Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C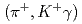 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 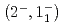 was measured to be
was measured to be 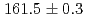 (stat)
(stat)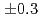 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 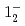 and
and 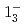 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 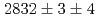 , keV and
, keV and 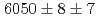 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nagae, Masahiro*; Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/10
The Thermochemical water-splitting cycle IS process constitutes severe environments to the materials of construction because of the corrosive chemicals. This paper discusses corrosion resistance of novel metallic materials in high temperature sulfuric and hydriodic acid. As for the sulfuric acid environment, corrosion resistances of MoN, Mo-Ta-N, and Mo-Cr-N alloys were examined. The experiments were performed for the duration of 5 hour in 90wt% sulfuric acid at 300 C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200
C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200 C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
Kawakami, Kazuto*; Tanaka, Masahiro*; Shirasu, Noriko; Kurata, Masaki; Nagae, Yuji
no journal, ,
JAEA and NSTec develop a thermodynamic database for fuel debris and concrete based on iron and concrete system, which has been developed for analysis of steel making process. Ionic two-sublattice model and cell model are examined for thermodynamic models of liquid oxide used in SA analysis. The current state and issues of the database used the models will be discussed.
Kurata, Masaki; To, Takehiko*; Tanaka, Masahiro*; Yamashita, Susumu; Nagae, Yuji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken; Furuya, Masahiro*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nagae, Yuji
no journal, ,
To facilitate the fuel debris retrieval as part of the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is necessary to grasp the in-depth debris distribution and status in the pedestal regions of the damaged units. For 1F Unit-3, it has been confirmed that the deposits in the pedestal region can be up to 2-3 meters high from the PCV internal investigations performed with remotely operated vehicles by TEPCO HD. This study will focus on the detailed evaluation of radiative heat transfer and convective vapor cooling boundaries applied on the free surfaces of debris and structures in the pedestal. Sensitivity analysis with different debris distributions, environment temperature, and emissivities was performed. The results show that remelting of debris and melting of pedestal structures are not expected during the re-heating phase if the pedestal background temperature is less than 1300 K.