Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
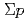 scattering experiment at J-PARC and the analysis status
scattering experiment at J-PARC and the analysis statusNakada, Yoshiyuki*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Nanamura, Takuya*; Naruki, Megumi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 26, p.023024_1 - 023024_5, 2019/11
 bound states in the
bound states in the  C
C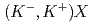 reaction at 1.8 GeV/
reaction at 1.8 GeV/ in J-PARC
in J-PARCNagae, Tomofumi*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; et al.
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 281, p.038_1 - 038_7, 2017/05
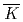 -nucleus interaction by using the
-nucleus interaction by using the  C(K
C(K , p) reaction at J-PARC
, p) reaction at J-PARCIchikawa, Yudai; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji; Nakada, Yoshiyuki; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 13, p.020007_1 - 020007_5, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)An interaction between K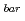 and nucleus is studied by using the X-ray from the kaonic atoms for a long time. However, it is difficult to determine the K
and nucleus is studied by using the X-ray from the kaonic atoms for a long time. However, it is difficult to determine the K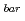 -nucleus interaction by using only kaonic-atoms data because the value of shift and width of the X-ray depend not only the potential depth but also the type of theoretical model. Thus, we study the
-nucleus interaction by using only kaonic-atoms data because the value of shift and width of the X-ray depend not only the potential depth but also the type of theoretical model. Thus, we study the 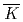 -nucleus interaction by comparing an observed missing-mass spectrum of the
-nucleus interaction by comparing an observed missing-mass spectrum of the  C(K
C(K , p) reaction with the DWIA calculation. Such a study has already reported from KEK-E548 experiment. However, their experiment is not enough to determine these interaction because they were pointed out about the experimental condition. Thus, we performed the further experiment to take the real spectrum of
, p) reaction with the DWIA calculation. Such a study has already reported from KEK-E548 experiment. However, their experiment is not enough to determine these interaction because they were pointed out about the experimental condition. Thus, we performed the further experiment to take the real spectrum of  C(K
C(K , p) reaction at J-PARC.
, p) reaction at J-PARC.
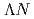 interaction;
interaction;  -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 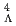 He
HeYamamoto, T. O.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Hwang, S.; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji; Nakada, Yoshiyuki; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 115(22), p.222501_1 - 222501_5, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:92.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Tsuru, Tomohito; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 74(12), p.1769 - 1774, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:51.43(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic state of a CaF -type (Am,U) mixed oxide using the all-electron full potential linear augmented plane wave method and compared it with those of Am
-type (Am,U) mixed oxide using the all-electron full potential linear augmented plane wave method and compared it with those of Am O
O , AmO
, AmO , UO
, UO , and La
, and La U
U O
O . The valence of Am in the mixed oxide was close to that of Am
. The valence of Am in the mixed oxide was close to that of Am O
O and the valence of U in the mixed oxide was pentavalent. The electronic structure of AmO
and the valence of U in the mixed oxide was pentavalent. The electronic structure of AmO was different from that of Am
was different from that of Am O
O , particularly just above the Fermi level. In addition, the electronic states of Am and U in the mixed oxide were similar to those of trivalent Am and pentavalent U oxides. These electronic states reflected the high oxygen potential of AmO
, particularly just above the Fermi level. In addition, the electronic states of Am and U in the mixed oxide were similar to those of trivalent Am and pentavalent U oxides. These electronic states reflected the high oxygen potential of AmO and the heightened oxygen potential resulting from the addition of Am to UO
and the heightened oxygen potential resulting from the addition of Am to UO and also suggested the occurrence of charge transfer from Am to U in the solid solution process.
and also suggested the occurrence of charge transfer from Am to U in the solid solution process.
