Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)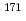 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Fujisawa, Yuita*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Tadashi*; Okada, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Understanding the nature of vortices in type-II superconductors has been vital for deepening the physics of exotic superconductors and applying superconducting materials to future electronic devices. A recent study has shown that the LiTi O
O (111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi
(111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi O
O (111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
(111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
 Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag, and
Ag, and  In
InNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1415 - 1430, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted for decommissioning are necessary to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivity produced. The present study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag and
Ag and  In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18
In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18 0.28 barn for
0.28 barn for  Sc(n,
Sc(n,  )
)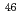 Sc, 4.34
Sc, 4.34 0.06 barn for
0.06 barn for  Cu(n,
Cu(n,  )
) Cu, 0.719
Cu, 0.719 0.011 barn for
0.011 barn for  Zn(n,
Zn(n,  )
) Zn, 4.05
Zn, 4.05 0.05 barn for
0.05 barn for  Ag(n,
Ag(n,  )
)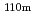 Ag and 8.53
Ag and 8.53 0.27 barn for
0.27 barn for  In(n,
In(n,  )
) 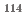 In
In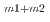 . The results for
. The results for  Sc and
Sc and  Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Osawa, Takahito; Terada, Kentaro*; Wada, Taiga*; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Chiu, I.-H.; Nakamura, Tomoki*; 40 of others*
Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 59(8), p.2044 - 2057, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Samples from asteroid Ryugu, brought back by asteroid explorer Hayabusa2 are important for investigating the origin and evolution of the solar system. Here, we report the elemental compositions of a 123 mg Ryugu sample determined with a nondestructive muon elemental analysis method. This method is a powerful tool for determining bulk chemical composition, including light elements such as C, N, and O. From the muonic X-ray spectra with three carbonaceous chondrites, the relationship between the elemental composition and muonic X-ray intensity was determined for each element. Calibration curves showed linearity, and the elemental composition of Ryugu was quantitatively determined. The results reflect the average bulk elemental composition of asteroid Ryugu owing to the large amount of samples. Ryugu has an elemental composition similar to that of Orgueil (CI1), and should be classified as CI1. However, the O/Si ratio of Ryugu is 25% lower than that of Orgueil, indicating that Orgueil may have been seriously contaminated by terrestrial materials after its fall to Earth. These results indicate that the Ryugu sample is more representative than the CI chondrites as a solid material of the solar system.
 shetta lakes in the Soya Coast region and their paleoenvironmental significance with glacial isostatic adjustment in East Antarctica
shetta lakes in the Soya Coast region and their paleoenvironmental significance with glacial isostatic adjustment in East AntarcticaInoue, Genki*; Honda, Eisuke*; Ito, Keisuke*; Kang, I.*; Seto, Koji*; Tani, Yukinori*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kashima, Kaoru*; Otani, Shuji*; Yamanaka, Toshiro*; et al.
Quaternary Science Reviews, 338, p.108822_1 - 108822_18, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geography, Physical)We studied Holocene paleolimnological changes inferred from biomarkers and microscopic observation of microalgae and cyanobacteria in sediment cores from Rundv shetta lakes (Maruwanminami-ike and Maruwan o-ike) in the Soya Coast of East Antarctica, along with sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dating. Coastal marine environment: Maruwanminami-ike (147-72.5 cm, 5,010-2,590 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (226-47.2 cm, 5,700-3,190 cal BP) were characterized by low biological production with the predominance of diatoms. Transition period of stratified brackish lake environment: Maruwanminami-ike (72.5-65.6 cm, 2,590-2,500 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (47.2-28.8 cm, 3,190-2,890 cal BP) were characterized by stratified conditions with marine water overlain by freshwater, and a chemocline developed together with an anoxic layer in the bottom of photic zone.
shetta lakes (Maruwanminami-ike and Maruwan o-ike) in the Soya Coast of East Antarctica, along with sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dating. Coastal marine environment: Maruwanminami-ike (147-72.5 cm, 5,010-2,590 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (226-47.2 cm, 5,700-3,190 cal BP) were characterized by low biological production with the predominance of diatoms. Transition period of stratified brackish lake environment: Maruwanminami-ike (72.5-65.6 cm, 2,590-2,500 cal BP) and Maruwan-oike (47.2-28.8 cm, 3,190-2,890 cal BP) were characterized by stratified conditions with marine water overlain by freshwater, and a chemocline developed together with an anoxic layer in the bottom of photic zone.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 46, 2024/07
The present work is an attempt to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for some nuclides which are of importance in decommissioning to evaluate produced radioactivity. This work selected some of objective nuclides for decommissioning, such as  Fe,
Fe,  Er and
Er and  Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23
Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23 0.03 barn for
0.03 barn for  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe reaction, 8.19
Fe reaction, 8.19 0.35 barn for
0.35 barn for  Er(n,
Er(n, )
)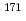 Er reaction and 13.57
Er reaction and 13.57 0.14 barn for
0.14 barn for  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427
Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427 0.006 barn for
0.006 barn for 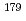 Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
 I and
I and  I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARC
I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
European Physical Journal A, 60(5), p.120_1 - 120_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.38(Materials Science, Ceramics)Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji
EPJ Web of Conferences, 294, p.01002_1 - 01002_7, 2024/04
 Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARC
Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.459 - 477, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ta
TaEndo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(4), p.786 - 803, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) I and
I and  I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARC
I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.74 - 79, 2024/02
Taniguchi, Koji*; Huang, P.-J.*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oishi, Kazuki*; Kito, Shunsuke*; Nakamura, Yuiga*; Miyasaka, Hitoshi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(2), p.024409_1 - 024409_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:51.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)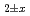 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) La and evaluation of resonance parameters
La and evaluation of resonance parametersEndo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Yoshikawa, Hiromoto*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
European Physical Journal A, 59(12), p.288_1 - 288_12, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 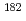 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.