Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
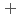 U
U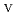
 Fe
Fe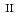
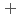 U
U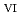 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
Segawa, Yukari; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nakada, Masami; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Tamura, Yukito*; Okamoto, Hisato; Otomo, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-039, 64 Pages, 2017/03
The laboratory building No.1 for the plutonium research program (Bldg. Pu1) was chosen as one of the facilities to decommission by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform in September, 2013. The research groups, users of Bldg. Pu1, were driven by necessity to remove used equipment and transport nuclear fuel to other facilities from Bldg. Pu1. Research Group for Radiochemistry proactively established the Used Equipment Removal Team for the smooth operation of the removal in April, 2015. The team classified six types of work into the nature of the operation, removal of used equipment, disposal of chemicals, stabilization of mercury, stabilization of nuclear fuel, transportation of nuclear fuel and radioisotope, and survey of contamination status inside the glove boxes. These works were completed in December, 2015. This report circumstantially shows six works process, with the exception of the approval of the changes on the usage of nuclear fuel in Bldg. Pu1 to help prospective decommission.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Nakada, Masami; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*; Akabori, Mitsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 471, p.110 - 115, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS) analyses were performed to evaluate REDOX (REDuction and OXidation) state of platinoid elements in simulated high-level nuclear waste glass samples prepared under different conditions of temperature and atmosphere. At first, EXAFS functions were compared with those of standard materials such as RuO . Then structural parameters were obtained from a curve fitting analysis. In addition, a fitting analysis used a linear combination of the two standard EXAFS functions of a given elements metal and oxide was applied to determine ratio of metal/oxide in the simulated glass. The redox state of Ru was successfully evaluated from the linear combination fitting results of EXAFS functions. The ratio of metal increased at more reducing atmosphere and at higher temperatures. Chemical form of rhodium oxide in the simulated glass samples was RhO
. Then structural parameters were obtained from a curve fitting analysis. In addition, a fitting analysis used a linear combination of the two standard EXAFS functions of a given elements metal and oxide was applied to determine ratio of metal/oxide in the simulated glass. The redox state of Ru was successfully evaluated from the linear combination fitting results of EXAFS functions. The ratio of metal increased at more reducing atmosphere and at higher temperatures. Chemical form of rhodium oxide in the simulated glass samples was RhO unlike expected Rh
unlike expected Rh O
O . It can be estimated rhodium behaves according with ruthenium when the chemical form is oxide.
. It can be estimated rhodium behaves according with ruthenium when the chemical form is oxide.
 Sn conductor for ITER central solenoid
Sn conductor for ITER central solenoidTakahashi, Yoshikazu; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Ozeki, Hidemasa; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Isono, Takaaki; Matsui, Kunihiro; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki; Uno, Yasuhiro; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 24(3), p.4802404_1 - 4802404_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:74.83(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is procuring all amounts of Nb Sn conductors for Central Solenoid (CS) in the ITER project. Before start of mass-productions, the conductor should be tested to confirm superconducting performance in the SULTAN facility, Switzerland. The original design of cabling twist pitches is 45-85-145-250-450 mm, called normal twist pitch (NTP). The test results of the conductors with NTP was that current shearing temperature (Tcs) is decreasing due to electro-magnetic (EM) load cycles. On the other hand, the results of the conductors with short twist pitches (STP) of 25-45-80-150-450 mm show that the Tcs is stabilized during EM load cyclic tests. Because the conductors with STP have smaller void fraction, higher compaction ratio during cabling is required and possibility of damage on strands increases. The technology for the cables with STP was developed in Japanese cabling suppliers. The several key technologies will be described in this paper.
Sn conductors for Central Solenoid (CS) in the ITER project. Before start of mass-productions, the conductor should be tested to confirm superconducting performance in the SULTAN facility, Switzerland. The original design of cabling twist pitches is 45-85-145-250-450 mm, called normal twist pitch (NTP). The test results of the conductors with NTP was that current shearing temperature (Tcs) is decreasing due to electro-magnetic (EM) load cycles. On the other hand, the results of the conductors with short twist pitches (STP) of 25-45-80-150-450 mm show that the Tcs is stabilized during EM load cyclic tests. Because the conductors with STP have smaller void fraction, higher compaction ratio during cabling is required and possibility of damage on strands increases. The technology for the cables with STP was developed in Japanese cabling suppliers. The several key technologies will be described in this paper.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 81(7), p.543 - 546, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:19.15(Electrochemistry)The molten state of simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitizing gray-scale values in the image. The existence of ruthenium element is emphasized as a black color in the CCD image at X-ray energy higher than the Ru K-absorption edge. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was also performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Proceedings of 4th Asian Conference on Molten Salt Chemistry and Technology & 44th Symposium on Molten Salt Chemistry, Japan, p.47 - 52, 2012/09
The molten state of the simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. The existence of ruthenium in the X-ray CCD image was emphasized over the energy of Ru K-absorption edge. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitalizing gray-scale values in the image. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(2), p.127 - 132, 2012/06
Distribution and the chemical state of Ru element in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. In this technique, a direct X-ray CCD camera is used in place of an ion chamber. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the X-ray CCD camera. At first, we measured a test sample containing RuO and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO
and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO .
.
 Am
Am )O
)O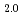
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Suzuki, Chikashi; Shibata, Hiroki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 418(1-3), p.311 - 312, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:79.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The XAFS measurements at U-L and Am-L
and Am-L absorption edge of (U
absorption edge of (U Am
Am )O
)O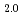 were performed in transmission mode. Moreover, to clarify the valence state of Am in (U,Am)O
were performed in transmission mode. Moreover, to clarify the valence state of Am in (U,Am)O , the XANES spectrum of Am-L
, the XANES spectrum of Am-L absorption edge of (U
absorption edge of (U Am
Am )O
)O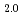 was verified using those of Am-L
was verified using those of Am-L absorption edge of AmO
absorption edge of AmO and Am
and Am O
O . It was found that the XANES spectrum of the Am-L
. It was found that the XANES spectrum of the Am-L edge of (U
edge of (U Am
Am )O
)O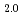 is in good accordance with that of Am
is in good accordance with that of Am O
O . Thus, Am in (U
. Thus, Am in (U Am
Am )O
)O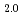 is almost trivalent state.
is almost trivalent state.
Amamoto, Ippei; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*; Takasaki, Yasushi*; Shibayama, Atsushi*; Yano, Tetsuji*; Nakada, Masami; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.503 - 508, 2010/10
The main objective of this development is to recycle the purified eutectic medium of the pyroreprocessing, delaying its disposal for as long as possible. We have introduced the simple filtration method to remove the rare earth element (REE) particles which were formed due to the conversion of REE chlorides to phosphates. Here, the iron phosphate glass is used as a filtration medium for the removal of FP particles. However, some soluble FP such as compounds of alkali-metals, alkaline-earth metals, etc. still remain in the eutectic medium. This time around, on an experimental basis, the iron phosphate glass has been used as a sorbent instead, to remove the soluble FP. We have obtained some positive results and have intention to incorporate it into the spent electrolyte recycle process as a part of the FP separation and immobilization system.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
The molten state of simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. The imaging XAFS results of our experiment clearly show that the ruthenium in the high temperature glass melt exists as oxide.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Nagayama, Sachiko*; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakada, Masami; Nagayama, Sachiko*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*
no journal, ,
The EXAFS measurement of simulated waste glass prepared under several heating conditions were performed to clarify redox state of Ru, Rh and Pd elements. The EXAFS functions were fitted by linear combination of standard functions of pure metal and its oxide. A ratio of metallic and oxide components in the simulated glass was obtained from the fitting analysis. We proposed we could evaluate redox state in the process of glass melters.
 ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopyMorii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Nakada, Masami; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Takahashi, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
To understand the influence of redox properties of structural Fe in clay minerals on removal and immobilization of radionuclides in geological disposal environment, we are investigating redox and structural properties of Fe in clay minerals over a large range of redox potentials. Clay mineral sample was reduced by controlled-potential electrolysis. Redox state and structural properties of Fe in this prepared clay mineral sample was investigated by Fe-57 M ssbauer spectroscopy. From the M
ssbauer spectroscopy. From the M ssbauer spectra, we obtained information about the amount of structural Fe(II) which reduced from structural Fe(III) and structural properties of Fe(II).
ssbauer spectra, we obtained information about the amount of structural Fe(II) which reduced from structural Fe(III) and structural properties of Fe(II).
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Akabori, Mitsuo
no journal, ,
Imaging XAFS technique using X-ray CCD camera has a remarkable feature of position sensitivity in contrast with the standard XAFS technique using ionic chambers. We have obtained XAFS spectra of nuclear materials at the BL-27B station located in the KEK and maintained by JAEA. In the present work, imaging XAFS measurement of actinide oxides was performed to confirm that it can be useful in researches on nuclear fuel and reprocessing of spent fuels in the future.
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Nakada, Masami; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Takahashi, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
The purpose of this research is to understand the redox reaction between structural Fe in clay minerals and concomitant elements in environments. Then, we are investigating redox properties of Fe in clay minerals over a large range of redox potentials (Eh) and pH. Redox state of the Fe-bearing clay mineral sample (nontronite) was controlled by potential electrolysis at various Eh-pH conditions. From this experiment, we obtained information about the dependence of the redox state of structural Fe in clay minerals on Eh and pH conditions.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Suzuki, Chikashi; Shibata, Hiroki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Distribution and the chemical state of fission product elements like Zr, Mo and Ru in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. We used the high resolution imaging system and the high-speed CCD camera for imaging XAFS measurement of the glass sample at molten state. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the CCD camera.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English