Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:48.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It has long been suspected that magnetism could play a vital role in the phase stability of multi- component high-entropy alloys. However, the nature of the magnetic order, if any, has remained elusive. Here, by using elastic and inelastic neutron scattering, we demonstrate evidence of antiferromagnetic order below  80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as
80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as  -Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the
-Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the 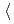 111
111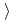 direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:95.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an in situ neutron diffraction study of 316 L that reveals an extraordinary work-hardening rate (WHR) of  7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite (
7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite ( -to-
-to- ') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the
') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the  '-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the
'-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the  -to-
-to- ' phase transformation was mediated by the
' phase transformation was mediated by the  -martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the
-martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the  phase with the
phase with the  phase.
phase.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lin, W.*; Kai, J.-J.*; Wu, Z.*; Lan, S.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 221, p.117371_1 - 117371_18, 2021/12
被引用回数:66 パーセンタイル:97.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi high-entropy alloy by in situ neutron diffraction at room temperature, intermediate low temperature of 140 K, low temperatures of 40 K (no serrated deformation) and 25 K (with massive serrations). The contributions from different deformation mechanisms to the yield strength and strain hardening have been estimated. The athermal contributions to the yield strength were  183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to
183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to  94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:78.00(Physics, Applied)We investigated the in situ deformation behavior of the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at a cryogenic temperature of 140 K and compared it with deformation at room temperature. The sample exhibited higher strength and larger ductility at the cryogenic temperature. The CrCoNi alloy remained single-phase face-centered cubic at room temperature, while deformation at 140 K resulted in a martensitic transformation to the hexagonal close-packed structure. The phase transformation, an additional deformation mechanism to stacking faults, twinning, and dis- location slip, resulted in a higher work hardening at cryogenic temperature. The study addresses the structure metastability in the CrCoNi alloy, which led to the formation of epsilon-martensite from the intrinsic stacking faults.
He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
被引用回数:72 パーセンタイル:96.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In CrCoNi, a so-called medium-entropy alloy, an fcc-to-hcp phase transformation has long been anticipated. Here, we report an in situ loading study with neutron diffraction, which revealed a bulk fcc-to-hcp phase transformation in CrCoNi at 15 K under tensile loading. By correlating deformation characteristics of the fcc phase with the development of the hcp phase, it is shown that the nucleation of the hcp phase was triggered by intrinsic stacking faults. The confirmation of a bulk phase transformation adds to the myriads of deformation mechanisms available in CrCoNi, which together underpin the unusually large ductility at low temperatures.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Zhang, F.*; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Lu, Z.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 188, p.21 - 25, 2020/11
被引用回数:89 パーセンタイル:98.25(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The deformation behavior of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction at an ultralow temperature of 15 K. Analysis of the diffraction peak widths showed an extremely high dislocation density at 15 K, reaching  10
10 m
m . In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
. In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
Woo, W.*; Naeem, M.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Lee, C.-M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 781, p.139224_1 - 139224_7, 2020/04
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:94.70(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)To elucidate deformation behavior behind the exceptional mechanical properties of CrCoNi based medium entropy alloys, the deformation related microstructural parameters were determined by using in situ neutron diffraction and peaks profile analysis methods. Superior tensile strength and elongation of the CrCoNi alloy is relevant to higher twin fault probability (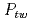 , up to 3.8%) and dislocation density (
, up to 3.8%) and dislocation density ( , up to 9.7
, up to 9.7  10
10 m
m ) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4
) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4  10
10 m
m , respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the
, respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the 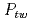 of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable
of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable  of
of  5.0
5.0  10
10 m
m and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Zhang, F.*; Huang, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 6(13), p.eaax4002_1 - eaax4002_8, 2020/03
被引用回数:237 パーセンタイル:99.38(Multidisciplinary Sciences)High-entropy alloys exhibit exceptional mechanical properties at cryogenic temperatures, due to the activation of twinning in addition to dislocation slip. The coexistence of multiple deformation pathways raises an important question regarding how individual deformation mechanisms compete or synergize during plastic deformation. Using in situ neutron diffraction, we demonstrate the interaction of a rich variety of deformation mechanisms in high-entropy alloys at 15 K, which began with dislocation slip, followed by stacking faults and twinning, before transitioning to inhomogeneous deformation by serrations. Quantitative analysis showed that the cooperation of these different deformation mechanisms led to extreme work hardening. The low stacking fault energy plus the stable face-centered cubic structure at ultralow temperatures, enabled by the high-entropy alloying, played a pivotal role bridging dislocation slip and serration.
Wang, B.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Lan, S.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Nie, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*; 他7名*
Scripta Materialia, 155, p.54 - 57, 2018/10
被引用回数:71 パーセンタイル:95.09(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The deformation behavior of an equi-atomic face-centered-cubic CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy was investigated by in-situ neutron diffraction under tensile loading up to 40% applied strain. A three-stage deformation behavior was fully captured by lattice strain and texture evolution. In spite of the chemical complexity, the deformation in CoCrFeNi is dominated by dislocation activities. Analysis of diffraction and microscopy data shows that the deformation progresses from dislocation slip to severe entanglement, where a sharp increase in dislocation density was observed. The neutron diffraction data, corroborated by transmission electron microscopy analysis, provided microscopic insights of the previously reported three-stage hardening behavior.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
no journal, ,
5元系CrMnFeCoNi高エントロピー合金を77Kで引張変形させると強度増加のみでなく伸びが増加したことが発見されて以来、高エントロピー合金の低温変形挙動に関する研究が重要なトピックスの一つとなった。変形挙動を理解するためには、低温下での機械的特性試験を行うと同時に、内部組織変化も調べて機械的特性変化との関連性の理解が必要である。今までの内部組織観察は、変形試験の前・後において、もしくは、変形試験の途中に中断して、顕微鏡を用いて行われたことは多く、全体の機械的試験の範囲をカバーすることができなかったり、観察領域が狭く試験片全体を代表した情報が得られなかったりすることはしばしばある。J-PARCのTAKUMIは、15Kの温度領域下での変形試験が行える周辺環境装置を完備し、その場中性子回折実験を行うことで、低温下の機械的特性を得ながら回折測定で内部組織変化を同時に調べることができる。得られたCrMnFeCoNi、CrFeCoNi及びCrCoNiの高・中エントロピー合金の低温変形挙動について紹介・比較する。