Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI in an NIS-expressing thyroid cancer mouse model
I]NaI in an NIS-expressing thyroid cancer mouse modelWatabe, Tadashi*; Liu, Y.*; Kaneda, Kazuko*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Shirakami, Yoshifumi*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Shimosegawa, Eku*; Wang, Y.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Internet), 23(16), p.9434_1 - 9434_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:73.73(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)In this study, we compare the therapeutic effect between [ At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI. In vitro analysis of double-stranded DNA break (DSB) and colony formation assay were performed using K1-NIS cells. [
I]NaI. In vitro analysis of double-stranded DNA break (DSB) and colony formation assay were performed using K1-NIS cells. [ At]NaAt induced higher numbers of DSBs and had a reduced colony formation than [
At]NaAt induced higher numbers of DSBs and had a reduced colony formation than [ I]NaI. In K1-NIS mice, dose-dependent therapeutic effects were observed in both [
I]NaI. In K1-NIS mice, dose-dependent therapeutic effects were observed in both [ At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI. The superior therapeutic effect of [
I]NaI. The superior therapeutic effect of [ At]NaAt suggests the promising clinical applicability of targeted alpha therapy using [
At]NaAt suggests the promising clinical applicability of targeted alpha therapy using [ At]NaAt in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to standard [
At]NaAt in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to standard [ I]NaI treatment.
I]NaI treatment.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Torikai, Kota*; Kawachi, Naoki; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sato, Takahiro; Nagao, Yuto; Fujimaki, Shu; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(9), p.3638 - 3644, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:99.10(Engineering, Biomedical)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Nagao, Yuto; Kawachi, Naoki; Sato, Takahiro; Fujimaki, Shu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Torikai, Kota*; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki*; Sakai, Makoto*; et al.
International Journal of PIXE, 26(1&2), p.61 - 72, 2016/00
no abstracts in English

 -semiquinone complex; A Possible dielectric response mechanism
-semiquinone complex; A Possible dielectric response mechanismMitsumi, Minoru*; Ezaki, Kazunari*; Komatsu, Yuki*; Toriumi, Koshiro*; Miyato, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Motohiro*; Azuma, Nobuaki*; Miyazaki, Yuji*; Nakano, Motohiro*; Kitagawa, Yasutaka*; et al.
Chemistry; A European Journal, 21(27), p.9682 - 9696, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:31.23(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ajimura, Shuhei*; Bezerra, T. J. C.*; Chauveau, E.*; Enomoto, T.*; Furuta, Hisataka*; Harada, Masahide; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hiraiwa, T.*; Igarashi, Yoichi*; Iwai, Eito*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(6), p.063C01_1 - 063C01_19, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The J-PARC E56 experiment aims to search for sterile neutrinos at the J-PARC Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). In order to examine the feasibility of the experiment, we measured the background rates of different detector candidate sites, which are located at the third floor of the MLF, using a detector consisting of plastic scintillators with a fiducial mass of 500 kg. The gammas and neutrons induced by the beam as well as the backgrounds from the cosmic rays were measured, and the results are described in this article.
Yoshida, Yukari*; Mizohata, Kensuke*; Matsumura, Akihiko*; Isono, Mayu*; Yako, Tomoko*; Nakano, Takashi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kanai, Tatsuaki*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 81, 2015/03
In the clinical application of carbon-ion (C-ion) radiation therapy in Japan, different RBE values of carbons have been used for clinical and biological endpoints. The biological RBE (bRBE) was estimated by a method that is based on the linear-quadratic (LQ) model, and was defined  at the 10% surviving fraction of human salivary gland (HSG) tumor cells. However, many of biological parameters, that is, type of tissues, different sort of cells, oxygenation levels, and all, could affect radiosensitivity. Thus, normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) cells were exposed to C-ion beams at Gunma University (10-80 keV/micrometer) and TIARA (108 and 158 keV/micrometer). The surviving fractions were analyzed with colony formation assays. The experimental RBE (eRBE) values were estimated from the radiation dose survival curve fitted by LQ model, and defined
at the 10% surviving fraction of human salivary gland (HSG) tumor cells. However, many of biological parameters, that is, type of tissues, different sort of cells, oxygenation levels, and all, could affect radiosensitivity. Thus, normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) cells were exposed to C-ion beams at Gunma University (10-80 keV/micrometer) and TIARA (108 and 158 keV/micrometer). The surviving fractions were analyzed with colony formation assays. The experimental RBE (eRBE) values were estimated from the radiation dose survival curve fitted by LQ model, and defined  .
