Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H.*; Lee, D.-Y.*; Han, J. H.*; Hong, S.-K.*; Na, Y. S.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Woo, W.*; Lee, S.-Y.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 899, p.146453_1 - 146453_7, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:79.11(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)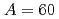
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:83.85(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Woo, W.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H. B.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Jeong, J. S.*; Lee, C. M.*; Won, J. W.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; et al.
Acta Materialia, 246, p.118699_1 - 118699_13, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:99.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)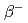 decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28
decay of exotic P and S isotopes with neutron number near 28Tripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064314_1 - 064314_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Walter, H.*; Colonna, M.*; Cozma, D.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Kumar, R.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. Y. B*; Xu, J.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; et al.
Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 125, p.103962_1 - 103962_90, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:95.20(Physics, Nuclear)Transport models are the main method to obtain physics information on the nuclear equation of state and in-medium properties of particles from low to relativistic-energy heavy-ion collisions. The Transport Model Evaluation Project (TMEP) has been pursued to test the robustness of transport model predictions to reach consistent conclusions from the same type of physical model. To this end, calculations under controlled conditions of physical input and set-up were performed by the various participating codes. These included both calculations of nuclear matter in a periodic box, which test individual ingredients of a transport code, and calculations of complete collisions of heavy ions. Over the years, five studies were performed within this project. They show, on one hand, that in box calculations the differences between the codes can be well understood and a convergence of the results can be reached. These studies also highlight the systematic differences between the two families of transport codes, known under the names of Boltzmann-Uehling-Uhlenbeck (BUU) and Quantum Molecular Dynamics (QMD) type codes. On the other hand, there still exist substantial differences when these codes are applied to real heavy-ion collisions. The results of transport simulations of heavy-ion collisions will have more significance if codes demonstrate that they can verify benchmark calculations such as the ones studied in these evaluations.
 resonances in a box
resonances in a boxOno, Akira*; Xu, J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Wolter, H.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; Chen, L.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044617_1 - 044617_35, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:98.53(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number and energies of collisions during the time evolution. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). This study showed that time step in the calculation is one of the biggest causes of the discrepancies. For example, the calculation by JQMD comprises 1-fm/c time steps, each of which is composed of transport, scattering and decay phases. Therefore a sequence of scattering, and decay followed by another scattering in 1 fm/c cannot be considered. Moreover, in JQMD particles are labeled by sequential numbers and scattering reactions are simulated by the order. Therefore scattering between low ID numbers, that between high ID numbers and that between the first (low ID) pair is overlooked in JQMD. Above indications obtained in this study must be kept in our mind for future JQMD upgrades.
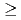 98 in multi-nucleon transfer reactions of
98 in multi-nucleon transfer reactions of  Ca+
Ca+ Cm
CmDevaraja, H. M.*; Heinz, S.*; Beliuskina, O.*; Hofmann, S.*; Hornung, C.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Ackermann, D.*; Gupta, M.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; Henderson, R. A.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Ackermann, D.*; Gupta, M.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; Henderson, R. A.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 55(2), p.25_1 - 25_9, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:77.31(Physics, Nuclear)Bentaib, A.*; Chaumeix, N.*; Grosseuvres, R.*; Bleyer, A.*; Gastaldo, L.*; Maas, L.*; Jallais, S.*; Vyazmina, E.*; Kudriakov, S.*; Studer, E.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2018/10
Zhang, Y.-X.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wolter, H.*; Xu, J.*; Chen, L.-W.*; Cozma, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034625_1 - 034625_20, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:117 Percentile:98.99(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and 320 neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number of particle-particle collisions as well as the energies of collisions during the time evolution. In addition to the calculation, their algorithms were compared. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). The results were compared with those calculated by the other 15 codes from over the world. Algorithm comparison showed that JQMD calculates collision probabilities from protons at first and collisions by neutrons are simulated later, which might be unreasonable. On the other hand, it was clarified that the calculation by JQMD agrees with those by the others. Despite the fact that some codes deviate from the average by a factor of 2, JQMD exhibited stable performance.
