Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Kasahara, Naoto*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakamura, Izumi*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Takuya*; Ichimiya, Masakazu*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/03
In this study, we propose failure mitigation methods by application of passive safety structures. The idea of the passive safety structures was applied to next generation fast reactors under high temperature conditions and excessive earthquake conditions.
 La and evaluation of resonance parameters
La and evaluation of resonance parametersEndo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Yoshikawa, Hiromoto*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
European Physical Journal A, 59(12), p.288_1 - 288_12, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kasahara, Naoto*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakamura, Izumi*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Takuya*; Ichimiya, Masakazu*
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/07
Utilizing fracture control, we are developing a technology to suppress the expansion of damage caused by an event that exceeds the design assumption. We made a plan to develop three issues; (1) Technology for mitigating failure consequence at extremely high temperatures, (2) Technology for mitigating failure consequence against excessive earthquakes, and (3) Methodology for improving reactor structure resilience.
Ishii, Mamoru*; Shiota, Daiko*; Tao, Chihiro*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Ishii, Takako*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Koga, Kiyokazu*; Kubo, Yuki*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.108_1 - 108_20, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.09(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We surveyed the relationship between the scale of space weather events and their occurrence rate in Japan and we discussed the social impact of these phenomena during the Project for Solar-Terrestrial Environment Prediction (PSTEP). The information was compiled for domestic users of space weather forecasts for appropriate preparedness against space weather disasters. This paper gives a comprehensive summary of the survey, focusing on the fields of electricity, satellite operations, communication and broadcasting, satellite positioning usage, aviation, human space activity, and daily life on the Earth's surface, using the cutting-edge knowledge of space weather. Quantitative estimations of the economic impact of space weather events on electricity and aviation are also given.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Tsutagi, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Kitao, Takahiko; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A.*; Browne, M.*
JAEA-Technology 2019-023, 160 Pages, 2020/03
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its Research and Development plan (STR-385), the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as a part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been tackling development of a new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous FPs as a joint research program with U.S. DOE to cover whole reprocessing process. In this study, High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant was used as the test field. At first, the design information of HALW storage tank and radiation (type and intensity) were investigated to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) model. And then, dose rate distribution outside/ inside of the concrete cell where the HALW tank is located was measured to design new detectors and check MCNP model applicability. Using the newly designed detectors, gamma rays and neutron were continuously measured at the outside/ inside of the concrete cell to assess the radiation characteristics and to optimize detector position. Finally, the applicability for Pu monitoring technology was evaluated based on the simulation results and gamma-ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination both of gamma-ray and neutron measurement. The results of this study suggested the applicability and capability of the Pu motoring to enhance safeguards for entire reprocessing facility which handles Pu with FP as a feasibility study. This is final report of this project.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Tsutagi, Koichi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A.*; Browne, M.*
Proceedings of IAEA Symposium on International Safeguards; Building Future Safeguards Capabilities (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/11
The IAEA has proposed, in its Research and Development plan (STR-385), the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, JAEA and JNFL had previously designed and developed a neutron coincidence based non-destructive assay system to monitor Pu in solution directly after a purification process. To enhance this technology for entire reprocessing facilities, as a feasibility study, JAEA has been tackling development of a new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous fission products (FPs) as a joint research program with the U.S. DOE. In this study, the High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) was used as the test bed. The design information of the HALW storage tank and radiation (type and intensity) were investigated, to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) model. Then, dose rate distribution inside the concrete cell where the HALW tank is located was measured, to enable design of new detectors and check the integrity of the MCNP model and its applicability. Using the newly-designed detectors,  -rays and neutrons could be measured continuously at the outside/inside of the concrete cell, to optimize detector position and the radiation characteristics. The applicability as a Pu-monitoring technology was evaluated, based on the simulation results and
-rays and neutrons could be measured continuously at the outside/inside of the concrete cell, to optimize detector position and the radiation characteristics. The applicability as a Pu-monitoring technology was evaluated, based on the simulation results and  -ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is a possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination of
-ray/neutron measurement results. We have found that there is a possibility to monitor the change of Pu amount in solution by combination of  -ray and neutron measurements. The results of this study suggest a feasibility study into the applicability and capability of Pu monitoring to enhance the entire reprocessing facility handling Pu with FPs. In this paper, a summary of the project will be presented.
-ray and neutron measurements. The results of this study suggest a feasibility study into the applicability and capability of Pu monitoring to enhance the entire reprocessing facility handling Pu with FPs. In this paper, a summary of the project will be presented.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Tokoro, Hayate; Tsutagi, Koichi; Kitao, Takahiko; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2018/07
In a reprocessing facility, it is necessary to develop a detector which can measure plutonium (Pu) content in the Pu solutions containing fission products (FP) in order to expand the application of Pu monitoring. In order to establish this technology, JAEA has studied a system measure  -rays was utilized since it applicable for Pu monitoring. Ce:GAGG (Ce:Gd
-rays was utilized since it applicable for Pu monitoring. Ce:GAGG (Ce:Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O ) scintillator detector can measure a wide energy range in a high-dose environment and has reasonable resolution.