.
Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kubo, Makoto*; Igarashi, Chie*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Nakano, Takashi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 82, 2015/03
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) induced by ionizing radiation pose a major threat to cell survival. The cell can respond to the presence of DSBs, through two major repair pathways: Homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). Higher levels of cell death are induced by high-LET radiation when compared to low-LET radiation, even at the same doses because of less effective or more inefficient DNA repair. In this study, we examine the effects of radiation with different LET values on DNA DSB repair and radiosensitivity. Wild-type cells and HR deficient (but NHEJ proficient) cells exhibited the high RBE values at LET values of 108 keV/ m. The RBE value for each cell type decreased with increasing LET values over 200 keV/
m. The RBE value for each cell type decreased with increasing LET values over 200 keV/ m. Although NHEJ proficient cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ deficient cells showed a high SER value when compared to NHEJ proficient cells, even with increasing LET values.
m. Although NHEJ proficient cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ deficient cells showed a high SER value when compared to NHEJ proficient cells, even with increasing LET values.
 -ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral water
-ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral waterYamamoto, Masahiro; Nakano, Junichi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
Corrosion protection of RPV and PCV is an important issue for the long term maintenance until the end of the decommissioning procedures. One of the uncertain factors for the issue is an effect of radioactivity on corrosion of LAS and CS. Corrosion tests using LAS and CS were conducted in  -rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by
-rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by  -rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with
-rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with  -ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H
-ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H O
O was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in
was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in  -ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
-ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kubo, Makoto*; Ma, H.*; Nakagawa, Akiko*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Isono, Mayu*; Kanai, Tatsuaki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Radiation Research, 182(3), p.338 - 344, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:89.83(Biology)To clarify whether high-LET radiation inhibits all repair pathways or specifically one repair pathway, studies were designed to examine the effects of radiation with different LET values on DNA DSB repair and radiosensitivity. Embryonic fibroblasts bearing repair gene KO were exposed to X rays, carbon-, iron-, neon- and argon-ion beams. Cell survival was measured with colony-forming assays. The sensitization enhancement ratio (SER) values were calculated using the 10% survival dose of wild-type cells and repair-deficient cells. Cellular radiosensitivity was listed in descending order: double-KO cells  NHEJ-KO cells
NHEJ-KO cells  HR-KO cells
HR-KO cells  wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.
wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.
 atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under
atmosphere on the corrosion of reactor vessel steels in diluted seawater under  -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.977 - 986, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)Seawater was injected into the reactor cores in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Corrosion of reactor vessel steels is considered to progress. To evaluate durability of the reactor vessel steels, corrosion tests were conducted in diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  -rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N
-rays irradiation. 10 mg/L and 100 mg/L N H
H were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N
were added to diluted seawater. Without addition of N H
H , weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N
, weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 0.2 kGy/h dose rate was comparable with those without irradiation and weight loss in the vessel steels irradiated with the 4.4 kGy/h dose rate was higher than those without irradiation. Under irradiation, weight loss in the vessel steels in diluted seawater containing N H
H was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N
was comparable with that in diluted seawater without N H
H . When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N
. When gas phase in the flask was replaced with N , weight loss in the vessel steels, and O
, weight loss in the vessel steels, and O and H
and H O
O concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
concentrations in the diluted seawater decreased.
