Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 76, p.123_1 - 123_11, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Marine terraces developed along the southeastern coast of Kii Peninsula, southwestern Japan, face a seismogenic region along the Nankai Trough. We determined the emergence age of one of these marine terraces by using feldspar OSL dating of the marine terrace sediments. The target marine terrace has previously been correlated with MIS 5e on the basis of morphostratigraphy. Samples for pIRIR dating were obtained from foreshore deposits of the marine terrace. pIRIR signals were measured at 150  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR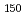 ) and 225
) and 225  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR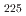 ). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
Kitamura, Akihisa*; Okazaki, Sota*; Kondo, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Hori, Rie*; Ikeda, Masayuki*; Ichimura, Koji*; Nakagawa, Yuki*; Mori, Hideki*
Shizuoka Daigaku Chikyu Kagaku Kenkyu Hokoku, (49), p.73 - 86, 2022/07
On July 3 2021, a debris flow caused by a landslide from a landfill occurred along the Aizome River in the Izusan area of Atami City, Shizuoka. In this study, debris flow deposits and soil samples were characterized in terms of their sedimentology and geochemically analyzed.
Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Ogata, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto; Yasue, Kenichi*
Gekkan Chikyu "Kiso deta Kara Kangaeru Dai Yonkigaku No Shintenkai-I" Gogai No.71, p.148 - 155, 2022/02
The formation process of terrace topography was investigated by observing and analyzing boring core samples collected in the middle reaches of the Kumano River. It was assumed that the older terrace topography was distributed higher than the current riverbed surface. However, since tributary debris flow deposits may be thickly distributed beneath the old gyre river valley, care must be taken when using the surface of the ground as an index of uplift and erosion.
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
Dai Yonki Kenkyu, 60(2), p.27 - 41, 2021/06
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Okuno, Mitsuru*; Yamasaki, Keiji*; Hong, W.*; Fujita, Natsuko; Nakamura, Toshio*; Horikawa, Yoshiyuki*; Sato, Eiichi*; Kimura, Haruo*; Tsutsumi, Hiroyuki*
Nagoya Daigaku Nendai Sokutei Kenkyu, 5, p.38 - 43, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*
no journal, ,
Marine terraces are formed by regional uplift and sea level change, being useful for estimating uplift rates on geomorphological time scale (10 -10
-10 years). However, the emergent ages, and then the uplift rates, are difficult to determine when the sediments include few organic materials and tephra. Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating method on feldspar is useful to date sediments on 10
years). However, the emergent ages, and then the uplift rates, are difficult to determine when the sediments include few organic materials and tephra. Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating method on feldspar is useful to date sediments on 10 -10
-10 -year timescales. Thus, this method has been applied to date marine terrace deposits in the last several years. In this presentation, we will present the case study for MIS 5e marine terraces in the Kii Peninsula, for which the depositional ages were estimated by using feldspar OSL dating.
-year timescales. Thus, this method has been applied to date marine terrace deposits in the last several years. In this presentation, we will present the case study for MIS 5e marine terraces in the Kii Peninsula, for which the depositional ages were estimated by using feldspar OSL dating.
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Ogata, Manabu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Kimori, Taiga*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hori, Kazuaki*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Hong, W.*; Nakashima, Rei*
no journal, ,
Event sediments by debris flows were evaluated based on the sedimentary facies and radiocarbon ages of four sediment cores from the eastern foot of the alluvial fan toes at the eastern foot of the Yoro Mountains. In addition, the marine reservoir effect (MRE) in the Holocene was measured by the offset of radiocarbon ages between terrestrial plant fragments and marine shell fragments found in the same stratum in the core sediments. On the results, nine coarse sediment were observed after 4070 cal BP in three cores. The average of MRE, ca 400 years (n = 13) and ca 330 years (n = 12), were identified on two cores.
Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Hongo, Misao*; Noguchi, Marie*; Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Kimori, Taiga*; Sugai, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Nanayama, Futoshi*; Hori, Kazuaki*; Niwa, Yuichi*; Komatsubara, Junko*; Kitamura, Akihisa*; Hong, W.*
no journal, ,
To identify chronological and spatial changes in the radiocarbon ( C) marine reservoir effects, the
C) marine reservoir effects, the  C ages of eight pairs of marine shells and terrestrial plants were measured from the same horizons of one core of Holocene sediments around Japan. To determine the direct chronological changes of the marine reservoir effect between the Kuroshio and Oyashio Currents, radiocarbon ages were measured from the same stratigraphic horizons within Holocene sediment cores alomg the Pasific coast of Japan (eastern Hokkaido; Nanayama et al., 2003, Nanayama, 2020, Sanriku Coast; Niwa et al., 2017, 2019, Arakawa Lowland; Komatsubara et al., 2009, 2010, Shimizu Plain; Kitamura and Kobayashi, 2014; Nobi Plain) and Taiwan.