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 73(2), p.209 - 216, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:68.65(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The authors investigated theoretically core-hole effects on X-ray absorption near-edge structures (XANES) of Np and Am L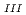 in neptunium dioxide (NpO
in neptunium dioxide (NpO ) and americium dioxide (AmO
) and americium dioxide (AmO ) with CaF
) with CaF -type crystal lattices using the all-electron full-potential linearized augmented plane-wave (FP-LAPW) method. The peak creation mechanism of XANES was shown by examining the electronic structures of these oxides, which indicated that core-hole screening was more marked for AmO
-type crystal lattices using the all-electron full-potential linearized augmented plane-wave (FP-LAPW) method. The peak creation mechanism of XANES was shown by examining the electronic structures of these oxides, which indicated that core-hole screening was more marked for AmO than for NpO
than for NpO because of the difference in the charge transfer between these oxides. Furthermore, the results of charge density analysis suggested that the white line was assigned to the quasi-bound state composed of the localized Np d or Am d components and O components, and that the tail structure was created as a result of delocalized standing waves between the Np or Am atoms.
because of the difference in the charge transfer between these oxides. Furthermore, the results of charge density analysis suggested that the white line was assigned to the quasi-bound state composed of the localized Np d or Am d components and O components, and that the tail structure was created as a result of delocalized standing waves between the Np or Am atoms.
 and Pr
and Pr O
O for XANES analysis with redox property
for XANES analysis with redox propertySuzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 109(12), p.2744 - 2752, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:32.22(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakada, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakada, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi
no journal, ,
A high statistical Sigma proton scattering experiment at J-PARC (J-PARC E40) is under preparation. High intensity  beam of
beam of 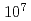 Hz will be used. It is very important to reject background events from a huge number of hit information including
Hz will be used. It is very important to reject background events from a huge number of hit information including 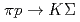 reaction events. We are developing a trigger system using complex hit information of counters in front and rear of a magnet. The developing status will be reported in this talk.
reaction events. We are developing a trigger system using complex hit information of counters in front and rear of a magnet. The developing status will be reported in this talk.
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Tsuru, Tomohito; Akabori, Mitsuo; Hirata, Masaru; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
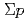 scattering experiment with the cylindrical scintillating fiber tracker and BGO calorimeters
scattering experiment with the cylindrical scintillating fiber tracker and BGO calorimetersNakada, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei
no journal, ,
The proton detection system is under construction for the 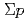 scattering experiment at J-PARC (J-PARC E40) for the purpose of investigating Baryon-Baryon interaction. The E40 experiment is a double-scattering experiment, that is,
scattering experiment at J-PARC (J-PARC E40) for the purpose of investigating Baryon-Baryon interaction. The E40 experiment is a double-scattering experiment, that is, 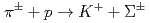 followed by
followed by 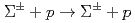 in the liquid hydrogen (
in the liquid hydrogen (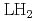 ) target. Then, the
) target. Then, the 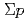 scattering events are identified by tagging the
scattering events are identified by tagging the  production with spectrometer systems, and by measuring the scattered proton with the proton detection system. The momentum of produced
production with spectrometer systems, and by measuring the scattered proton with the proton detection system. The momentum of produced  can be calculated from the momenta of
can be calculated from the momenta of  and
and  measured by the spectrometer systems. We can reconstruct
measured by the spectrometer systems. We can reconstruct 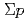 scattering events using their kinematics. The scattered proton detection system (CATCH: Cylindrical Active Tracker and Calorimeter system for Hyperon scattering) for this experiment is composed of cylindrical scintillating fiber tracker (CFT) and calorimeter of bismuth orthogermanate (BGO) crystals. Enough energy resolution of CFT to separate protons and
scattering events using their kinematics. The scattered proton detection system (CATCH: Cylindrical Active Tracker and Calorimeter system for Hyperon scattering) for this experiment is composed of cylindrical scintillating fiber tracker (CFT) and calorimeter of bismuth orthogermanate (BGO) crystals. Enough energy resolution of CFT to separate protons and  s is essential for good S/N. The construction of the 2 layer of CFT (CFT-
s is essential for good S/N. The construction of the 2 layer of CFT (CFT- 2 and CFT-UV2) was completed. We performed a test experiment at the Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center in Tohoku University to evaluate its performance.
2 and CFT-UV2) was completed. We performed a test experiment at the Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center in Tohoku University to evaluate its performance. 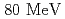 proton beams were irradiated to polyethylene (
proton beams were irradiated to polyethylene ( ) film target, and proton scattering data were acquired. Using the
) film target, and proton scattering data were acquired. Using the 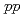 and
and  scattering data, we evaluated proton detection efficiency of CFT-
scattering data, we evaluated proton detection efficiency of CFT- 2 and -UV2 and their energy resolution.
2 and -UV2 and their energy resolution.
Nakada, Yoshiyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English