Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Inuzuka, Taisuke*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Nagai, Keiichi; Ide, Akihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(1), p.9 - 23, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)In sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), it is necessary to remove the sodium remaining on spent fuel assemblies (FAs) before storing them in a spent fuel water pool (SFP) in order to minimize plant operating loads. A next-generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning process which consists of the following steps: argon gas blowing to remove the metallic residual sodium on the FA, moist argon gas blowing to deactivate the residual sodium, and direct storage in the SFP. This process increases economic competitiveness and reduces waste products. In this R&D work, performance of the dry cleaning process has been investigated. This paper describes experimental and analytical work focusing on the amount of residual sodium remaining on FA components, for instance the handling head, the wrapper tube, the upper shielding, and the entrance nozzle which was conducted after investigation of residual sodium on fuel pin bundles as a part of series study of the cleaning process.
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Otani, Yuichi*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
A next generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of the argon gas blowing process to reduce the amount of metallic residual sodium remaining on spent fuel assemblies. This paper describes experimental and analytical work focusing on the amount of residual sodium remaining on a fuel pin bundle before and after the argon gas blowing process. The experiments were conducted using a sodium test loop and a short specimen consisting of a 7 pin bundle. The effects of the blowing gas velocity and the blowing time were quantitatively analyzed in the experiments. On the basis of these experimental results, evaluation models predicting the amount of the residual sodium were constructed.
Ide, Akihiro*; Kudo, Hideyuki*; Inuzuka, Taisuke*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
A next generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of the following process of argon gas blowing to reduce the amount of metallic sodium, moist argon gas blowing to deactivate the residual sodium, and direct storage in the SFP without using storage containers. This three-step process increases economic competitiveness and reduces waste products. In this Research and Development work, the amount of residual sodium and performance of the dry cleaning process were investigated. This paper describes experimental and analytical work for all parts of a fuel assembly except for a fuel pin bundle.
Ichikawa, Kenta*; Kanda, Hironori; Yoshioka, Naoki*; Ara, Kuniaki; Saito, Junichi; Nagai, Keiichi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
Studies on the suppression of the reactivity of sodium itself have been performed on the basis of the concept of suspended nanoparticles in liquid sodium (sodium nanofluid). According to the experimental and theoretical results of studies for sodium nanofluid, velocity and heat of sodium nanofluid-water reaction are lower than those of the pure sodium-water reaction. The analytical model for the peak temperature of a sodium nanofluid-water reaction jet has been developed in consideration of these suppression effects by the authors. In this paper, the prediction method for mitigation effects for a damage of adjacent tubes in a steam generator tube rupture (SGTR) accidents is arranged by applying this analytical model for the peak temperature of the reaction jet. On the assumption that the sodium nanofluid is used for the secondary coolant of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), mitigation effects under the design-base accident (DBA) condition and the design-extension condition (DEC) of SGTR are estimated by using this method. As a result, there is a possibility to reduce the number of damaged tubes and to suppress the pressure generated by SGTR accidents by using sodium nanofluid in the secondary coolant.
Abe, Yuta; Nagai, Keiichi; Maie, Mitsuyoshi*; Nakano, Natsuko*; Kawashima, Yuichi*; Takesue, Naohisa*; Saito, Junichi
Dai-23-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Kato, Atsushi; Nagai, Keiichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Otaka, Masahiko; Oka, Nobuki*; Tanaka, Masako*; Otani, Yuichi*; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
In a fuel handling system (FHS) of a sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is necessary to reduce residual sodium on a spent fuel subassembly before storing at a spent fuel water-pool (SFP) in order to minimize design loads. Although the wet cleaning process adopted on MONJU could eliminate almost all of residual sodium, a large amount of radioactive liquid waste occurs and it needs long duration of cleaning treatment and large plant commodities. On the other hand, Japan sodium-cooled fast reactor adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of roughly blowing massive sodium on the fuel subassembly out by 300 C argon gas, inactivation of residual sodium to NaOH by moist argon gas and directly immersion into the SFP to achieve economic competitiveness and waste reduction. This paper reports current status of recent R&D activities to demonstrate a performance of the dry cleaning process in Japan which are for improvement of the cleaning performance and optimizing the FHS design.
C argon gas, inactivation of residual sodium to NaOH by moist argon gas and directly immersion into the SFP to achieve economic competitiveness and waste reduction. This paper reports current status of recent R&D activities to demonstrate a performance of the dry cleaning process in Japan which are for improvement of the cleaning performance and optimizing the FHS design.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Nagai, Keiichi; Onojima, Takamitsu; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(1), p.71 - 77, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oxidation in the early stage of sodium combustion is especially important regarding the aspect of reaction continuity. The purpose of this study is to understand the sodium reaction precisely in order to apply the knowledge of the sodium reaction to promoting further safety of FRs.