Murata, Kazutoshi*; Noda, Shinei*; Oike, Takahiro*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Takahashi, Takeo*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(4), p.658 - 664, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.32(Biology)The effect of carbon ion irradiation on cell motility through the Rho signaling pathway in the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 was studied. At 48 h after irradiation, the cell motility of A549 cells became significantly greater, and the formation of protrusions significantly increased in cells irradiated with carbon ion. The observed increase in cell motility due to carbon ion irradiation was similar to that observed due to X-ray irradiation. Western-blot analysis showed that carbon ion irradiation increased P-MLC2-S19 expression compared with in unirradiated controls, while total MLC2 expression was unchanged. Exposure to a non-toxic concentration of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of ROCK, reduced the expression of P-MLC2-S19 after C-ion irradiation, resulting in a significant reduction in migration. These data suggest that carbon irradiation increases cell motility in A549 cells via the Rho signaling pathway and that ROCK inhibition reduces that effect.
 -rays irradiation
-rays irradiationNakano, Junichi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(1), p.1 - 6, 2014/03
The seawater was injected into reactor cores of Units 1, 2 and 3 in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To investigate effects of  rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50
rays irradiation on corrosion of carbon steel and low alloy steel, corrosion tests were performed in the diluted seawater at 50  C under
C under  rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N
rays irradiation with dose rates of 4.4 kGy/h and 0.2 kGy/h. Hydrazine (N H
H ) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N
) was added to the diluted seawater. In the diluted seawater without N H
H , the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N
, the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 0.2 kGy/h were similar to those of the unirradiated steels, and the weight losses of the steels irradiated with 4.4 kGy/h increased to approximate 1.7 times of those of the unirradiated steels. The weight losses of the steels irradiated in the diluted seawater containing N H
H were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N
were similar to those in the diluted seawater without N H
H . When N
. When N was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during
was introduced to gas phase in the flasks during  rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
rays irradiation, the weight losses of the steels decreased.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 444(1-3), p.454 - 461, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cracking growth tests were conducted in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H
) at 561 to 423 K to evaluate the effects of H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of stainless steel (SS) at temperature lower than the boiling water reactor (BWR) operating temperature. Small compact tension (CT) specimens were prepared from thermally sensitized type 304 SS. Despite the observation of only a small portion intergranular SCC (IGSCC) near the side groove of the CT specimen at 561 K in high-temperature water containing 100 ppb of H O
O , the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H
, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens at 423 and 453 K. Effects of H O
O on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
on SCC appeared intensely at temperature lower than the BWR operating temperature. To estimate the environment in the cracks, outer oxide distribution on the fracture surface and fatigue pre-crack were examined by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermal equilibrium calculation was performed.
Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 441(1-3), p.348 - 356, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crack growth tests were performed in high-temperature water containing hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H
) to evaluate the relationships between the crevice structure and H O
O on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20
on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) growth morphology of stainless steel (SS). Small compact tension (CT) specimens with different fatigue pre-crack lengths were prepared. 20 300 ppb H
300 ppb H O
O was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H
was injected into the high-temperature water at 561 K. Intergranular SCC (IGSCC) was observed only near the side grooves of the CT specimens. Owing to pre-crack shortening, the IGSCC area expanded to the central region of the CT specimens. The effects of H O
O on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H
on SS appeared intensely near the surfaces exposed to high levels of H O
O . The calculations for the percentage of H
. The calculations for the percentage of H O
O remaining showed that the effects of H
remaining showed that the effects of H O
O flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
flowed from both sides of the crack were more obvious than those flowed from the crack mouth.
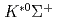 photoproduction with evidence for the Kappa Meson Exchange at SPring-8/LEPS
photoproduction with evidence for the Kappa Meson Exchange at SPring-8/LEPSHwang, S. H.*; Hicks, K.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Nakano, Takashi*
Few-Body Systems, 54(7-10), p.1037 - 1041, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton camera
-ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton cameraSuzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Torikai, Kota*; Sato, Takahiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kawachi, Naoki; Watanabe, Shigeki; et al.
Radiology, 267(3), p.941 - 947, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.15(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)