Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mo for production of medical
Mo for production of medical  Tc by
Tc by  Mo(
Mo(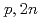 )
) Tc
TcHashimoto, Shintaro; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(12), p.124202_1 - 124202_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Tc, which is a daughter nuclide of
Tc, which is a daughter nuclide of  Mo, is used worldwide for medical imaging. However, there is a problem with the supply of
Mo, is used worldwide for medical imaging. However, there is a problem with the supply of  Tc (
Tc ( Mo) due to the replacement of aging reactors. A method to produce
Mo) due to the replacement of aging reactors. A method to produce  Tc by irradiating
Tc by irradiating  Mo with protons using medical cyclotrons has been proposed. In this study, we presented a method to determine individual excitation functions for Mo(
Mo with protons using medical cyclotrons has been proposed. In this study, we presented a method to determine individual excitation functions for Mo(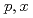 )Tc using measured excitation functions for
)Tc using measured excitation functions for  Mo(
Mo(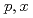 )Tc. The method was validated by comparing estimated radionuclide purities of
)Tc. The method was validated by comparing estimated radionuclide purities of  Tc in enriched
Tc in enriched  Mo samples using the determined excitation functions with measured ones. In this study, we found that the content of
Mo samples using the determined excitation functions with measured ones. In this study, we found that the content of  Mo,
Mo, 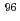 Mo, and
Mo, and  Mo should be low in order to produce
Mo should be low in order to produce  Tc with high radionuclide purity. The results of this study play an important role in discussion of the required Mo compositions in enriched
Tc with high radionuclide purity. The results of this study play an important role in discussion of the required Mo compositions in enriched  Mo, taking into account the constraints of each facility.
Mo, taking into account the constraints of each facility.
 Yb for producing
Yb for producing  Lu with high radionuclide purity by
Lu with high radionuclide purity by  Yb(
Yb(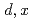 )
) Lu
LuNagai, Yasuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motomura, Arata*; Minato, Futoshi; Ito, Masatoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(4), p.044201_1 - 044201_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:46.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently,  Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce
Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce  Lu with high purity by using enriched
Lu with high purity by using enriched  Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than
Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than  Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of
Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of  Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(
Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(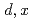 )Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity
)Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity  Lu using accelerators.
Lu using accelerators.
 Cu and
Cu and  Cu via the
Cu via the  Zn(n, p)
Zn(n, p) Cu and
Cu and  Zn(n, np/d)
Zn(n, np/d) Cu reactions using accelerator neutrons
Cu reactions using accelerator neutronsKawabata, Masako*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ota, Akio*; Motomura, Arata*; Saeki, Hideya*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 330(3), p.913 - 922, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.37(Chemistry, Analytical)Both  Cu and
Cu and  Cu are promising radionuclides in nuclear medicine. Production yields of these radionuclides were quantified by irradiating 55.4 g of natural zinc with accelerator neutrons. Clinically suitable
Cu are promising radionuclides in nuclear medicine. Production yields of these radionuclides were quantified by irradiating 55.4 g of natural zinc with accelerator neutrons. Clinically suitable  Cu and
Cu and  Cu yields were estimated by experimental based numerical simulations using 100 g of enriched
Cu yields were estimated by experimental based numerical simulations using 100 g of enriched  Zn and
Zn and  Zn, respectively, and elevated neutron fluxes from 40 MeV, 2 mA deuterons. A combined thermal- and resin-separation method was developed to isolate
Zn, respectively, and elevated neutron fluxes from 40 MeV, 2 mA deuterons. A combined thermal- and resin-separation method was developed to isolate  Cu and
Cu and  Cu from zinc, resulting in 73% separation efficiency and 97% zinc recovery. Such methods can provide large scale production of
Cu from zinc, resulting in 73% separation efficiency and 97% zinc recovery. Such methods can provide large scale production of  Cu and
Cu and  Cu for clinical applications.
Cu for clinical applications.
