Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n,  ) method, 4
) method, 4Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Ngo, M. C.*; Do, T. M. D.*; Hu, X.*; Yang, Y.*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 118, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
 Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Nakano, Tomohide; Shumack, A.*; Maggi, C. F.*; Reinke, M.*; Lawson, K.*; Coffey, I.*; P tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; et al.
tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; et al.
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 48(14), p.144023_1 - 144023_11, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:82.88(Optics)The 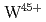 and
and 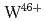 3p-4d inner shell excitation lines in addition to
3p-4d inner shell excitation lines in addition to 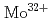 2p-3s lines have been identified from the spectrum taken by an upgraded high-resolution X-ray spectrometer. It is found from analysis of the absolute intensities of the
2p-3s lines have been identified from the spectrum taken by an upgraded high-resolution X-ray spectrometer. It is found from analysis of the absolute intensities of the 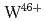 and
and 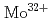 lines that W and Mo concentrations are in the range of
lines that W and Mo concentrations are in the range of 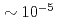 and
and 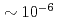 , respectively, with a ratio of
, respectively, with a ratio of  5% for ELMy H-mode plasmas with a plasma current of 2.0- 2.5 MA, a toroidal magnetic field of 2.7 T and a neutral beam injection power of 14-18 MW. For the purpose of checking self-consistency, it is confirmed that the W concentration determined from the
5% for ELMy H-mode plasmas with a plasma current of 2.0- 2.5 MA, a toroidal magnetic field of 2.7 T and a neutral beam injection power of 14-18 MW. For the purpose of checking self-consistency, it is confirmed that the W concentration determined from the 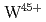 line is in agreement with that from the
line is in agreement with that from the 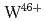 line within 20% and that the plasma effective charge determined from the continuum of the first order reflection spectrum is also in agreement with that from the second order within 50%. Further, the determined plasma effective charge is in agreement with that determined from a visible spectroscopy, confirming that the sensitivity of the X-ray spectrometer is valid and that probably the W and the Mo concentrations are also valid.
line within 20% and that the plasma effective charge determined from the continuum of the first order reflection spectrum is also in agreement with that from the second order within 50%. Further, the determined plasma effective charge is in agreement with that determined from a visible spectroscopy, confirming that the sensitivity of the X-ray spectrometer is valid and that probably the W and the Mo concentrations are also valid.
Nakano, Tomohide; Shumack, A. E.*; Maggi, C.*; Reinke, M.*; Lawson, K. D.*; P tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 38F, p.P1.019_1 - P1.019_4, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Joffrin, E.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Povinec, P. P.*; Aoyama, Michio*; Biddulph, D.*; Breier, R.*; Buesseler, K. O.*; Chang, C. C.*; Golser, R.*; Hou, X. L.*; Je kovsk
kovsk , M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
, M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
Biogeosciences, 10(8), p.5481 - 5496, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:93.94(Ecology)Radionuclide impact of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident on the distribution of radionuclides in seawater of the NW Pacific Ocean is compared with global fallout from atmospheric tests of nuclear weapons. Surface and water column seawater samples collected during the international expedition in June 2011 were analyzed for  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H. The
H. The  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8
H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8  Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed
Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed  Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
 Al
Al and NpPd
and NpPd Al
Al
Sakai, Hironori; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Haga, Yoshinori; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(Suppl.B), p.SB003_1 - SB003_6, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the so-called 115 family members with chemical formulae of Ce In
In (
( =Co, Rh, Ir) and
=Co, Rh, Ir) and 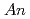
 Ga
Ga (
(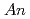 =U, Np, Pu), our analysis of the Knight shift and spin-lattice relaxation rates suggests that larger XY-type anisotropy in the antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in the normal states would favor
=U, Np, Pu), our analysis of the Knight shift and spin-lattice relaxation rates suggests that larger XY-type anisotropy in the antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in the normal states would favor  -wave superconductivity with higher
-wave superconductivity with higher  . In order to examine this working hypothesis, the anisotropy ratios of antiferromagnetic fluctuations are derived from our NMR results for the superconductor NpPd
. In order to examine this working hypothesis, the anisotropy ratios of antiferromagnetic fluctuations are derived from our NMR results for the superconductor NpPd Al
Al and antiferromagnet CePd
and antiferromagnet CePd Al
Al , which are tetragonal compounds with a 115-related structure. CePd
, which are tetragonal compounds with a 115-related structure. CePd Al
Al shows Ising-type anisotropy, which is the same anisotropy as in the ordered state. On the other hand, NpPd
shows Ising-type anisotropy, which is the same anisotropy as in the ordered state. On the other hand, NpPd Al
Al shows XY-type anisotropy just above
shows XY-type anisotropy just above  .