C ages of eight pairs of marine shells and terrestrial plants were measured from the same horizons of one core of Holocene sediments around Japan. To determine the direct chronological changes of the marine reservoir effect between the Kuroshio and Oyashio Currents, radiocarbon ages were measured from the same stratigraphic horizons within Holocene sediment cores alomg the Pasific coast of Japan (eastern Hokkaido; Nanayama et al., 2003, Nanayama, 2020, Sanriku Coast; Niwa et al., 2017, 2019, Arakawa Lowland; Komatsubara et al., 2009, 2010, Shimizu Plain; Kitamura and Kobayashi, 2014; Nobi Plain) and Taiwan.
Nakanishi, Toshimichi; Nanayama, Futoshi*; Katsuki, Kota*; Yamada, Keitaro*
no journal, ,
The Holocene sediments of Lake Harutori in Kushiro City, eastern Hokkaido, are mainly composed of annually laminated sediments, organic mud layers with plant fragments, sand layers with shell and plant fragments and tephra layers. Fluctuations of the marine reservoir effect of radiocarbon and the information on the paleo-tsunami caused by the huge interplate earthquakes were identified by the high-resolution sedimentological analysis.
Noguchi, Marie*; Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Suginaka, Yusuke*; Endo, Kunihiko*
no journal, ,
Discussions on the history of crustal development based on sedimentary facies analysis using the boring cores GC-NG-1, GC-OY-1, and GC-OY-2 in the central Kanto Plain, from the Sarushima Plateau to the Takaragi Plateau, are underway. In the study, paleoenvironmental restoration based on diatom analysis was performed. These core samples are likely to preserve sea-level changes and landing processes since MIS9. From the results of the diatom community analysis, the paleoenvironment in each core was found to change according to the boring site, such as inner bay, brackish water to freshwater, freshwater, lakes, river environment, and land environment. We also attempted to objectively present changes in community composition by cluster analysis of diatom analysis results.
Kawamura, Makoto; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Jia, H.*; Koizumi, Yukiko*; Umeda, Koji*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*
no journal, ,
The topography around the river is flat with wide plains near the river mouth, but deep valleys are formed upstream. These differences in topography reflect the relationship between the hardness of the ground, the rate of uplift, and the erosive force of rivers that carve the ground. In this presentation, we will use the topography around the Abe River and Oi River in Shizuoka Prefecture as an example, and introduce a research example in which cross-sectional data of rivers from the coast to the upper reaches are analyzed. The examples introduced in this article will provide clues to the process by which Shizuoka Prefecture's alluvial fan-like coastal plains and upstream relief are formed by uplift of the ground and erosion by rivers.
Tsukahara, Yuzuko; Saito, Toshihito*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Fujita, Natsuko; Kawamura, Makoto; Umeda, Koji*
no journal, ,
Paleo-sea levels estimated from the elevation and age of emerged shoreline features and fossil calcareous assemblages are one of the useful tools for reconstructing the tectonic features of the Holocene. In this study, we reconstruct the paleo-sea levels around the eastern part of Izu Peninsula using fossil calcareous assemblages to verify case studies in areas with active volcanism and seismic activity. In addition, we will infer the characteristics of crustal deformation through comparison with previous studies. Shishikura et al. (2023) surveyed emerged shoreline features and fossil calcareous assemblages around the coast in the vicinity of Ito, the northeastern part of the Izu Peninsula, to clarify the emerged process. They concluded that the cause of the emergence is associated with a volcanotectonic uplift due to subsurface magma movement. In order to verify the representativeness of this crustal feature, we conducted a field survey of the Jogasaki Coast, 8 9 km south of the area studied by Shishikura et al. (2023). We found four fossil calcareous assemblages at three sites on the Jogasaki Coast, and dated them to 1356
9 km south of the area studied by Shishikura et al. (2023). We found four fossil calcareous assemblages at three sites on the Jogasaki Coast, and dated them to 1356 1470 CE using the
1470 CE using the  C. Fossil assemblages with similar ages have been reported by Shishikura et al. (2023), but the elevation in this study is about 1 m higher. This difference may suggest a spatial variation in tectonic features in this area.
C. Fossil assemblages with similar ages have been reported by Shishikura et al. (2023), but the elevation in this study is about 1 m higher. This difference may suggest a spatial variation in tectonic features in this area.
Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Kimori, Taiga*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimori, Taiga*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Niwa, Yuichi*; Hiura, Yuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Tatsuki*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Niwa, Yuichi*; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Hiura, Yuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English