Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 319(3), p.767 - 773, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:72.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Adachi, Taihei*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Strasser, P.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kojima, Kenji*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036017_1 - 036017_4, 2015/09
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Takao*; et al.
Analytical Chemistry, 87(9), p.4597 - 4600, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:69.26(Chemistry, Analytical) =20 shell in
=20 shell in 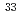 Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole moment
Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole momentShimada, Kenji*; Ueno, Hideki*; Neyens, G.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Balabanski, D. L.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Depuydt, M.*; De Rydt, M.*; Gaudefroy, L.*; Gr vy, S.*; et al.
vy, S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 714(2-5), p.246 - 250, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.81(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 85(2), p.228 - 230, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:60.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Elemental analysis of bulk materials can be performed by detecting the high-energy X-rays emitted from muonic atoms. Muon irradiation of standard bronze samples was performed to determine the muon capture probabilities for the elemental components from muonic X-ray spectra. Nondestructive elemental analysis of an ancient Chinese coin was also performed.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Saito, Tsutomu*; Higemoto, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012040_1 - 012040_4, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:96.63(Physics, Applied)Muon irradiation and muonic X-ray detection can be applied to non-destructive elemental analysis. In this study, in order to develop the elemental analysis by muonic X-ray measurement we constructed a new X-ray measuring system in J-PARC muon facility. We performed muon irradiation for Tempo-koban (Japanese old coin) for test experiment of elemental analysis.
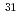 Al and determination of the effective proton charge in the sd-shell
Al and determination of the effective proton charge in the sd-shellDe Rydt, M.*; Neyens, G.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Balabanski, D. L.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Depuydt, M.*; Gaudefroy, L.*; Gr vy, S.*; Hasama, Yuka*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; et al.
vy, S.*; Hasama, Yuka*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 678(4), p.344 - 349, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:68.84(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Bulanov, S. V.; Bolton, P. R.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.449 - 454, 2009/06
The acceleration of protons driven by a high-intensity laser is comprehensively investigated via control of the target density by using ASE just before the time of the main-laser interaction. Two cases were investigated for which the ASE intensity differed by three orders of magnitude: In the low contrast case the beam centre for higher energy protons is shifted closer to the laser-propagation direction of 45 , while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
, while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ma, J.-L.; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1812 - 1816, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We observe UV harmonics and protons with a thin-foil target irradiated with a high-intensity Ti:sapphire laser. The laser intensity dependency of UV harmonics and proton signal is measured by varying the distance between the target surface and the best focus of the laser beam. In the case of appropriate condition for proton generation with a maximum energy of  2.7 MeV, the weak broad spectrum in the UV region is generated. The UV harmonics up to fourth-order are generated as the target is moved away from the best focus position. In this condition the maximum energy of protons is reduced to
2.7 MeV, the weak broad spectrum in the UV region is generated. The UV harmonics up to fourth-order are generated as the target is moved away from the best focus position. In this condition the maximum energy of protons is reduced to  1 MeV.
1 MeV.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Bulanov, S. V.; Nemoto, Koshichi*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physical Review E, 77(1), p.016401_1 - 016401_6, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:117 Percentile:97.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The duration-controlled amplified spontaneous emission with intensity of 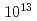 W/cm
W/cm is used to convert a 7.5
is used to convert a 7.5  m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the
m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the  -polarized, 45 fs,
-polarized, 45 fs, 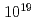 W/cm
W/cm laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45
laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45 . Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nemoto, Koshichi*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 112, p.042034_1 - 042034_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this work, we present a new method to enhance the proton generation by a 10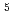 -contrast laser. High-energy protons up to 3.8 MeV are observed with 7.5-
-contrast laser. High-energy protons up to 3.8 MeV are observed with 7.5- m-thick insulator (Polyimide) target irradiated by a laser pulse having energy of 0.8 J and an intensity of 10
m-thick insulator (Polyimide) target irradiated by a laser pulse having energy of 0.8 J and an intensity of 10 -W/cm
-W/cm . Using two time-of-flight (TOF) spectrometers simultaneously in different directions, we measure the direction dependency of proton-energy spectra. As a result, we find that high-energy component of proton beam is shifted away from the target normal toward the laser-propagation direction, when the laser is focused with 45
. Using two time-of-flight (TOF) spectrometers simultaneously in different directions, we measure the direction dependency of proton-energy spectra. As a result, we find that high-energy component of proton beam is shifted away from the target normal toward the laser-propagation direction, when the laser is focused with 45 incident angle. The TOF measurements over 130 laser shots confirm that the generation of the high-energy protons, which are steered away from the target normal, depends strongly on the laser-focusing condition.
incident angle. The TOF measurements over 130 laser shots confirm that the generation of the high-energy protons, which are steered away from the target normal, depends strongly on the laser-focusing condition.
