Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tonegawa, Toru*; Ikoma, Toshiyuki*; Suetsugu, Yasushi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsushita, Yoshitaka*; Yoshioka, Tomohiko*; Hanagata, Nobutaka*; Tanaka, Junzo*
Materials Science & Engineering B, 173(1-3), p.171 - 175, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal expansion and crystal structure of A-type carbonate apatite with the monoclinic symmetry was investigated using the neutron powder diffraction at room temperature, 200, 300, 400 and 500 C. The
C. The  -axis and
-axis and  -axis lattice parameters were 0.9568 and 0.6868 nm at room temperature, and those were linearly increased with the increase of temperature. It was found that the linear thermal expansion coefficient of
-axis lattice parameters were 0.9568 and 0.6868 nm at room temperature, and those were linearly increased with the increase of temperature. It was found that the linear thermal expansion coefficient of  -axis was 1.31
-axis was 1.31 10
10 /
/ C and
C and  -axis 8.07
-axis 8.07 10
10 /
/ C.
C.
Tonegawa, Toru*; Ikoma, Toshiyuki*; Suetsugu, Yasushi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsushita, Yoshitaka*; Yoshioka, Tomohiko*; Hanagata, Nobutaka*; Tanaka, Junzo*
Proceedings of 22nd International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine (BIOCERAMICS-22), p.93 - 96, 2009/12
Hydroxyapatite is the main inorganic component of bone and tooth minerals, in which CO ions partially substitute for OH and/or PO
ions partially substitute for OH and/or PO ions. In this study, high purity type A carbonate apatite, Ca
ions. In this study, high purity type A carbonate apatite, Ca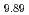 (PO
(PO )
)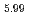 (CO
(CO )
)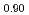 powder completely substituted by carbonate ions were synthesized by a treatment of low crystalline hydroxyapatite powder, Ca
powder completely substituted by carbonate ions were synthesized by a treatment of low crystalline hydroxyapatite powder, Ca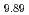 (PO
(PO )
)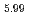 (OH)
(OH)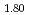 ) in a dry CO
) in a dry CO flow at 1000
flow at 1000  C. The crystal structure of the sample was the monoclinic symmetry with space group of
C. The crystal structure of the sample was the monoclinic symmetry with space group of 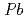 and the lattice parameters,
and the lattice parameters,  = 0.9566 (1),
= 0.9566 (1),  = 1.9063 (2),
= 1.9063 (2),  = 0.6867 (1) nm and
= 0.6867 (1) nm and  =119.84 (1)
=119.84 (1) , which was refined by a Rietveld method with neutron diffraction data.
, which was refined by a Rietveld method with neutron diffraction data.

Takahiro, Katsumi*; Oizumi, Shinnosuke*; Morimoto, Keiichi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Applied Surface Science, 256(4), p.1061 - 1064, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:36.66(Chemistry, Physical)Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
 (
(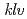 ), a novel hypernodulation mutant of
), a novel hypernodulation mutant of 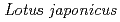 affected in vascular tissue organization and floral induction
affected in vascular tissue organization and floral inductionKira, Erika*; Tateno, Kumiko*; Miura, Kinichiro*; Haga, Tatsuya*; Hayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Kyuya*; Sato, Shusei*; Tabata, Satoshi*; Shikazono, Naoya; Tanaka, Atsushi; et al.
Plant Journal, 44(3), p.505 - 515, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:86.71(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Oizumi, Shinnosuke*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 )
)Asaka, Tomomi*; Hashimoto, Chika*; Ito, Kazusa*; Yasuda, Takako*; Nagata, Kento*; Nishimaki, Toshiyuki*; Katsumura, Takafumi*; Ota, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
It is thought that the irradiation to the particular area of the individual could induce the irradiation impact to the outside of the irradiated area in addition to the irradiated region. In this study, we established the procedures to conduct carbon ion irradiation on adult Medaka, which can irradiate only either dorsal or ventral side of the fish, using the broad-beam irradiation system of JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were examined heart rate before the fixation. Thereafter, the systemic alteration was evaluated by serial cross sections of the whole body of the fish. Tissues at the irradiated side were seriously injured that corresponded to the range of the beam. However, secondary gill lamella showed the characteristic edema in either the ventral or dorsal irradiated fish unless the gill located at ventral, suggesting the systemic irradiation effect. There was no alteration in the heart rate after the irradiation suggesting no severe effects in blood flow in this condition.
Asaka, Tomomi*; Ito, Kazusa*; Hashimoto, Chika*; Yasuda, Takako*; Nagata, Kento*; Nishimaki, Toshiyuki*; Katsumura, Takafumi*; Ota, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
Radiotherapy has been widely used in cancer target. It is thought that the irradiation to the particular area of the individual could induce the irradiation impact to the nearby and distant tissues of the irradiated area in addition to the irradiated region. However, it is still difficult to analyze influences to the whole body using mice because of its big body size. Medaka,  , is small enough to examine the acute somatic effects induced in all tissues at the cellular levels. In this study, we developed a method to conduct local irradiation on adult medaka using low energy carbon-ion beam in TIARA, JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were measured the heart rate to evaluate the impact to the heart, chemically fixed, serially sectioned and Hematoxylin/eosin stained. The results suggested that there would be the systemic effects by local irradiation in addition to the effects in the irradiated region, which is probably caused by immune system though blood.
, is small enough to examine the acute somatic effects induced in all tissues at the cellular levels. In this study, we developed a method to conduct local irradiation on adult medaka using low energy carbon-ion beam in TIARA, JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were measured the heart rate to evaluate the impact to the heart, chemically fixed, serially sectioned and Hematoxylin/eosin stained. The results suggested that there would be the systemic effects by local irradiation in addition to the effects in the irradiated region, which is probably caused by immune system though blood.
Sugiyama, Koichi*; Go, Shintaro*; Tomimatsu, Taro*; Kai, Tamito*; Nagae, Daisuke*; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Matsunaga, Sotaro*; Nagata, Yuto*; Nishibata, Hiroki*; Washiyama, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully performed in-beam gamma-ray spectroscopy using the isomer-scope technique to study excited-state structure of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei. The neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei were produced in the multinucleon-transfer reactions with a  Cm target and
Cm target and  O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E-
O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E- E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.