Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Yamaguchi, Yoshitaka*; Suzaki, Fumi; 27 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(1), p.014310_1 - 014310_13, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:84.33(Physics, Nuclear)Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.33(Instruments & Instrumentation) C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C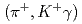 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 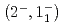 was measured to be
was measured to be 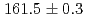 (stat)
(stat)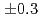 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 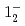 and
and 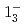 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 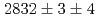 , keV and
, keV and 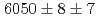 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
 Zn
ZnImai, Nobuaki*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nagae, Daisuke*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 46(2), p.157 - 160, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.02(Physics, Nuclear) -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 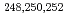 Cf by neutron-transfer reactions using a Cf target
Cf by neutron-transfer reactions using a Cf targetTakahashi, Ryuta; Ishii, Tetsuro; Asai, Masato; Nagae, Daisuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Yasuo; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(5), p.057303_1 - 057303_4, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.77(Physics, Nuclear)The ground-state bands of 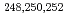 Cf have been established up to 10
Cf have been established up to 10 , 12
, 12 , and 10
, and 10 states, respectively, by in-beam
states, respectively, by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using neutron-transfer reactions with a
-ray spectroscopy using neutron-transfer reactions with a  O beam and a highly radioactive Cf target. The deexcitation
O beam and a highly radioactive Cf target. The deexcitation  rays in
rays in 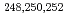 Cf were identified by taking coincidences with outgoing particles of
Cf were identified by taking coincidences with outgoing particles of 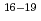 O measured with Si
O measured with Si 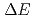 -
- detectors, and by selecting their kinetic energies. This is the first in-beam
detectors, and by selecting their kinetic energies. This is the first in-beam  -ray spectroscopy for Cf isotopes.
-ray spectroscopy for Cf isotopes.
 states in
states in 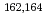 Gd populated by the
Gd populated by the  decay of
decay of 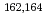 Eu
EuNagae, Daisuke*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Asai, Masato; Makii, Hiroyuki; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Shimizu, Yoshifumi*; Shoji, Takuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1224, p.156 - 160, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.32(Physics, Nuclear)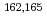 Gd using a total absorption detector
Gd using a total absorption detectorAsai, Masato; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Nagae, Daisuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Miyashita, Yuji*; Ouchi, Hiroyuki*; Izumi, Sayaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a new method to measure lifetime of long-lived isomers populated through the  decay, using a total absorption detector. Using this method, we have determined lifetime of the K isomers in
decay, using a total absorption detector. Using this method, we have determined lifetime of the K isomers in 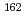 Gd and
Gd and 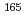 Gd for the first time. The short-lived neutron-rich nuclei
Gd for the first time. The short-lived neutron-rich nuclei 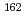 Eu and
Eu and 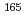 Eu were produced and mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator (ISOL) at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Beta- and
Eu were produced and mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator (ISOL) at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Beta- and  rays emitted by the
rays emitted by the  decay of
decay of 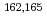 Eu were total-absorbed by the detector, and all the events were recorded with time stamps. This method enabled us to determine lifetime of the isomers with more than 100-
Eu were total-absorbed by the detector, and all the events were recorded with time stamps. This method enabled us to determine lifetime of the isomers with more than 100- s lifetime.
s lifetime.
 -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 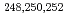 Cf using neutron-transfer reactions
Cf using neutron-transfer reactionsTakahashi, Ryuta; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nagae, Daisuke; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Yasuo; Matsuda, Makoto; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Makii, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagae, Daisuke; Takemuara, Makoto*; Ueno, Hideki*; Kameda, Daisuke*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Yoshimi, Akihiro*; Sugimoto, Takashi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Uchida, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
An electric quadrupole moment ( moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the
moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the  -moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the
-moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the  -detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply
-detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply 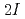 resonance frequencies, where
resonance frequencies, where  denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the
denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the 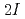 transitions. The application of the
transitions. The application of the 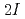 frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of
frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of  -ray asymmetry change for polarized
-ray asymmetry change for polarized  B. Using this system, the
B. Using this system, the  moments of
moments of 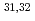 Al have been measured to be
Al have been measured to be 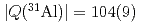
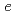
 mb and
mb and 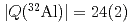
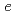
 mb by the sequential RF pulse method.
mb by the sequential RF pulse method.
Nagae, Daisuke; Ishii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta
no journal, ,
Construction of a linear ion trap is now in progress at JAEA-ISOL. We trapped  Na,
Na, 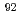 Rb, and
Rb, and 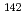 Cs ions successfully. We will talk about a development of the trap.
Cs ions successfully. We will talk about a development of the trap.
Nagae, Daisuke; Ishii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Zn by thick target inverse kinematics proton resonance scattering
Zn by thick target inverse kinematics proton resonance scatteringImai, Nobuaki*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nagae, Daisuke; Nishinaka, Ichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
The isobaric analog resonance of 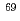 Zn was investigated by resonance elastic scattering of p(
Zn was investigated by resonance elastic scattering of p( Zn,p) with a 5.5 MeV/nucleon
Zn,p) with a 5.5 MeV/nucleon  Zn beam and a thick CH
Zn beam and a thick CH target at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Excitation function of the differential cross section of proton elastic scattering was measured around 0 degree in the laboratory frame. Angular momentum, and proton and total widths of the resonance determined using
target at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Excitation function of the differential cross section of proton elastic scattering was measured around 0 degree in the laboratory frame. Angular momentum, and proton and total widths of the resonance determined using  -matrix calculation are in good agreement with earlier measurements performed in normal kinematics.
-matrix calculation are in good agreement with earlier measurements performed in normal kinematics.
Sugiyama, Koichi*; Go, Shintaro*; Tomimatsu, Taro*; Kai, Tamito*; Nagae, Daisuke*; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Matsunaga, Sotaro*; Nagata, Yuto*; Nishibata, Hiroki*; Washiyama, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully performed in-beam gamma-ray spectroscopy using the isomer-scope technique to study excited-state structure of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei. The neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei were produced in the multinucleon-transfer reactions with a  Cm target and
Cm target and  O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E-
O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E- E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.