Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (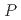
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 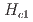 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 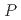 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
 Si
Si
Kon, Fusako*; Tabata, Chihiro; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044701_1 - 044701_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:99.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takagi, Rina*; Matsuyama, Naofumi*; Ukleev, V.*; Yu, L.*; White, J. S.*; Francoual, S.*; Mardegan, J. R. L.*; Hayami, Satoru*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.1472_1 - 1472_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:111 Percentile:99.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Otsuka, Yusuke*; Kanazawa, Naoya*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Matsui, Akira*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Arita, Ryotaro*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Ukleev, V.*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 7(47), p.eabj0498_1 - eabj0498_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:61.77(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okuma, Ryutaro*; Kofu, Maiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Avdeev, M.*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.4382_1 - 4382_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences) PdSi
PdSi
Hirschberger, M.*; Nakajima, Taro*; Kriener, M.*; Kurumaji, Takashi*; Spitz, L.*; Gao, S.*; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Yamasaki, Yuichi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(22), p.220401_1 - 220401_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:90.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakajima, Taro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Oike, Hiroshi*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Tokura, Yoshinori*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(1), p.014424_1 - 014424_5, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the phase-transition kinetics of magnetic skyrmion lattice (SkL) in MnSi by means of stroboscopic small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Temporal evolutions of SANS patterns were measured with time resolution of 13 ms while sweeping temperature as fast as 50 Ks . It turned out that the paramagnetic-to-SkL transition immediately occurs upon traversing the equilibrium phase boundary on the rapid cooling, whereas the SkL-to-conical transition can be kinetically avoided to realize the low-temperature metastable SkL with a long-range magnetic order. The formation of the metastable SkL was found to be strongly dependent not only on cooling rate, but also on magnetic eld and trajectory in the H-T phase diagram.
. It turned out that the paramagnetic-to-SkL transition immediately occurs upon traversing the equilibrium phase boundary on the rapid cooling, whereas the SkL-to-conical transition can be kinetically avoided to realize the low-temperature metastable SkL with a long-range magnetic order. The formation of the metastable SkL was found to be strongly dependent not only on cooling rate, but also on magnetic eld and trajectory in the H-T phase diagram.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
 CoSb
CoSb O
O
Ito, Saya*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ito, Shinichi*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.235_1 - 235_6, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:94.72(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ohae, Chiaki*; Harries, J.; Iwayama, Hiroshi*; Kawaguchi, Kentaro*; Kuma, Susumu*; Miyamoto, Yuki*; Nagasono, Mitsuru*; Nakajima, Kyo*; Nakano, Itsuo*; Shigemasa, Eiji*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 85(3), p.034301_1 - 034301_10, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary) C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C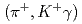 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 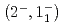 was measured to be
was measured to be 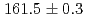 (stat)
(stat)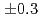 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 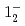 and
and 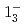 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 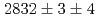 , keV and
, keV and 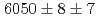 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Enoeda, Mikio; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Hirose, Takanori; Nakajima, Motoki; Sato, Satoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Konno, Chikara; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(7-8), p.1131 - 1136, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:82.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The development of a Water Cooled Ceramic Breeder (WCCB) Test Blanket Module (TBM) is being performed as one of the most important steps toward DEMO blanket in Japan. Regarding the fabrication technology development using F82H, the fabrication of a real scale mockup of the back wall of TBM was completed. Also the assembling of the complete box structure of the TBM mockup and planning of the pressurization testing was studied. The development of advanced breeder and multiplier pebbles for higher chemical stability was performed for future DEMO blanket application. From the view point of TBM test result evaluation and DEMO blanket performance design, the development of the blanket tritium simulation technology, investigation of the TBM neutronics measurement technology and the evaluation of tritium production and recovery test using D-T neutron in the Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS) facility has been performed.
Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Suzuya, Kentaro; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi
Physical Review E, 87(6), p.062314_1 - 062314_8, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:73.39(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) experiment is a particular technique that endeavors to define a relationship between time and space for the diffusion dynamics of atoms and molecules. However, in most cases, analyses of QENS data are model dependent. We have developed a new method for processing QENS data without a specific model, wherein all modes can be described as combinations of the relaxations based on the exponential law. By this method, we can obtain a new distribution function, 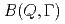 , which we call the mode distribution function (MDF), to represent the number of relaxation modes and distributions of the relaxation times in the modes. The deduction of MDF is based on the maximum entropy method. We report the first application to experimental data of liquid water. In addition to the two known modes, the existence of a new relaxation mode of water molecules with an intermediate time scale has been discovered.
, which we call the mode distribution function (MDF), to represent the number of relaxation modes and distributions of the relaxation times in the modes. The deduction of MDF is based on the maximum entropy method. We report the first application to experimental data of liquid water. In addition to the two known modes, the existence of a new relaxation mode of water molecules with an intermediate time scale has been discovered.
 -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals embedded in Si
nanocrystals embedded in SiMaeda, Yoshihito; Nishimura, Kentaro*; Nakajima, Takahito*; Matsukura, Bui*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji
Physica Status Solidi (C), 9(10-11), p.1888 - 1891, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:81.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have systematically investigated photoluminescence (PL) properties of  -phase nanocrystals which are formed by a phase transition from metastable
-phase nanocrystals which are formed by a phase transition from metastable  -FeSi
-FeSi with a Fluorite structure to
with a Fluorite structure to  -FeSi
-FeSi , and succeeded in enhancement of the PL intensity in the optimum conditions of double annealing process. For the PL enhancement, the time of postannealing at 800
, and succeeded in enhancement of the PL intensity in the optimum conditions of double annealing process. For the PL enhancement, the time of postannealing at 800 C is dominated by the time of the preannealing at 400 or 500
C is dominated by the time of the preannealing at 400 or 500 C which is related to amount of the
C which is related to amount of the  -phase. After discussing some possible factors, we speculate that the PL enhancement observed in this study may be attributed mainly to improvement of the interface condition between the nanocrystal and Si, because the crystallographic epitaxial relationship among the phases, Si(111)//
-phase. After discussing some possible factors, we speculate that the PL enhancement observed in this study may be attributed mainly to improvement of the interface condition between the nanocrystal and Si, because the crystallographic epitaxial relationship among the phases, Si(111)// (111)//
(111)// (202)/(220) can be maintained during precipitation of the nanocrystal on Si(111).
(202)/(220) can be maintained during precipitation of the nanocrystal on Si(111).
 -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals
nanocrystalsMaeda, Yoshihito; Nishimura, Kentaro*; Nakajima, Takahito*; Matsukura, Bui*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji
Physica Status Solidi (C), 9(10-11), p.1884 - 1887, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report enhancement of intrinsic photoluminescence (PL) from  -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals by doping carbon. In the appropriate dose of C
nanocrystals by doping carbon. In the appropriate dose of C
 ion implantation into the average nanocrystal size of 14 nm, the PL intensity was enhanced by 260% and increase of the exciton binding energy of 1.8 meV in comparison with that of the non-doped nanocrystal. Furthermore, we found that there was a clear correlation between the PL enhancement and increase of the exciton binding energy. This important result suggests that carbon atoms doped in the silicide lattice may play as an isoelectronic trap and probably form bound excitons with stable states as predicted theoretically. We found a new mechanism of the PL enhancement for
ion implantation into the average nanocrystal size of 14 nm, the PL intensity was enhanced by 260% and increase of the exciton binding energy of 1.8 meV in comparison with that of the non-doped nanocrystal. Furthermore, we found that there was a clear correlation between the PL enhancement and increase of the exciton binding energy. This important result suggests that carbon atoms doped in the silicide lattice may play as an isoelectronic trap and probably form bound excitons with stable states as predicted theoretically. We found a new mechanism of the PL enhancement for  -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals.
nanocrystals.
 Ga
Ga O
O (
( = 0, 0.018)
= 0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:64.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ga
Ga O
O (x =0, 0.018)
(x =0, 0.018)Nakajima, Taro*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Takahashi, Keiichiro*; Yoshitomi, Keisuke*; Masuda, Kazuya*; Kaneko, Chikafumi*; Homma, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kosaka, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094710_1 - 094710_8, 2012/09