.
Litaudon, X.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Tala, T.*; Angioni, C.*; Benkadda, S.*; Beurskens, M. N. A.*; Bourdelle, C.*; Brix, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073020_1 - 073020_13, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A variety of triggering mechanisms and structures of internal transport barrier (ITB) has been observed in various devices or depending on operation scenarios. Thus identity experiments on ITB in JT-60U and JET have been performed to shed light on the physics behind ITBs. Because of their similar size, the dimensionless parameters between both devices are the same. These experiments were performed with near identical magnetic configurations, heating waveforms and normalized quantities such as safety factor, magnetic shear, normalized Larmor radius, normalized collision frequency, beta, temperatures ratio. Similarities of the ITB triggering mechanism and the ITB strength have been observed when a proper match is achieved of the most relevant profiles of the normalized quantities. This paper will report on the detail comparison of transport properties of ITBs obtained in these JET/JT-60U identity experiments.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 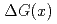 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 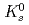 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Fujisawa, Akihide*; Ido, Takeshi*; Shimizu, Akihiro*; Okamura, Shoichi*; Matsuoka, Keisuke*; Iguchi, Harukazu*; Hamada, Yasuji*; Nakano, Haruhisa*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Ito, Kimitaka*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(10), p.S718 - S726, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:106 Percentile:95.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Present status of experiments on zonal flows is overviewed. Innovative use of modern diagnostics has revealed the existence of zonal flows, their spatio-temporal characteristics, their relationship with turbulence, and their effects on confinement. Particularly a number of observations have been accumulated on the oscillatory branch of the zonal flow, dubbed as geodesic acoustic modes suggesting necessity of theories to give their proper description. Several new methods have elucidated the zonal flow generation processes from the turbulence. Further investigation of relationship between the zonal flows and confinement is strongly encouraged as cross-device activity.
Lipschultz, B.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Bonnin, X.*; Coster, D. P.*; Counsell, G.*; Doerner, R.*; Dux, R.*; Federici, G.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Fundamenski, W.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
The work of the ITPA SOL/divertor group is reviewed. The high-n nature of ELMs has been elucidated and new measurements have determined that they carry 10-20% of the ELM energy to the far SOL with implications for ITER limiters and the upper divertor. Analysis of ELM measurements imply that the ELM continuously loses energy as it travels across the SOL. The prediction of ITER divertor disruption power loads have been reduced as a result of finding that the divertor footprint broadens during the thermal quench and that the plasma can lose up to 80% of its thermal energy before the thermal quench (not for VDEs or ITBs). Disruption mitigation through massive gas puffing has been successful at reducing divertor heat loads but estimates of the effect on the main chamber walls indicate 10s of kG of Be would be melted/mitigation. Long-pulse studies have shown that the fraction of injected gas that can be recovered after a discharge decreases with discharge length. The use of mixed materials gives rise to a number of potential processes.
Fujisawa, Akihide*; Ido, Takeshi*; Shimizu, Akihiro*; Okamura, Shoichi*; Matsuoka, Keisuke*; Hamada, Yasuji*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; Nakano, Haruhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2007/03
Present status of experiments on zonal flows is overviewed. Innovative use of traditional and modern diagnostics has revealed unambiguously the existense of the zonal flows, their spatio-temporal caracteristics, their relationship with turbulence, and their effects on confinement. Particularly, a number of observations have been accumulated on the oscillatory branch of zonal flows, dubbed geodesic acoustic modes, suggesting necessity of theories to give their proper description. Furthur investigation of relationship between zonal flows and confinement is strongly encouraged as cross-device activity.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Higashijima, Satoru; Konoshima, Shigeru; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; Porter, G. D.*; Rognlien, T. D.*; Rensink, M. E.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1618 - 1627, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:53.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English