Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Naito, Masanori*; Kojima, Masayoshi*; Kikura, Hiroshige*; Lister, D. H.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 341, p.112 - 123, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)Improvement of plant reliability based on reliability-centered-maintenance (RCM) is going to be undertaken in NPPs. RCM is supported by risk-based maintenance (RBM). The combination of prediction and inspection is one of the key issues to promote RBM. Early prediction of IGSCC occurrence and its propagation should be confirmed throughout the entire plant systems which should be accomplished by inspections at the target locations followed by timely application of suitable countermeasures. From the inspections, accumulated data will be applied to confirm the accuracy of the code, to tune some uncertainties of the key data for prediction, and then, to increase their accuracy. The synergetic effects of prediction and inspection on application of effective and suitable countermeasures are expected. In the paper, the procedures for the combination of prediction and inspection are introduced.
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Iwasaki, Daisuke*; Higashino, Yuji*; Yoshimi, Chiaki*; Nakagawa, Koya*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(11), p.115103_1 - 115103_10, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:57.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigate three-dimensional(3D) momentum-resolved electronic structures of Ruddlesden-Popper-type iridium oxides Sr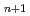 Ir
Ir O
O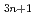 using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO
using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO -plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled
-plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled 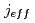 = 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO
= 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO and
and 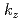 -dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr
-dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
. To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Sugawara, Hirotaka*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '16) (Internet), p.906 - 909, 2016/06
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The required beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present design of this compact, medium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.948 - 950, 2015/09
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The reqired beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present designof this compact, midium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Hori, Toshihiko; Oguri, Hidetomo; Sato, Fumiaki; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sugimura, Takashi*; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 16(4), p.040102_1 - 040102_8, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.42(Physics, Nuclear)We performed a high-power test of a new radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ II) for the J-PARC linac. RFQ II was developed as a spare RFQ because the operating J-PARC RFQ has suffered from a sparking problem. First, the conditioning of RFQ II was carried out; after 50 h of conditioning, RFQ II became very stable with a nominal power and duty of 330 kW and 3%, respectively. Next the thermal properties were measured because the resonant frequency of RFQ II is tuned by changing the temperature of the cooling water. The frequency response was measured and compared to finite-element method simulation results, confirming that the simple two-dimensional model reproduces the experimental data well. The differences in the field distribution with changes in the rf loading and the cooling-water temperature were also measured, and no serious field distortion was observed. Therefore, we conclude that RFQ II can perform well as a high-power rf cavity.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Naito, Fujio*
Proceedings of 26th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2012) (Internet), p.972 - 974, 2012/09
In this paper, we will report recent topics about J-PARC RFQs. First, the operating RFQ (RFQ I) have been recovered from the long shutdown due to the earthquake. This RFQ have been suffered from breakdown problem since 2008, therefore we have been developing a back-up RFQ (RFQ II). In April 2012, the high power test was successfully performed. It was confirmed to be able to stably operate at nominal power and duty factor (333 kW and 3%). Finally, we are fabricating a new RFQ for the beam-current upgrade of the J-PARC linac (RFQ III). The brazing of the first unit will be done in this September. The status of these RFQs are described.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Naito, Fujio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 667, p.5 - 10, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a new on-machine non-contact dimension-measurement system using a laser displacement sensor (LDS) for machining the vane tips of RFQs. The LDS was attached to a milling machine, and the dimensions of a test piece (TP) with a modulated vane tip were measured to evaluate the performance of the system. A longitudinal profile was measured with the LDS and it was compared with the profile measured with a coordinate measuring machine (CMM). A transverse profile was also measured. The required accuracy of dimension measurement was achieved using our system.
Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Naoki; Matsui, Hiroya; Tanai, Kenji; Maekawa, Keisuke; Sawada, Atsushi; Makino, Hitoshi; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Shibata, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-001, 193 Pages, 2011/03
This report summarizes the progress of research and development on geological disposal during the surface-based investigation phase (2001-2005) in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project, of which aims are to apply the design methods of geological disposal and mass transport analysis to actual geological conditions obtained from the surface-based investigations in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project as an example of actual geological environment.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.521 - 523, 2010/09
The fabrication of a new RFQ has been started as a backup machine for the J-PARC linac. The RFQ cavity is divided by three unit tanks in the longitudinal direction. The unit tank consists of two major vanes and two minor vanes, those are brazed together. A one-step vacuum brazing of a unit tank was adopted to unite these four vanes together with the flanges and ports. At the first tank brazing, the vacuum leak has been occurred due to the non-uniform temperature rise during the heating. Repair of this leakage and the results of the improved brazing of the second tank are reported.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.518 - 520, 2010/09
The fabrication of a new RFQ has been started in the J-PARC linac. The RFQ cavity is divided by three unit tanks in the longitudinal direction. The unit tank consists of two major vanes and two minor vanes, those will be brazed together. To reduce the costs and periods to develop the special formed bite for the modulation machining, a numerical controlled machining using a conventional ball-end-mill was adopted for the vane modulation cutting instead of the wheel shape cutter. The dimension accuracy was confirmed by cutting test pieces. Moreover, the obtained surface seems smooth enough for the operation. Results of the ball-end-mill machining for the vanes are described.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.783 - 785, 2010/05
The J-PARC RFQ (length 3.1 m, 4-vane type, 324 MHz) accelerates a negative hydrogen beam from 0.05 MeV to 3 MeV toward the following DTL. The stability of the operating RFQ decreased for a few months at the end of 2008, then, we started a preparation of a new RFQ as a backup machine in the case of RFQ problem. The beam dynamics design of the new RFQ is the same as the current cavity for a quick resumption of operation, however, the engineering and RF designs are changed to improve stability. The processes of the vane machining and the surface treatments have been carefully considered to reduce the discharge problem. The vacuum brazing technique has been chosen for vane jointing. The design of the new RFQ and the fabrication progress is descried in this proceeding.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.780 - 782, 2010/05
A new RFQ for the J-PARC linac is under construction for more stable operation. The requirement of this RFQ is almost same as the now-operating one; the resonant frequency is 324 MHz, the injection energy is 50 keV, the extraction energy is 3 MeV, peak beam current is 30 mA, and RF duty is 1.5%. The resonant frequency tuning during operation will be done by adjusting the temperatures of the cooling waters. We investigate with FEM model both cases; change vane water temperature and change cavity-wall water temperature. The frequency range was 0.35 MHz and 0.28 MHz, respectively. However in the transient analysis, the frequency change of the vane case was smaller than that of the cavity-call case. In this paper, thermal characteristics of this RFQ and control system of the cooling water temperature is described.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kubota, Chikashi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.621 - 623, 2010/05
The J-PARC RFQ accelerates a negative hydrogen beam from 50 keV to 3 MeV. Beam commissioning of the J-PARC linac started in November 2006 and the linac has delivered beams to the 3 GeV synchrotron since September 2007. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, unexpectedly increased in September 2008. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, improvement of vacuum properties, etc. User operations for the Material and Life Experimental Facilities were successfully carried out at 20 kW in June 2009, and the beam power was increased to 120 kW in November. The high power operation at 300 kW for one hour was also demonstrated. Status and improvement of the J-PARC RFQ are presented.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.1050 - 1052, 2010/03
The beam commissioning of J-PARC linac has been started since November 2006. After the scheduled shutdown in summer 2007, the beam is successfully delivered from the linac to the RCS. Since then, a stable beam provision to RCS was emphasized. However, the trip in the RFQ was increased at the end of Sept. 2008, then, the stability of the beam operation decreased. To improve this situation, we started to prepare a new RFQ cavity as a backup machine. The RF simulation is underway for the design of this backup RFQ. A basic estimation on the key components on RF properties such as a tuner, a dipole stabilizer, and a local field correction at the vacuum port are described in this proceeding.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Saito, Yoshio*; Baba, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.1047 - 1049, 2010/03
The beam commissioning of J-PARC linac has been started since November 2006. After the scheduled shutdown in summer 2007, the beam is successfully delivered from the linac to the RCS. Since then, a stable beam provision was emphasized. However, the trip in the RFQ was increased at the end of Sept. 2008, then, the stability of the beam operation decreased. To improve this situation, we started to prepare a new RFQ cavity as a backup machine. The basic concept of the engineering design is the simplicity and the effective vacuum pumping aiming at the stable operation. A 3m long cavity is divided into 3 modules longitudinally. A numerical control machining with ball-end mill is chosen for a vane machining. Four vanes are vacuum brazed each other after machining. Each modules are aligned on the platform using a linear motion guide. A basic design of the key components on machining and brazing are described in this proceeding.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.693 - 695, 2010/03
The J-PARC RFQ (length 3.1m, 4-vane type, 324 MHz) accelerates a beam from the ion source to the DTL. The beam test of the linac was started in November 2006 and 181 MeV beam was successfully accelerated in January 2007. Since then, the linac has been delivered beams for commissioning of the linac itself, downstream accelerators and facilities. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, suddenly increased in Autumn 2008, and we are suffering from this issue for user run operation. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, modification of RF control, improvement of vacuum and so on. We manage to have beam operation. In this report, we describe the status of the RFQ.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2009/05
A computer code, named COMPASS, is developed for multi-physics analysis of core disruptive accidents of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). A meshless method, called MPS method, is employed since complex thermal-hydraulics and structural problems with various phase change processes have to be analyzed. Verification for separeted basic processes and validation for practical phenomena are carried out. COMPASS is also expected to investigate molten fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality in large size SFR cores. Both MOX and metal fuels are considered. Eutectic reactions between the metal fuel and the cladding material are investigated by phase diagram calculation, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics. Basic studies relevant to the numerical methods support the code development of COMPASS. Parallel processing is implemented by OpenMP to treat large-scale problems. A visualization tool is also prepared by using AVS.