Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Honda, Masaki*; Saiki, Yohei*; Takahashi, Masashi*; Ohira, Koichi*; Nakano, Masaaki*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a plutonium (Pu) burner HTGR is proposed to incarnate highly-effective Pu utilization by its inherent safety features. The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
 as a source of atmospheric I
as a source of atmospheric I
Watanabe, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Shohei; Cuevas, C. A.*; Saiz-Lopez, A.*; Yabushita, Akihiro*; Nakano, Yukio*
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 3(4), p.669 - 679, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:43.59(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The photooxidation of aqueous iodide ions (I
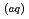 ) at sea surface results in the emission of gaseous iodine molecules (I
) at sea surface results in the emission of gaseous iodine molecules (I
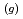 ) into the atmosphere. It plays a certain role in the transport of iodine from ocean to the atmosphere in the natural cycle of iodine. In this study, we determined the photooxidation parameters, the molar absorption coefficient (
) into the atmosphere. It plays a certain role in the transport of iodine from ocean to the atmosphere in the natural cycle of iodine. In this study, we determined the photooxidation parameters, the molar absorption coefficient (
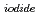 (
( )) and the photooxidative quantum yields (
)) and the photooxidative quantum yields (
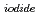 (
( )) of I
)) of I
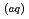 , in the range of 290-500 nm. Through the investigation of the influence of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO) on
, in the range of 290-500 nm. Through the investigation of the influence of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO) on 
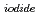 (
( ), the subsequent emission rates of I
), the subsequent emission rates of I
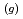 following the photooxidation of I
following the photooxidation of I
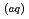 in deionized water solution (pH 5.6, DO 7.8 mg L
in deionized water solution (pH 5.6, DO 7.8 mg L ) and artificial seawater solution (pH 8.0, DO 7.0 mg L
) and artificial seawater solution (pH 8.0, DO 7.0 mg L ) were estimated. A global chemistry-climate model employed herein to assess the I
) were estimated. A global chemistry-climate model employed herein to assess the I
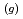 ocean emission on a global scale indicated that the photooxidation of I
ocean emission on a global scale indicated that the photooxidation of I
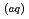 by solar light can enhance the atmospheric iodine budget by up to
by solar light can enhance the atmospheric iodine budget by up to  8% over some oceanic regions.
8% over some oceanic regions.
Goto, Minoru; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Ueta, Shohei; Nakano, Masaaki*; Honda, Masaki*; Tachibana, Yukio; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Aihara, Jun; Fukaya, Yuji; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.507 - 513, 2015/09
A concept of a plutonium burner HTGR named as Clean Burn, which has a high nuclear proliferation resistance, had been proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In addition to the high nuclear proliferation resistance, in order to enhance the safety, we propose to introduce PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Passive heat removal performance of the reactor vessel cavity cooling system (RCCS) is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat must be removed by radiation and natural convection of RCCS. Thus thermal hydraulic analysis of reactor internals and RCCS is powerful means for evaluation of the heat removal performance of RCCS. The thermal hydraulic analyses using CFD computation tools are conducted for normal operation of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and are compared to the temperature distribution of measured data. The calculated temperatures on outer faces of the permanent side reflector (PSR) blocks are in fair agreement with measured data. The transient analysis for decay heat removal mode in HTTR is also conducted.
 C high temperature gas-cooled reactor
C high temperature gas-cooled reactorNakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The conceptual core design study of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is performed. The major specifications are 600 MW thermal output, 950 C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release,
C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release, 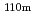 Ag and
Ag and  Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio*; Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Tsukada, Takashi; Takakura, Kenichi*; Nakata, Kiyotomo*
International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering, 2(3), p.65 - 71, 2012/09
Crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been conducted with neutron irradiated compact tension (CT) specimens. The specimens were irradiated in the core region of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in simulated BWR water environments at 288  C from 0.37 to 5.55
C from 0.37 to 5.55 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1 MeV) (0.62 to 9.2 dpa). The CGRs of base metals in high electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition with 10
1 MeV) (0.62 to 9.2 dpa). The CGRs of base metals in high electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition with 10  stress intensity factor, K
stress intensity factor, K  30 MPam
30 MPam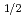 , increased with increasing neutron fluence until 2 dpa and the CGRs were almost the same from 2 to 10 dpa. We investigated the influence of microstructure on CGR by microstructure observation and local strain measurement around the precipitate. This paper will discuss the relationship between CGR and microstructure, radiation hardening, radiation induced segregation.
