Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yasuda, Yosuke*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Nabeshima, Fumika*; Horiuchi, Keisuke*; Nagai, Hiroki*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 213, p.124291_1 - 124291_2, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.99(Thermodynamics)Kadowaki, Masanao; Nagai, Haruyasu; Yoshida, Toshiya*; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(10), p.1194 - 1207, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:87.3(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study develops an estimation method using machine learning for uncertainty in forecasted plume directions. Bayesian machine learning was used in the machine learning approach. A three-day forecast simulation was conducted every day from 2015-2020, considering a hypothetical release of  Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Yoshida, Toshiya; Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(1), p.55 - 66, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atmospheric transport, dispersion, and deposition models (ATDMs) can support decision-making during nuclear emergencies; however, uncertainties in the ATDM results need to be carefully evaluated. To investigate the uncertainties derived from meteorological forecast inputs, we conducted three-day forecast simulations every day for one year with hypothetical releases of radionuclides (one-hour releases every 6 h) from a nuclear facility. The forecast outputs were compared with the analysis outputs during the same period. The difference between the outputs is treated as the uncertainty in the forecasts and is represented as an angle based on the discrepancy in the plume directions between the analysis and forecast outputs. Using meteorological inputs made by Japan Meteorological Agency, the discrepancy angle (Ang) increased by approximately 10 per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
Nagai, Yuki; Qi, Y.*; Isobe, Hiroki*; Kozii, V.*; Fu, L.*
Physical Review Letters, 125(22), p.227204_1 - 227204_7, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:94.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 As
As
Iida, Kazuki*; Nagai, Yuki; Ishida, Shigeyuki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Murai, Naoki; Christianson, A. D.*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Hiroki; Nakao, Akiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(1), p.014506_1 - 014506_8, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:84.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic excitations and magnetic structure of EuRbFe As
As were investigated by neutron scattering measurements.
were investigated by neutron scattering measurements.
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Nagai, Shin*; Kim, Y.*; Yan, W.*; Ikeda, Kyoko*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Suzuki, Rikie*
Remote Sensing, 10(7), p.1071_1 - 1071_19, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.87(Environmental Sciences)Plant phenology timings, such as spring green-up and autumn senescence, are essential state information characterizing biological responses and terrestrial carbon cycles. Current efforts for the in situ reflectance measurements are not enough to obtain the exact interpretation of how seasonal spectral signature responds to phenological stages in boreal evergreen needleleaf forests. This study shows the first in situ continuous measurements of canopy scale (overstory + understory) and understory spectral reflectance and vegetation index in an open boreal forest in interior Alaska. Two visible and near infrared spectroradiometer systems were installed at the top of the observation tower and the forest understory, and spectral reflectance measurements were performed in 10 min intervals from early spring to late autumn. We found that canopy scale normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) varied with the solar zenith angle. On the other hand, NDVI of understory plants was less sensitive to the solar zenith angle. Due to the influence of the solar geometry, the annual maximum canopy NDVI observed in the morning satellite overpass time (10-11 am) shifted to the spring direction compared with the standardized NDVI by the fixed solar zenith angle range (60-70 degree). We also found that the in situ NDVI time-series had a month-long high NDVI plateau in autumn, which was completely out of photosynthetically active periods when compared with eddy covariance net ecosystem exchange measurements. The result suggests that the onset of an autumn high NDVI plateau is likely to be the end of the growing season. In this way, our spectral measurements can serve as baseline information for the development and validation of satellite-based phenology algorithms in the northern high latitudes.
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 85(7), p.074707_1 - 074707_18, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.6(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 As
As )
)
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kuroki, Kazuhiko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.093702_1 - 093702_4, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from
Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo and fission of
Mo and fission of  U
UHashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ota, Masayuki; Konno, Chikara; Ochiai, Kentaro; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(4), p.043202_1 - 043202_4, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(3), p.033703_1 - 033703_4, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We numerically show that zero-energy Majorana surface states are suppressed around a vortex in three-dimensional topological superconductors such as Cu Bi
Bi Se
Se and Sn
and Sn In
In Te. On the other hand, zero-energy Majorana bound states along the vortex line are robust against a cut on the surface. The suppression of the surface-bound states is similar to that with a magnetic impurity on the surface of a topological insulator. The suppression of the surface-bound states around a vortex can be observed as an unconventional energy dependence of imaging by scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy.
Te. On the other hand, zero-energy Majorana bound states along the vortex line are robust against a cut on the surface. The suppression of the surface-bound states is similar to that with a magnetic impurity on the surface of a topological insulator. The suppression of the surface-bound states around a vortex can be observed as an unconventional energy dependence of imaging by scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy.
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.015013_1 - 015013_6, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(6), p.064703_1 - 064703_7, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:76.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(5), p.053705_1 - 053705_4, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 494, p.17 - 19, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.96(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 393, p.012017_1 - 012017_8, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.5(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Bi
Bi Se
Se
Nagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Physical Review B, 86(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_5, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:77.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In the promising candidate for topological superconductors, Cu Bi
Bi Se
Se , we propose a way to exclusively determine the pairing symmetry. The proposal suggests that the angle dependence of the thermal conductivity in the basal
, we propose a way to exclusively determine the pairing symmetry. The proposal suggests that the angle dependence of the thermal conductivity in the basal 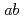 plane shows a distinct strong anisotropy only when the pairing symmetry is an odd-parity spin-polarized triplet below the superconducting transition temperature (
plane shows a distinct strong anisotropy only when the pairing symmetry is an odd-parity spin-polarized triplet below the superconducting transition temperature (
 ). Such striking isotropy breaking below
). Such striking isotropy breaking below 
 is explicitly involved in the Dirac formalism for superconductors, in which the spin-orbit coupling is essential. We classify possible gap functions based on the Dirac formalism and clarify an origin of the isotropy breaking.
is explicitly involved in the Dirac formalism for superconductors, in which the spin-orbit coupling is essential. We classify possible gap functions based on the Dirac formalism and clarify an origin of the isotropy breaking.