Chikhray, Y.*; Kulsartov, T.*; Shestakov, V.*; Kenzhina, I.*; Askerbekov, S.*; Sumita, Junya; Ueta, Shohei; Shibata, Taiju; Sakaba, Nariaki; Abdullin, Kh.*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2016) (CD-ROM), p.572 - 577, 2016/11
Application of SiC as corrosion-resistive coating over graphite remains important task for HTGR. This study presents the results of chemical interaction of the SiC gradient coating over the high-density IG-110 graphite with water vapor in the temperature up to 1673 K. The experiments at 100 Pa of water vapor showed that the passive reaction caused to form SiO film on the surface of SiC coating. Active corrosion of SiC in 1Pa of water vapor leads to deposits of various carbon composites on its surface.
film on the surface of SiC coating. Active corrosion of SiC in 1Pa of water vapor leads to deposits of various carbon composites on its surface.
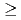 92 in multinucleon transfer reactions
92 in multinucleon transfer reactionsDevaraja, H. M.*; Heinz, S.*; Beliuskina, O.*; Comas, V. F.*; Hofmann, S.*; Hornung, C.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ackermann, D.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ackermann, D.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 748, p.199 - 203, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:96.92(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Polevoi, A. R.*; Loarte, A.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; Murakami, Masakatsu*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063019_1 - 063019_8, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:87.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Kim, H.-S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Na, Y.-S.*; Ghim, Y.-C.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Bak, J. G.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083012_1 - 083012_11, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.69(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We evaluate the characteristics of global energy confinement in KSTAR (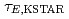 ) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database,
) quantitatively by comparing it with multi-machine scalings, by deriving multiple regression equations for the L- and the H-mode plasmas, and evaluating confinement enhancement of the H-mode phase compared with the L-mode phase in each discharge. From the KSTAR database, 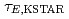 of L-mode plasmas exhibits
of L-mode plasmas exhibits 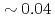 s to
s to 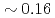 s and
s and 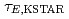 of H-mode plasmas
of H-mode plasmas 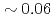 s to
s to 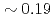 s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation
s. The multiple regression equations derived by statistical analysis present the similar dependency on PL and slightly higher dependency on IP compared with the multi-machine scalings, however the dependency on elongation  in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of
in both L- and H-mode plasmas draw the negative power dependency of 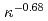 and
and 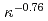 for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as
for H-mode and for L- mode database, respectively on the contrary to the positive dependency in all multi-machine empirical scalings. Although the reason is not clear yet, two possibilities are addressed. One is that the wall condition of KSTAR was not clean enough. The other is that striking points on the divertor plate were uncontrolled. For these reasons, as  increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
increases, the impurities from the wall can penetrate into plasmas easily. As a consequence, the confinement is degraded on the contrary to the expectation of multi-machine scalings.
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Joffrin, E.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Polevoi, A. R.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Loarte, A.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; Murakami, Masakatsu*; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 37D, p.P2.135_1 - P2.135_4, 2013/07
Yoon, S. W.*; Ahn, J.-W.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hahn, S. H.*; Ko, W. H.*; Lee, K. D.*; Chung, J. I.*; Nam, Y. U.*; Kim, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113009_1 - 113009_9, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:77.91(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Typical ELMy H-mode discharges have been achieved on the KSTAR tokamak with the combined auxiliary heating of NBI and ECRH. The minimum external heating power required is about 1.1 MW at a line-averaged density higher than 1.4 10
10 m
m and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than
and a toroidal field of 2 T. There is a clear indication of the increase of the L-H threshold power at densities lower than 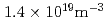 . The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
. The initial analysis of energy confinement time (
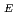 ) predicted that
) predicted that 
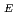 was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account,
was higher than the prediction of multi-machine scaling laws by a factor 1.4-1.6. However, when the contribution of fast ion confinement to the total energy was taken into account, 
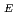 better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
better agreed with the scaling results. A clear increase of electron and ion temperature in the pedestal was observed in the H-mode phase but the core ion temperature did not change significantly. On the other hand, the toroidal rotation also increased over all radii in the H-mode phase. The measured ELM frequency was from 30-50 Hz and the drop of total energy appeared to be less than 5%. Between large ELM spikes, small/grassy ELMs were also identified when mixed heating of NBI and ECRH was applied.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 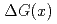 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.