 -wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the
-wave direct capture and interference effect observed in the  O
O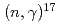 O reaction
O reactionNagai, Yasuki*; Kinoshita, Mitsutaka*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Nobuhara, Yuriko*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mishima, Kenji*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Mengoni, A.*
Physical Review C, 102(4), p.044616_1 - 044616_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear) ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutrons
ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutronsTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Minato, Futoshi; Kawabata, Masako*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034201_1 - 034201_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.68(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We found anomalously large yields of  Ga,
Ga, 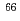 Ga,
Ga, 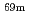 Zn and
Zn and  Cu by neutron irradiation on a
Cu by neutron irradiation on a  ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the
ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the  Be(
Be(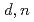 ) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of
) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of  Ga,
Ga, 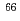 Ga,
Ga, 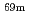 Zn and
Zn and  Cu from a metallic
Cu from a metallic  Zn sample and the yields of
Zn sample and the yields of  Cu,
Cu,  Ni and
Ni and  Zn from the
Zn from the  ZnO and
ZnO and  Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.
Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.
 Mo yield using large sample mass of MoO
Mo yield using large sample mass of MoO for sustainable production of
for sustainable production of  Mo
MoTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Minato, Futoshi; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ito, Masatoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(4), p.043201_1 - 043201_5, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Mo production yield by
Mo production yield by  Mo(
Mo(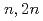 )
) Mo
MoMinato, Futoshi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Saeki, Hideya*; Kawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(11), p.114803_1 - 114803_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have measured the yield of  Mo, the mother nuclide of
Mo, the mother nuclide of  Tc used in nuclear diagnostic procedure.
Tc used in nuclear diagnostic procedure.  Mo was produced by
Mo was produced by  Mo(
Mo( ,
,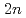 )
) Mo using neutrons with thermal energy up to about 40 MeV, provided by C(
Mo using neutrons with thermal energy up to about 40 MeV, provided by C( ,
, ). The
). The  Mo yield agrees with an estimated yield with the use of the latest data of C(
Mo yield agrees with an estimated yield with the use of the latest data of C( ,
, ) and the evaluated cross section given in the JENDL. Based on this, a new calculation was carried out to produce
) and the evaluated cross section given in the JENDL. Based on this, a new calculation was carried out to produce  Mo to seek for a good economical condition. Various conditions such as the
Mo to seek for a good economical condition. Various conditions such as the  MoO
MoO sample mass, the distance between the carbon target and the sample, the radius of the deuteron beam, and the neutron irradiation time were considered. The calculated
sample mass, the distance between the carbon target and the sample, the radius of the deuteron beam, and the neutron irradiation time were considered. The calculated  Mo yield indicates that about 30% of the
Mo yield indicates that about 30% of the  Mo demand in Japan can be fulfilled with a single accelerator. The elusion of
Mo demand in Japan can be fulfilled with a single accelerator. The elusion of  Tc from the
Tc from the  Mo twice per day would meet about 50% of the
Mo twice per day would meet about 50% of the  Mo demand.
Mo demand.
 Cu suitable for both cancer diagnosis and therapy
Cu suitable for both cancer diagnosis and therapyNagai, Yasuki*; Tsukada, Kazuaki
Isotope News, (753), p.28 - 32, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
 Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Zn(
Zn(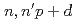 )
) Cu to biodistribution study in tumor-bearing mice
Cu to biodistribution study in tumor-bearing miceSugo, Yumi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Saeki, Hideya*; Sato, Shunichi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_3, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cu produced by the
Cu produced by the  Zn(
Zn(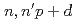 )
) Cu reaction was used for the first time to determine the biodistribution of
Cu reaction was used for the first time to determine the biodistribution of  CuCl
CuCl in colorectal tumor-bearing mice. High uptake of
in colorectal tumor-bearing mice. High uptake of  Cu was observed in the tumor as well as in the liver and kidney which are the major organs for copper metabolism. The result showing
Cu was observed in the tumor as well as in the liver and kidney which are the major organs for copper metabolism. The result showing  Cu accumulation in the tumor suggests that
Cu accumulation in the tumor suggests that  CuCl
CuCl can be a potential radionuclide agent for cancer radiotherapy. It would also encourage further studies on the therapeutic effect in small animals using an increased dose of
can be a potential radionuclide agent for cancer radiotherapy. It would also encourage further studies on the therapeutic effect in small animals using an increased dose of  Cu produced by the
Cu produced by the  Zn(
Zn(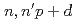 )
) Cu reaction using intense neutrons available at present.