 (As
(As ,P
,P )
) using realistic three-dimensional 10-orbital tight-binding model
using realistic three-dimensional 10-orbital tight-binding modelNagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Usui, Hidetomo*; Kuroki, Kazuhiko*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.B), p.SB021_1 - SB021_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We calculate spin susceptibility on the basis of the multi-orbital random-phase approximation with use of the realistic three-dimensional 10-orbital tight-binding model for an iron-based superconductor BaFe (As
(As ,P
,P )
) which seems to have gap-nodes. We show that the shape of nodes on the Fermi surface for BaFe
which seems to have gap-nodes. We show that the shape of nodes on the Fermi surface for BaFe (As
(As ,P
,P )
) is distinguishable according to inelastic neutron scattering experiments. Our results are consistent with the recent neutron scattering experiments for BaFe
is distinguishable according to inelastic neutron scattering experiments. Our results are consistent with the recent neutron scattering experiments for BaFe (As
(As ,P
,P )
) with Tc = 30 K.
with Tc = 30 K.
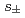 -like spin resonance in the iron-based nodal superconductor BaFe
-like spin resonance in the iron-based nodal superconductor BaFe (As
(As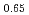 P
P )
) observed using inelastic neutron scattering
observed using inelastic neutron scatteringIshikado, Motoyuki; Nagai, Yuki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(14), p.144517_1 - 144517_5, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:70.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed inelastic neutron scattering on a powder sample of iron-based superconductor BaFe (As
(As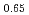 P
P )
) with
with  = 30 K. Although this system is expected to have line nodes in its superconducting order parameter, we have observed spin resonance at the same scattering vector as that appeared in the
= 30 K. Although this system is expected to have line nodes in its superconducting order parameter, we have observed spin resonance at the same scattering vector as that appeared in the 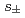 -wave iron-based superconductors without line nodes. Moreover, the resonance enhancement, which can be a measure of the area of sign reversal between the hole and electron Fermi surfaces (FSs), is comparable to those without line nodes. These facts indicate that the sign reversal between the FSs is still dominant in this system, and the line nodes should create only limited area of sign-reversal on a single FS. Hence the system can hold higher Tc than the other iron-based superconductors with nodal symmetry, such as LaFePO
-wave iron-based superconductors without line nodes. Moreover, the resonance enhancement, which can be a measure of the area of sign reversal between the hole and electron Fermi surfaces (FSs), is comparable to those without line nodes. These facts indicate that the sign reversal between the FSs is still dominant in this system, and the line nodes should create only limited area of sign-reversal on a single FS. Hence the system can hold higher Tc than the other iron-based superconductors with nodal symmetry, such as LaFePO and KFe
and KFe As
As (
(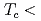 10 K).
10 K).
 ClO
ClO with anion ordering; First-principles calculations and quasiclassical analysis for angle-resolved heat capacity
with anion ordering; First-principles calculations and quasiclassical analysis for angle-resolved heat capacityNagai, Yuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Physical Review B, 83(10), p.104523_1 - 104523_8, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:64.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate angle-dependent heat capacity in a low magnetic field range on the basis of Kramer-Pesch approximation together with an electronic structure obtained by first-principles calculations to determine a superconducting gap function of (TMTSF) ClO
ClO through its comparisons with experiments. The present comparative studies reveal that a nodal d-wave gap function consistently explains the experimental results for (TMTSF)
through its comparisons with experiments. The present comparative studies reveal that a nodal d-wave gap function consistently explains the experimental results for (TMTSF) ClO
ClO . Especially, it is emphasized that the observed unusual axis-asymmetry of the angle-dependence eliminates the possibility of s-wave and node-less d-wave functions. It is also found that the directional ordering of ClO
. Especially, it is emphasized that the observed unusual axis-asymmetry of the angle-dependence eliminates the possibility of s-wave and node-less d-wave functions. It is also found that the directional ordering of ClO anions does not have any significant effects on the Fermi surface structure contrary to the previous modelings since the two Fermi surfaces obtained by the band calculations almost cross within the present full accuracy in first-principles calculations.
anions does not have any significant effects on the Fermi surface structure contrary to the previous modelings since the two Fermi surfaces obtained by the band calculations almost cross within the present full accuracy in first-principles calculations.
 s-wave superconducting states of iron-based superconductors
s-wave superconducting states of iron-based superconductorsMachida, Masahiko; Nagai, Yuki*; Ota, Yukihiro; Nakai, Noriyuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Hayashi, Nobuhiko*
Physica C, 470(Suppl.1), p.S372 - S374, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.09(Physics, Applied)We briefly present three phenomenological theoretical works for superconducting properties in iron-based superconductors. The first is a suggestion of multi-band  s-wave pairing model consistently explaining different measurement data, the second a proposal to detect
s-wave pairing model consistently explaining different measurement data, the second a proposal to detect  s-wave signature, and the third an evaluation of the critical current in polycrystalline samples by considering
s-wave signature, and the third an evaluation of the critical current in polycrystalline samples by considering  s-wave symmetry.
s-wave symmetry.