) scintillator detector can measure a wide energy range in a high-dose environment and has reasonable resolution.  -ray measurements were performed inside of the concrete cell containing the High Active Liquid Waste tank at the Tokai reprocessing plant. In the spectra, the two significant peaks were measured by the GAGG above 800 keV and were considered to be from Eu-154. There
-ray measurements were performed inside of the concrete cell containing the High Active Liquid Waste tank at the Tokai reprocessing plant. In the spectra, the two significant peaks were measured by the GAGG above 800 keV and were considered to be from Eu-154. There  -ray measurements will be combined with previous neutron measurements and both will be compared to MCNP models for future Pu monitoring technology. This presentation will describe the detector selection, the design system, the results of
-ray measurements will be combined with previous neutron measurements and both will be compared to MCNP models for future Pu monitoring technology. This presentation will describe the detector selection, the design system, the results of  -ray spectral measurements and the applicability for Pu monitoring. This project has been carried out under the support of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of the Japanese government.
-ray spectral measurements and the applicability for Pu monitoring. This project has been carried out under the support of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of the Japanese government.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Tokoro, Hayate; Tsutagi, Koichi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-38-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/04
In a reprocessing facility, it is necessary to develop a detector which is measurable plutonium (Pu) amount in the Pu solution containing the Fission Product (FP) in order to expand the application of Pu monitoring. To investigate  rays which is applicable for Pu monitoring, Ce:GAGG (Ce: Gd
rays which is applicable for Pu monitoring, Ce:GAGG (Ce: Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O ) scintillator which can measure a wide range of energy at high dose and has high resolution (Target: High Active Liquid Waste (HALW)) was newly designed and developed in deal with aim for Pu quantitativeness.
) scintillator which can measure a wide range of energy at high dose and has high resolution (Target: High Active Liquid Waste (HALW)) was newly designed and developed in deal with aim for Pu quantitativeness.  ray measurement was performed to the HALW in the concrete cell using the detector, and it was confirmed that high energy
ray measurement was performed to the HALW in the concrete cell using the detector, and it was confirmed that high energy  rays (9.5 MeV) could be measured and high energy
rays (9.5 MeV) could be measured and high energy  rays spectra over 3 MeV without deriving from FP at the first time. In this presentation, detector design, results of
rays spectra over 3 MeV without deriving from FP at the first time. In this presentation, detector design, results of  ray spectra measurement, applicability evaluation to Pu monitoring and the future plan are presented. This project has been carried out under the support of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of the Japanese government.
ray spectra measurement, applicability evaluation to Pu monitoring and the future plan are presented. This project has been carried out under the support of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of the Japanese government.
Matsuki, Takuya; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Sekine, Megumi; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Browne, M. C.*
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2017/07
The Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has been developing a new detector from 2015 to 2017 for purpose to monitor Pu amount in High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) containing FP. It can make a contribution to an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities because it becomes available to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously by a new detector, which has proposed by IAEA. For the second step of this project, we conducted dose rate measurement on the guide rail installing in the cell storing the HALW tank and comparison between measured dose rate distribution and calculation result by MCNP simulation in order to investigate the dose rate distribution which is needed for shielding design of a new detector that is used for radiation (neutron/ spectrum) measurement in the cell and inquest on the monitoring position of the detector for Pu monitoring. In this paper, we report the result of the dose rate measurement in the cell, improvement of the simulation model which is cleared by comparison between measurement result and calculation result and our future plan.
spectrum) measurement in the cell and inquest on the monitoring position of the detector for Pu monitoring. In this paper, we report the result of the dose rate measurement in the cell, improvement of the simulation model which is cleared by comparison between measurement result and calculation result and our future plan.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Suzuki, Satoshi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; LaFleur, A. M.*; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.788 - 796, 2017/00
The IAEA has proposed in its long-term R&D plan, the development of technology to enable real-time flow measurement of nuclear material as a part of an advanced approach to effective and efficient safeguards for reprocessing facilities. To address this, JAEA has designed and developed a neutron coincidence based nondestructive assay system to monitor Pu directly in solutions which is after purification process and contains very little fission products (FPs). A new detector to enable monitoring of Pu in solutions with numerous FPs is being developed as a joint research program with U.S. DOE at the High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) Storage Facility in Tokai Reprocessing Plant. As the first step, the design information of HALW tank was investigated and samples of HALW was taken and analyzed for Pu concentration and isotope composition, density, content of dominant nuclides emitting  ray or neutron, etc. in order to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) of the HALW tank. In addition,
ray or neutron, etc. in order to develop a Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code (MCNP) of the HALW tank. In addition,  ray source spectra simulated by Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) was developed by extracting peaks from the analysis data with germanium detector. These outputs are used for the fundamental data in the MCNP model which is then used to evaluate the type of detector, shielding design and measurement positions. In order to evaluate available radiations to measure outside the cell wall, continuous
ray source spectra simulated by Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) was developed by extracting peaks from the analysis data with germanium detector. These outputs are used for the fundamental data in the MCNP model which is then used to evaluate the type of detector, shielding design and measurement positions. In order to evaluate available radiations to measure outside the cell wall, continuous  ray and neutron measurement were carried out and the results were compared to the simulation results. The measurement results showed that there are no FP peaks above 3 MeV. This paper presents an overview of the research plan, characteristics of HALW, development of source term for MCNP, simulation of radiation dose from the HALW tank and radiation measurement results at outside of cell wall.
ray and neutron measurement were carried out and the results were compared to the simulation results. The measurement results showed that there are no FP peaks above 3 MeV. This paper presents an overview of the research plan, characteristics of HALW, development of source term for MCNP, simulation of radiation dose from the HALW tank and radiation measurement results at outside of cell wall.