, increased with increasing neutron fluence until 2 dpa and the CGRs were almost the same from 2 to 10 dpa. We investigated the influence of microstructure on CGR by microstructure observation and local strain measurement around the precipitate. This paper will discuss the relationship between CGR and microstructure, radiation hardening, radiation induced segregation.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Tsukada, Takashi; Takakura, Kenichi*; Nakata, Kiyotomo*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems (CD-ROM), p.1181 - 1191, 2009/08
The CGR tests of neutron irradiated Type 304 SS were conducted in BWR conditions and the results were compared with those of Type 304L and 316L SS, and following results were obtained. (1) The CGR increase with increasing neutron fluence and the power law of K on the CGR was observed above F2 neutron fluence level (1.4 dpa). The different tendency is observed between Type 304 SS and L-grade SS (Type 304L and 316L SS) with increasing neutron fluence above F3 (4.3 dpa) level. (2) The CGR of Type 304 SS is slightly small as compared with those of Type 304L and 316L SS at the same neutron fluence and shows an increasing tendency above 4 dpa and reaches to 1.0 10
10 m/s in 9 dpa. (3) The neutron fluence dependence on uniform elongation is different with Type 304, 304L SS and Type 316L SS, that is, the neutron fluence in which the local deformation like channeling deformation is dominant, is high for Type 316L SS.
m/s in 9 dpa. (3) The neutron fluence dependence on uniform elongation is different with Type 304, 304L SS and Type 316L SS, that is, the neutron fluence in which the local deformation like channeling deformation is dominant, is high for Type 316L SS.
Izumo, Hironobu; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishida, Takuya; Kawamata, Kazuo; Inoue, Shuichi; Ide, Hiroshi; Saito, Takashi; Ise, Hideo; Miwa, Yukio; Ugachi, Hirokazu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-011, 31 Pages, 2009/04
Regarding Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking (IASCC) for austenitic stainless steel of the light water reactor (LWR), a lot of data that concerns the post irradiation evaluation (PIE) is acquired. However, IASCC occurs in LWR condition. Therefore, it is necessary to confirm adequacy of the PIE data comparing the experiment data under the simulated LWR condition. Bigger specimen is needed to acquire the effective data for the destruction dynamics in the study of stress corrosion cracking under neutron irradiation condition. Therefore, development of a new crack growth unit which can load to bigger is necessary to the neutron irradiation test. As a result, a prospect was provided in the unit that could load to specimen by changing load mechanism to the lever type from the linear type. And also, in the development of crack propagation unit, some technical issues were extracted from the discussion of the unit structure adopting the LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer).
 10
10 n/m
n/m
Nakano, Junichi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Usami, Koji; Tsukada, Takashi; Hide, Koichiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.281 - 285, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crack initiation and crack growth processes of irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking on stainless steels were studied by slow strain rate testing in oxygenated high temperature water at 561 K. In-situ observation was carried out during SSRT. Specimens of type 304 stainless steel were subjected to a solution annealing (SA), a thermally sensitization (TS), or a cold working (CW) and irradiated to 1.0 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E  1 MeV) at 323 K in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). Crack initiations were observed before the maximum stress would be reached for the CW material in in-situ observation. In fracture surface examination, the TS material exhibited almost intergranular stress corrosion cracking while mixtures of transgranular stress corrosion cracking and ductile dimple fracture were observed for the SA and the CW materials.
1 MeV) at 323 K in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). Crack initiations were observed before the maximum stress would be reached for the CW material in in-situ observation. In fracture surface examination, the TS material exhibited almost intergranular stress corrosion cracking while mixtures of transgranular stress corrosion cracking and ductile dimple fracture were observed for the SA and the CW materials.
Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Miwa, Yukio; Nakano, Junichi; Sato, Tomonori; Uchida, Shunsuke
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Since the intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) has been a major issue of degradation and failure of structural materials in the boiling water reactors (BWRs), various types of experiments were carried out to investigate IGSCC behavior under the environmental conditions simulated those in BWR. This paper describes a summary of the relevant experimental techniques and the experiences of two types of experiments performed by the authors. For the in-pile SCC experiments, IGSCC crack growth rates were obtained as a function of stress intensity factor in high temperature water. On the other hand, SCC and corrosion tests were performed on un-irradiated specimens in high temperature water by injecting hydrogen peroxide, H O
O to simulate water radiolysis condition. In order to understand IGSCC behavior under irradiation in the reactor core from a mechanistic viewpoint, combinations of various types of experiments are essentially required.
to simulate water radiolysis condition. In order to understand IGSCC behavior under irradiation in the reactor core from a mechanistic viewpoint, combinations of various types of experiments are essentially required.
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takase, Yuichi*; Nakamura, Yukio*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(5), p.297 - 298, 2008/05
no abstracts in English
Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mase, Atsushi*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(9), p.779 - 782, 2007/09
This is a report of highlights from 2007 spring meetings of seven Topical Groups (TG) of International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA). In each meeting, high priority issues in physics of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and other burning plasma experiments have been discussed and investigated. Twenty-seven scientists from Japan have participated in those meetings. Dates and places of the meetings are shown below. (1) Diagnostics TG: 26-30 March, Princeton (USA), (2) Transport Physics TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (3) Confinement Database and Modeling TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (4) Edge Pedestal Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany) (5) Steady State Operation TG: 9-11 May, Daejeon (South Korea), (6)MHD TG: 21-24 May, San Diego (USA), (7) Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany).