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:88.92(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Ito, Takashi; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
We determined muon capture probability for cupper, tin and lead atoms in bronze from muonic X-ray measurement. We also performed muon irradiation for old Chinese coin and determined contents of this sample.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Ito, Takashi; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is expected that muon irradiation and muonic X-ray detection emitted after formation of muonic atom can be applied to non-destructive elemental analysis. In this study, we performed muon irradiation for old Chinese bronze coin at MUSE in J-PARC and determined contents of this sample.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muonic atom is an atom like system that has one negatively charged muon instead of an electron. It is known that the formation process of muonic atom is influenced by the structure of muon capturing molecule (molecular effect). In this study, we performed systematic muon irradiation for low pressure nitrogen oxide samples and discuss the molecular effect on muon capture phenomena.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic atom is an atomic system that contains one negatively charged muon (muon is one of elementally particles) instead of an electron. When a muon is injected in material, the muon is slowing down by collisions with atomic electrons, and then low energy muon is captured on the coulomb field of a nucleus. As a result, the muon forms an atomic orbit around the nucleus, that is, a muonic atom is formed. It is considered that a muon capture phenomenon proceeds through muon collision and replacement with loosely binding electron, however the intrinsic mechanism of muon capture have not been investigated yet. In this study, we examine the formation processes of muonic atoms for nitrogen oxide samples (NO, N O and NO
O and NO ) by measuring muon characteristic X-rays (muonic X-rays) emitted after formation of muonic atoms.
) by measuring muon characteristic X-rays (muonic X-rays) emitted after formation of muonic atoms.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Taichi*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic atom is an atomic system that has one negatively charged muon instead of an electron. In this study, we examine the formation processes of muonic atoms for nitrogen oxide samples (NO, N O and NO
O and NO ) by measuring muon characteristic X-rays emitted after formation of muonic atoms, and the muon capture probabilities for these samples were determined. In the previous muon capture model, muon capture probability for each atom in molecule muonic atom is strongly influenced by the number of localized electrons in the atom. However, in our work, the experimental results were not reproduced by the previous model. In this paper, we discuss what influences on the muon capture probability.
) by measuring muon characteristic X-rays emitted after formation of muonic atoms, and the muon capture probabilities for these samples were determined. In the previous muon capture model, muon capture probability for each atom in molecule muonic atom is strongly influenced by the number of localized electrons in the atom. However, in our work, the experimental results were not reproduced by the previous model. In this paper, we discuss what influences on the muon capture probability.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ma, J.-L.; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high energy ions, electrons, X-ray, high-order harmonics, and THz radiation. High-energy protons driven by the high-intensity laser is paid attention as a compact ion source for medical application. The simultaneous generation of the protons and THz or harmonics will provide us high-density plasma diagnostic or unique pump-probe techniques. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (JLITE-X) in JAEA for THz radiation. The laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the 5  m thick Ti target. We observe simultaneously both the high-energy proton and THz radiation by changing the duration of ASE preceding the main pulse. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system in CRIEPI for harmonic generation. The laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the 7.5
m thick Ti target. We observe simultaneously both the high-energy proton and THz radiation by changing the duration of ASE preceding the main pulse. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system in CRIEPI for harmonic generation. The laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the 7.5  m thick polyimide target surface. The high-energy protons and UV harmonics are observed at the target is moved away from the best focus.
m thick polyimide target surface. The high-energy protons and UV harmonics are observed at the target is moved away from the best focus.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Taichi*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muonic atom is an atomic system that has one negatively charged muon instead of an electron. Muonic atom is formed when a negative muon is stopped in matter. There are many studies of muonic atom formation by measuring muonic X-rays emitted after formation of muonic atom. From these studies, "molecular effect" on muonic atom formation becomes clear; different muonic X-ray structures are obtained from muon irradiations between allotropes. In addition, muonic X-ray intensity patterns are also influenced by density of muon irradiation sample (density effect). The quantitative examination of molecular and density effect is essential to investigate muonic atom formation process by measuring muonic X-rays. In this study, we investigated density effect of muonic X-ray structure for nitrogen oxide samples.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Taichi*; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic atom is an atomic system that has one negatively charged muon instead of an electron. There are many studies related to the formation process of muonic atom by measuring muon characteristic X-rays. It is known that muon characteristic X-ray intensities are influenced by the density of the sample itself. However, most of previous studies did not consider this effect. In this study, we measured muon characteristic X-rays for dinitrogen mono-oxide with 0.1-1.0 atm. The same muonic X-ray intensities were obtained below 0.2 atm condition. This result means the density effect is neglectable below 0.2 atm for dinitrogen mono-oxide gas.