Matsuki, Takuya; Masui, Kenji; Sekine, Megumi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Ishiyama, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development (R&D) plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. Since the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has solutions containing both Pu and fission products (FP), a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in the TRP. For the first step of this project, as the confirmation of composition of high active liquid waste (HALW) to evaluate neutron/ -ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted
-ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted  -ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/
-ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/ -ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/
-ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/ -ray detector. In this paper, we report three
-ray detector. In this paper, we report three  -ray peaks related with
-ray peaks related with  Pu and
Pu and  Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. In the reprocessing plant, since solutions containing both Pu and FP exist, a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP). In this paper, an overview of the technology development, simulation results of preliminary evaluation of the characteristics of radiation emitted from the HALW tank at TRP, and the future research plan are presented.
Komori, Yukiko*; Yokokita, Takuya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Toyomura, Keigo*; Nakamura, Kohei*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Huang, M.*; Kudo, Yuki*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1385 - 1388, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.52(Chemistry, Analytical)We studied solid-liquid extraction behavior of carrier-free Mo and W radiotracers onto an Aliquat 336-loaded resin from HCl solutions toward extraction chromatography experiments of element 106, seaborgium(Sg). Distribution coefficients (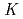
 ) of Mo and W on the resin were determined as a function of HCl concentration by a batch method. On-line extraction chromatography of Mo and W was also carried out in 2-8 M HCl solutions with an automated rapid chemistry apparatus. The order of extraction probability from 2 to 8 M HCl was Mo
) of Mo and W on the resin were determined as a function of HCl concentration by a batch method. On-line extraction chromatography of Mo and W was also carried out in 2-8 M HCl solutions with an automated rapid chemistry apparatus. The order of extraction probability from 2 to 8 M HCl was Mo W, which reflected the order of the
W, which reflected the order of the 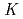
 values in the batch experiment.
values in the batch experiment.
Ishida, Takuya; Tanimoto, Masataka; Shibata, Akira; Kitagishi, Shigeru; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Nakamura, Jinichi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Testing 2011-001, 44 Pages, 2011/06
The Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center has developed new irradiation technologies to provide irradiation data with high technical value for the refurbishment and resume of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). For the purpose to perform assembling of capsules, materials tests, materials inspection and analysis of irradiation specimens for the development of irradiation capsules, improvement and maintenance of facilities were performed. The RI application development building was refurbished and maintained for above-mentioned purpose. After refurbishment, the building was named Irradiation Technology Development Building. It contains eight laboratories based on the purpose of use, and experimental apparatuses were installed. This report describes the refurbishment work of the RI application development building, the installation work and operation method of the experimental apparatuses and the basic management procedure of the Irradiation Technology Development Building.
Ogura, Koichi; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kado, Masataka; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(10), p.570 - 574, 2009/10
For accurate control of relativistic laser-plasma interaction under the repetitive operation, we have to measure and control the laser irradiation conditions such as laser parameters, the target shooting accuracy and so on as well as measuring proton parameter on each laser shot. The displacement of the laser shooting position on a tape target, that are used in the high energy proton generation using an ultra-short Ti:sapphire laser system, is measured by observing an X-ray image from laser plasma with an X-ray pinhole camera for each laser shot. The displacement of the shooting position on the target is about 20micron and the accuracy of the target positioning is within 20micron which is small enough for present laser focusing optics with an F number of 3.6 (f=179mm). The technique contributes to accurate control of a repetitive laser driven proton accelerators.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Bulanov, S. V.; Bolton, P. R.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.449 - 454, 2009/06
The acceleration of protons driven by a high-intensity laser is comprehensively investigated via control of the target density by using ASE just before the time of the main-laser interaction. Two cases were investigated for which the ASE intensity differed by three orders of magnitude: In the low contrast case the beam centre for higher energy protons is shifted closer to the laser-propagation direction of 45 , while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
, while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Hayashi, Kimio; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Onose, Shoji; Ishida, Takuya; Nakamichi, Masaru; Takatsu, Hideyuki; Nakamura, Mutsumi*; Noguchi, Tsuneyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.1083 - 1086, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Kimio; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Onose, Shoji; Ishida, Takuya; Nakamichi, Masaru; Katsuyama, Kozo; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hasegawa, Teiji; Kodaka, Hideo; Takatsu, Hideyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-007, 168 Pages, 2009/03
In-pile functional tests of breeding blankets have been planned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), using a test blanket module (TBM) which will be loaded in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). In preparation for the in-pile functional tests, JAEA has been being performed irradiation experiments of lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.39(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.