Muto, Keitaro
no journal, ,
In fast breeder reactor (FBR), it is important to detect a small sodium leak surely for safety. As the coolant sodium used in FBR is low pressure, a small leak occurs from a crack before a pipe breaks, therefore it is possible to detect a sodium leak so as to shutdown a reactor before a pipe completely breaks. The sodium leaking from piping of cooling system reacts with oxygen etc. including with the ambient gas to form aerosols. In the second coolant system of the prototype liquid metal FBR Monju, the ambient air around piping is drawn into radiative ionization detector (RID). When sodium aerosols are detected by RID, chemical analysis of aerosols and the viewing of the leak point are carried out, then sodium leak is confirmed. As the signal of RID depends on temperature strongly and RID detects the aerosols which do not include sodium, the improvements of RID are demanded for reliability. Moving fluid ionization detector (MID) and laser leak detector (LLD) have been developed to improve these points. MID can reduce the dependence for temperature of the signal strength, and LLD can detect sodium atoms which are included in aerosols by means of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. An experiment was carried out for validating sodium leak detection system with MID and LLD under real environment installed in the second coolant system of Monju. In the experiments, sodium was not leaked, and ambient air around piping of the secondary coolant system was introduced through actual sampling line and measured by MID and LLD. In addition a sodium level in the ambient air was measured by means of ion chromatography. The experiment showed that the background signals of MID and LLD were stable and low and that the sodium level due to the background of salinity (NaCl) contained in the ambient air was lower than three orders of magnitude than the sodium level for small sodium leak. The plant applicability of MID and RID was validated by this experiment.