Takeda, Junichi*; Suzuki, Yutaka*; Nakao, Mitsuteru*; Barrero, R. A.*; Koyanagi, Kanako*; Jin, L.*; Motono, Chie*; Hata, Hiroko*; Isogai, Takao*; Nagai, Keiichi*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 34(14), p.3917 - 3928, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:53.19(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We report the first genome-wide identification and characterization of alternative splicing in human gene transcripts based on analysis of the full-length cDNAs. Applying both manual and computational analyses for 56 419 completely sequenced and precisely annotated full-length cDNAs selected for the H-Invitational human transcriptome annotation meetings, we identified 6877 alternative splicing genes with 18 297 different alternative splicing variants. A total of 37 670 exons were involved in these alternative splicing events. The encoded protein sequences were affected in 6005 of the 6877 genes. Notably, alternative splicing affected protein motifs in 3015 genes, subcellular localizations in 2982 genes and transmembrane domains in 1348 genes. Genome-wide annotations of alternative splicing, relying on full-length cDNAs, should lay firm groundwork for exploring in detail the diversification of protein function which is mediated by the alternative splicing variants.
Nagai, Keiichi; Nagai, Keiichi; Otaka, Masahiko; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Onojima, Takamitsu
JNC TN9400 2003-058, 35 Pages, 2003/05
A preliminary examination was carried out for evaluation of the detection sensitivity of Laser Sodium Leak Detector (LLD) based on a principle of Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Evaluation criteria and examination conditions were planned based on the results of preliminary experiments.The main results are as follows:(1) Signal intensity of LLD was obtained with parameter of sodium concentration in combustion aerosols. The signal intensity in the combustion aerosols was nearly equivalent to that in case of sodium mist using carrier gas of nitrogen. It was shown that LLD was effective to detect sodium in the combustion aerosols.(2) Diameter or chemical component of sodium aerosols are one of significant factors for the detection sensitivity of LLD. Preliminary experiments were carried out with parameters of humidity, oxygen concentration, and pressure of carrier gas. The obtained experimental data of a few cases showed that influence of these parameters was limited on the detection sensitivity of LLD.3) Based on the preliminary experimental results, main conditions of a sensitivity evaluation test plan were decided for LLD.
Yoshiasa, Akira*; Murai, Keiichiro*; Nagai, Takaya*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 40(4A), p.2395 - 2398, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.87(Physics, Applied)The pressure dependence of extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) Debye-Waller factors in AgBr has been investigated using the cumulant expansion method. The Br K-edge EXAFS spectra were measured in the transmission mode under high pressure ( 9.1GPa) at room temperature using a cubic anvil type apparatus (MAX90) and synchrotron radiation from the Photon Factory, Tsukuba. The effective pair potentials
9.1GPa) at room temperature using a cubic anvil type apparatus (MAX90) and synchrotron radiation from the Photon Factory, Tsukuba. The effective pair potentials 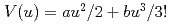 , were evaluated and the potential coefficient
, were evaluated and the potential coefficient  at 2.1, 4.2 and 6.1GPa are 1.59(4), 1.75(4) and 1.91(4) eV/
at 2.1, 4.2 and 6.1GPa are 1.59(4), 1.75(4) and 1.91(4) eV/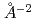 , respectively. The energies of the third-order anharmonic potential coefficient
, respectively. The energies of the third-order anharmonic potential coefficient  maintain nearly constant values with pressure though the third-order cumulant
maintain nearly constant values with pressure though the third-order cumulant 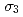 decreases with increasing in pressure.
decreases with increasing in pressure.
Nagai, Keiichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Saito, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Masahiro; Nagai, Keiichi; Onojima, Takamitsu; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Keiichi; Nishimura, Masahiro; Onojima, Takamitsu; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishimura, Masahiro; Nagai, Keiichi; Onojima, Takamitsu; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*
no journal, ,
The suppression effect of reaction of sodium with suspended nano-particles was confirmed by some experiments. Furthermore, the mechanism of suppression effect of reaction was grasped from the result of reaction experiments, physical property and theoretical consideration of interaction between nano-particles and sodium.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Nagai, Keiichi; Onojima, Takamitsu; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Nagai, Keiichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onojima, Takamitsu; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Nagai, Keiichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
Nagai, Keiichi; Onojima, Takamitsu; Nishimura, Masahiro; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English