Cu reaction using intense neutrons available at present.
 Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from
Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo and fission of
Mo and fission of  U
UHashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ota, Masayuki; Konno, Chikara; Ochiai, Kentaro; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(4), p.043202_1 - 043202_4, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)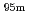 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1283 - 1285, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.04(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV
Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV  rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy
rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy  -rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some
-rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some  rays around 800 keV was produced by the
rays around 800 keV was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n)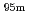 Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
 Tc from molten
Tc from molten  MoO
MoO
Kawabata, Masako; Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ota, Akio*; Shiina, Takayuki*; Kawauchi, Yukimasa*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_4, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Tc for medical use can be separated by thermochromatography from a molten
Tc for medical use can be separated by thermochromatography from a molten  MoO
MoO sample. Effect of moist oxygen gas on the
sample. Effect of moist oxygen gas on the  Tc release from molten
Tc release from molten  MoO
MoO samples was investigated using a
samples was investigated using a  Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator.
Tc generator.  Mo was produced with
Mo was produced with  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo. A new phenomenon has been observed: release rate, separation- and recovery-efficiencies of
Mo. A new phenomenon has been observed: release rate, separation- and recovery-efficiencies of  Tc were higher in the moist oxygen gas than those in the dry oxygen gas. The present result is a significant progress towards the stable production of a high quality
Tc were higher in the moist oxygen gas than those in the dry oxygen gas. The present result is a significant progress towards the stable production of a high quality  Tc from a molten MoO
Tc from a molten MoO sample with high separation efficiency. The result would also give us a new insight into the interaction between the moist oxygen gas and the molten MoO
sample with high separation efficiency. The result would also give us a new insight into the interaction between the moist oxygen gas and the molten MoO .
.
 Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Z(
Z( ,
, ) reaction using
) reaction using  C(
C( ,
, ) neutrons
) neutronsSato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Kawabata, Masako; Saeki, Hideya; Nagai, Yasuki; Kin, Tadahiro*; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(7), p.073201_1 - 073201_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have for the first time demonstrated that the therapeutic nuclide of  Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Zn(
Zn( ,
, )
) Cu has highest radionuclide purity compared to previous ones. We measured a
Cu has highest radionuclide purity compared to previous ones. We measured a  -ray spectrum of the reaction product produced by bombarding an enriched
-ray spectrum of the reaction product produced by bombarding an enriched  Zn sample with neutrons with a HPGe detector. The neutrons were obtained by
Zn sample with neutrons with a HPGe detector. The neutrons were obtained by  C(
C( ,
, ) using 41 MeV deuterons provided from Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Relative production yields of impurity radionuclides such as
) using 41 MeV deuterons provided from Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Relative production yields of impurity radionuclides such as  Zn to
Zn to  Cu are extremely low, which allow us to chemically separate
Cu are extremely low, which allow us to chemically separate  Cu from an irradiated
Cu from an irradiated  Zn sample with a few steps and to reuse high cost an enriched
Zn sample with a few steps and to reuse high cost an enriched  Zn sample. The present result strongly suggest that the
Zn sample. The present result strongly suggest that the  Zn(
Zn( ,
, )
) Cu reaction is the most promising route to produce high quality
Cu reaction is the most promising route to produce high quality  Cu and could solve a longstanding problem of establishing an appropriate production method of
Cu and could solve a longstanding problem of establishing an appropriate production method of  Cu.
Cu.
