Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) ion complex; Presence of a Rh
ion complex; Presence of a Rh Intermediate in Direct Photoreduction
Intermediate in Direct PhotoreductionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(12), p.5607 - 5616, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.66(Chemistry, Physical)The reaction mechanism of the direct photoreduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh
species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh
species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh . Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh
. Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh
species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh species. The Rh
species. The Rh species were assigned to Rh
species were assigned to Rh , Rh
, Rh , and Rh
, and Rh species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
 Rh
Rh
 Rh
Rh . A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh
. A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh
, photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , and photooxidation of Rh
, and photooxidation of Rh , well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh
, well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh species.
species.
Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 29(4), p.5205 - 5212, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:83.13(Optics)Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with liquid jets was applied to the detection of trace sodium (Na) in aqueous solutions. The sensitivities of two types of liquid jets were compared: a liquid cylindrical jet with a diameter of 500  m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20
m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20  m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57
m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57  g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5
g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5  g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Oba, Hironori*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1371 - 1378, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10(Chemistry, Analytical)We measured X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and Raman spectra of isopolymolybdates(VI) in HNO solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo
solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo O
O (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [Mo
[Mo O
O (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [HMoO
[HMoO (H
(H O)
O) ]
] in the highly concentrated HNO
in the highly concentrated HNO solution.
solution.
 solution by Raman and EXAFS spectroscopies
solution by Raman and EXAFS spectroscopiesSaeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
Speciation of isopolymolybdates in a highly concentrated HNO solution was investigated by Raman spectroscopy and Mo K-edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). A series of Raman spectra and EXAFS oscillations were analyzed using Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS). The MCR-ALS analysis gives us the fraction profile in change of [Mo
solution was investigated by Raman spectroscopy and Mo K-edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). A series of Raman spectra and EXAFS oscillations were analyzed using Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares (MCR-ALS). The MCR-ALS analysis gives us the fraction profile in change of [Mo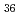 O
O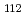 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]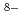
 [Mo
[Mo O
O ]
]
 [MoO
[MoO ]
] with the increase of the HNO
with the increase of the HNO concentration.
concentration.
 O / EtOH Solution
O / EtOH SolutionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yomogida, Takumi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
When nanosecond pulsed UV laser is irradiated into a H O / EtOH solution of platinum group metal (PGM) ions, PGM particles with sub-micron size are formed. We investigated laser induced particle formation of Pd
O / EtOH solution of platinum group metal (PGM) ions, PGM particles with sub-micron size are formed. We investigated laser induced particle formation of Pd in the H
in the H O / EtOH solution by in situ time-resolved XAFS spectroscopy and showed dependence of the reaction rate of laser-induced particle formation on the laser fluence. The dependence on the laser fluence elucidated that the photons contribute not only to the reduction of the Pd
O / EtOH solution by in situ time-resolved XAFS spectroscopy and showed dependence of the reaction rate of laser-induced particle formation on the laser fluence. The dependence on the laser fluence elucidated that the photons contribute not only to the reduction of the Pd , but also to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles.
, but also to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles.

 using ns pulsed UV laser; Dependence of chemical kinetics on laser pulse energy
using ns pulsed UV laser; Dependence of chemical kinetics on laser pulse energySaeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
In the absence of a photoactivator, the laser-induced particle formation in an H O/ EtOH solution of PdCl
O/ EtOH solution of PdCl
 was performed by three kinds of irradiation condition using fourth harmonics of the pulsed UV laser (266 nm). In the irradiation, pulsed laser energy was arranged to 5, 10 and 25 mJ, where average laser power is kept to 250 mW. The reaction kinetics of the laser-induced particle formation was observed using dispersive XAFS measurement. About half of Pd ions were reduced with 5 mJ pulsed laser irradiation. In contrast, all Pd ions were reduced with 25 mJ pulsed laser irradiation. The result elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the generation of Pd metals by the multi-photon process.
was performed by three kinds of irradiation condition using fourth harmonics of the pulsed UV laser (266 nm). In the irradiation, pulsed laser energy was arranged to 5, 10 and 25 mJ, where average laser power is kept to 250 mW. The reaction kinetics of the laser-induced particle formation was observed using dispersive XAFS measurement. About half of Pd ions were reduced with 5 mJ pulsed laser irradiation. In contrast, all Pd ions were reduced with 25 mJ pulsed laser irradiation. The result elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the generation of Pd metals by the multi-photon process.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Oba, Hironori; Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Saeki, Morihisa; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; et al.
no journal, ,
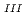 ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysis
ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysisSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The precious metal (PM) ions complexed with negative ions and water molecules in solution has a charge transfer absorption band in the UV region. When alcohol is added to such a PM complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM
complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM
complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM . The reduced PM
. The reduced PM spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh
spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh
ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh
reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh to Rh
to Rh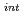 (intermediate) to Rh
(intermediate) to Rh .
.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Shibata, Takuya
no journal, ,
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Shibata, Takuya; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Karino, Takahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Shibata, Takuya
no journal, ,
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Shibata, Takuya; Karino, Takahiro
no journal, ,
 ion complex in a H
ion complex in a H O/EtOH solution
O/EtOH solutionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The reaction mechanism of the direct photo-reduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh
species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh
species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh
intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh
species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh intermediate to the Rh
intermediate to the Rh species.
species.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Shibata, Takuya; Karino, Takahiro
no journal, ,
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Shibata, Takuya; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Karino, Takahiro; Sakamoto, Kan*; Ikeda, Yuji*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,