Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
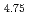 Sn
Sn by time resolved X-ray diffraction
by time resolved X-ray diffractionMachida, Akihiko; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.124 - 130, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.77(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Structural changes on hydrogen absorption process of hydrogen absorbing alloy LaNi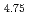 Sn
Sn have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi
have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi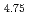 Sn
Sn under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi
under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi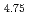 Sn
Sn has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La
has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La Ni
Ni (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) octahedron and La
octahedron and La (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 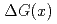 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:175 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 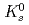 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
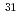 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Deguchi, Shigeki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; Inabe, Naoto*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:198 Percentile:97.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Oya, Kaoru*; Inai, Kensuke*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Toma, Mitsunori*; Tomita, Yukihiro*; Kawamura, Gakushi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(10), p.695 - 703, 2009/10
no abstracts in English
Shiina, Junichi*; Oikawa, Masataka; Nakamura, Kensuke; Obata, Rika*; Nishiyama, Shigeru*
European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2007(31), p.5190 - 5197, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:50.13(Chemistry, Organic)It is important to synthesize bio-active compounds which will affect DNA repair system. The total synthesis of pinguisane-type sesquiterpenoids, acutifolone A and pinguisenol, has been achieved by using the Mukaiyama aldol reaction as the key step. The intermolecular Diels-Alder reaction of these monomeric natural products successfully led to stereoselective dimerization, leading to bisacutifolones A and B. Theoretical calculations revealed that the dimerization reaction proceeded through the most stable transition state.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.6(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Gong, X.*; Nakamura, Kensuke; Yura, Kei; Go, Nobuhiro
IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 11(4), p.428 - 434, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.84(Computer Science, Information Systems)The emerging grid computing technologies enable bioinformatics scientists to conduct their researches in a virtual laboratory. However, the development of grid applications is still a nightmare for general bioinformatics scientists, due to the lack of grid programming environments. Here, we present a system, which we named Bioinformatics: Ask Any Questions (BAAQ), to automate this development procedure as much as possible. BAAQ allows scientists to store and manage remote biological data and programs, to build analysis workflows that integrate these resources seamlessly, and to discover knowledge from available resources. This paper addresses two issues in building grid applications in bioinformatics: how to smoothly compose an analysis workflow using heterogeneous resources and how to efficiently discover and re-use available resources in the grid community. Correspondingly an intelligent grid programming environment and an active solution recommendation service are proposed.
Mizutani, Miho*; Nakamura, Kensuke; Ichinose, Tazuko*; Itai, Akiko*
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 54(12), p.1680 - 1685, 2006/12
Upon completion of ongoing project about DNA repairing system, it would be desired to design chemical compound which accelerate or interfere the function of the DNA repairing system. Obtaining three-dimensional (3D) structures from structural formulae is a crucial process in such a molecular design. We have developed a new 3D model builder, Key3D, in which the simplified distance geometry technique and structure optimization based on the MMFF force field are combined. In an evaluation study using 598 crystal structures, the high performance and accuracy of Key3D were demonstrated. In the "flexible-fitting" test, which is focused on practical usefulness in the molecular design process, 88% of the Key3D structures acceptably reproduced the reference crystal structures (root-mean-square deviation  0.6
0.6 ) upon rotation of acyclic bonds. These results indicate that Key3D will be very effective in providing starting points for practical molecular design.
) upon rotation of acyclic bonds. These results indicate that Key3D will be very effective in providing starting points for practical molecular design.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Sato, Masayasu; Isono, Takaaki; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Ando, Masami; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1151 - 1158, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:123 Percentile:99.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Kensuke; Go, Nobuhiro
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 62(18), p.2050 - 2066, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:214 Percentile:86.8(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Multicopper blue proteins (MCBPs) are multi-domain proteins that utilize the distinctive redox ability of copper ions. There are variety of MCBPs that have been roughly classified into three different groups, (1)nitrite reductase-type with two domains, (2)laccase-type with three domains, and (3)ceruloplasmin-type with six domains. Together, the second and third group are often commonly called multicopper oxidases (MCOs). The rapid accumulation of genome sequence information in recent years has revealed several new types of proteins containing MCBP domains, mainly from bacteria. In this review, the recent research on the functions and structures of MCBPs is summarized, mainly focusing on the new types. The latter half of this review focusses on the two-domain MCBPs, which we propose as the evolutionary intermediate of the MCBP family.
Nakamura, Kensuke; Yura, Kei; Go, Nobuhiro
no journal, ,
Amount of information produced by genome projects is increasing at exponential rate. Yet, identifying the functions of unknown genes is still a slow process. Therefore techniques of bioinformatics should be developed to help enhance the rate of analysis. Metal-binding proteins are forming important subgroup of proteins. The knowledge of which, how many and where the metal ion can bind to a protein should give a good clue to how the protein function. The experimental analysis of metal binding property of a protein can be extensive. Recently, a high-throughput technique that roughly assigns the kind and amount of metal ions became available. Combination of the experimental data and bioinformatics analysis may lead to the determination of previously unknown metal-binding sites, then to the prediction of the function of the protein. In the present study, we describe results of our bioinformatics analysis on a set of proteins that are known to bind transition-metal ions.
Nakamura, Kensuke; Yura, Kei; Go, Nobuhiro
no journal, ,
Metal-binding proteins are forming important subgroup of proteins. The knowledge of which, how many and where the metal ion bind to a protein should give a good clue to how the protein function. The experimental analysis of metal binding property of a protein can be extremely laborious. Combination of the experimental data and bioinformatics analysis may lead to the prediction of new function of the protein. A method that exploits evolutionary information was employed to predict the potential metal- binding residues. Since diversity of sequences within a protein family can vary, we have developed an interactive tool to carefully analyze the evolutionary information. Our prediction was confirmed for the sequences whose three-dimensional structure with metal ions is already solved. Then we made prediction for the sequence whose metal-binding site was unknown.
Nakamura, Kensuke
no journal, ,
All the living things on the earth have evolved exploiting metal elements in the environment. Transition metals such as iron, zinc, copper, manganese, nickel, cobalt, vanadium, molybdenum are essential to most organisms. Most of these transition metals in our body exist coordinating specific binding site in protein. Recently, the importance of these metal elements in biological system has been attracting attention from biologists. There are several biological function of these metal elements, such as the stabilization of protein structure, electron/oxygen transportation, redox mediator and catalysis. I intend to clarify the function of these metal binding proteins, by designing a database that include the all known local structure of metal binding sites in PDB (protein data bank). In this presentation, I will describe the policy of the database construction, applications developed for the database, and preliminary results.
Higuchi, Kensuke; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Higuchi, Kensuke; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
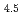 Al
Al alloy on hydrogen absorption process
alloy on hydrogen absorption processHiguchi, Kensuke; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English