 Tc from molten
Tc from molten  MoO
MoO samples by repeated milking tests
samples by repeated milking testsNagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(8), p.083201_1 - 083201_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 69(6), p.370 - 375, 2014/06
In Japan, about 0.9 million diagnostic procedures are carried out using  Tc, the daughter nuclide of
Tc, the daughter nuclide of  Mo with a half-life of 66 h, separated from
Mo with a half-life of 66 h, separated from  Mo; all
Mo; all  Mo radioisotopes are imported. Most of
Mo radioisotopes are imported. Most of  Mo has been produced by the fission reaction of highly enriched
Mo has been produced by the fission reaction of highly enriched  U in research reactors in the world. However, a number of incidents of the reactors caused the shortage of
U in research reactors in the world. However, a number of incidents of the reactors caused the shortage of  Mo worldwide, which triggered widespread discussions on the reliable supply of
Mo worldwide, which triggered widespread discussions on the reliable supply of  Mo. We proposed a new route to produce a large quantity of high quality
Mo. We proposed a new route to produce a large quantity of high quality  Mo using fast neutrons from an accelerator.
Mo using fast neutrons from an accelerator.
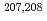 Pb
PbSegawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Fukahori, Tokio; Oshima, Masumi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1594, p.339 - 344, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki
Comprehensive Biomedical Physics, Vol.8, p.219 - 227, 2014/00
Radionuclides for medical use are produced in nuclear reactors and in accelerators. The thermal neutron fluxes in nuclear reactors are several orders of magnitude higher than those of other neutron sources, such as accelerator neutrons. Hence, nuclear reactors have been playing important roles in the production of large quantity of medical radionuclides with their half-lives longer than several days. In accelerators, medical radionuclides with their half-lives longer than several minutes are produced. Recent progresses in accelerator technology as well as targetry technology, however, could enable one to obtain high-flux bremsstrahlung and intense energetic accelerator neutrons, and thereby to study new routes to produce medical radionuclides.
Nagai, Yasuki
Hoshasen, 39(2), P. 43, 2013/11
When I was carrying out a basic study of nucleus physics using an accelerator, I was impressed with the ability of the accelerator. I thought that accelerators could contribute innovative works in many industry fields. In the practical application of accelerators in the medicine and industry, one has to find an important and interesting subject to be worth challenge on the basis of one's own knowledge and experience. Here, I would like to report my experience of the medicine and industrial use of accelerators.
Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji; Sonoda, Nozomi; Kawabata, Masako; Harada, Hideo; Kin, Tadahiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_7, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:85.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cu and
Cu and  Cu using accelerator neutrons
Cu using accelerator neutronsKin, Tadahiro*; Nagai, Yasuki; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Segawa, Mariko; Harada, Hideo; Konno, Chikara; Ochiai, Kentaro; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(3), p.034201_1 - 034201_8, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:79.70(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have measured the activation cross sections producing  Cu and
Cu and  Cu, promising medical radioisotopes for molecular imaging and radioimmunotherapy, by bombarding a natural zinc sample with 14 MeV neutrons. We estimated the production yields of
Cu, promising medical radioisotopes for molecular imaging and radioimmunotherapy, by bombarding a natural zinc sample with 14 MeV neutrons. We estimated the production yields of  Cu and
Cu and  Cu by fast neutrons from
Cu by fast neutrons from  C(d,n) with 40 MeV 5 mA deuterons. The calculated
C(d,n) with 40 MeV 5 mA deuterons. The calculated  Cu yield is 1.8 TBq (175 g
Cu yield is 1.8 TBq (175 g  Zn) for 12 h of irradiation; the yields of
Zn) for 12 h of irradiation; the yields of  Cu by
Cu by  Zn(n,p)
Zn(n,p) Cu and
Cu and  Zn(n,x)
Zn(n,x) Cu were 249 GBq (184 g
Cu were 249 GBq (184 g  Zn) and 287 GBq (186 g
Zn) and 287 GBq (186 g  Zn) at the end of 2 days of irradiation, respectively. From the results, we proposed a new route to produce
Zn) at the end of 2 days of irradiation, respectively. From the results, we proposed a new route to produce  Cu with very little radionuclide impurity via the
Cu with very little radionuclide impurity via the  Zn(n,x)
Zn(n,x) Cu reaction, and showed the
Cu reaction, and showed the  Zn(n,p)
Zn(n,p) Cu reaction to be a promising route to produce
Cu reaction to be a promising route to produce  Cu.
Cu.