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(2), p.195 - 198, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Nakano, Tomohide; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Iio, Shunji*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Ono, Yasushi*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 82(7), p.448 - 450, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Ugachi, Hirokazu; Nakano, Junichi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Miwa, Yukio; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Kizaki, Minoru; Omi, Masao; Shimizu, Michio
JAEA-Conf 2006-003, p.253 - 265, 2006/05
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is one of the critical concerns when stainless steel components have been in service in the light water reactors (LWRs) for a long period. In general, IASCC can be reproduced on the materials irradiated over a certain threshold fluence level of fast neutron by the post-irradiation examinations (PIEs) at hot laboratories. On the other hand, recently in the Japanese boiling water reactor (BWR) power plants, many incidents of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of structural material such as the reactor core shrouds and primary loop recirculation (PLR) system piping were reported. In order to investigate the cause of SCC, PIEs at hot laboratories were carried out on the sample material extracted from BWR power plants. SCC studies require various kind of PIE techniques, because the SCC is caused by a complicated synergistic effects of stress and chemical environment on material that suffered degradations by irradiation and/or thermal aging. In this paper, we describe the PIE techniques adopted recently for our SCC studies, especially the crack growth measurement, uniaxial constant load (UCL) tensile test method, in-situ observation during slow strain rate test (SSRT) and several metallurgical test techniques using the FEtype transmission electron microscopy (FE-TEM), focused ion beam (FIB) processing technique, three Dimensional Atom Probe (3DAP) analysis and atomic force microscopy (AFM).
Nakano, Junichi; Miwa, Yukio; Koya, Toshio; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.643 - 647, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:48.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To study effects of minor elements on the irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC), high purity Type 304 and 316 stainless steels (SSs) were fabricated and added minor elements, Si or C. After neutron irradiation to 3.5 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1MeV), the slow strain rate tests (SSRT) for the irradiated specimens was conducted in oxygeneted high purity water at 561 K. Fracture surface of the specimens was examined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) after the SSRT. Fraction of intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) on the fracture surface after the SSRT increased with netron fluence. Suppression of irradiation hardening and increase of peiod to SCC fracture as benefitical effects of the additional elements, Si or Mo, were not observed obviously. In high purity SS added C, fraction of IGSCC was the smallest in the all SSs, although irraidiation hardening level was the largest in the all SSs. Addition of C suppressed the susceptibility to IGSCC.
1MeV), the slow strain rate tests (SSRT) for the irradiated specimens was conducted in oxygeneted high purity water at 561 K. Fracture surface of the specimens was examined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) after the SSRT. Fraction of intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) on the fracture surface after the SSRT increased with netron fluence. Suppression of irradiation hardening and increase of peiod to SCC fracture as benefitical effects of the additional elements, Si or Mo, were not observed obviously. In high purity SS added C, fraction of IGSCC was the smallest in the all SSs, although irraidiation hardening level was the largest in the all SSs. Addition of C suppressed the susceptibility to IGSCC.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi; Nakajima, Hajime*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Suzuki, Masahide; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Nakano, Junichi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2004-015, 114 Pages, 2004/03
The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) visually inspected the weld joint of core shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Station Unit-2 by a direction of the Nuclear and Industrial Agency, cracks were observed at outer side of the ring weld joint (H3) between a core shroud middle trunk and a middle ring. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co. Ltd. (NFD) on the specimen including cracks sampled from the core shroud. The present examination has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD from the planning stage. Based on results of the present examination, the probable presence of tensile residual stress by welding process and dissolved oxygen contents in the cooling water, it was shown that the cracks were considered to be stress corrosion cracking (SCC). However, the cause of the cracks needs more consideration on the way of shroud construction.
Nakano, Junichi; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Kita, Satoshi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1568 - 1572, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Type 316LN stainless steel of the international thermonuclear experimental reactor (ITER) Grade (316LN-IG SS) is being considered for the first wall/ blanket component. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) technique is expected for the fabrication of module. To evaluate the integrity and susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of HIPed 316LN-IG SS, tensile tests in vacuum and slow strain rate tests (SSRT) in high temperature water were performed. Specimen with the HIPed joint shows no deterioration of the tensile strength and susceptibility to SCC in oxygenated water. Thermally sensitized specimen with the HIPed joint was low susceptible to SCC in creviced environment. It is concluded that the strength at joint location is as high as that at the base alloy and the joint interface appears integrity.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Kita, Satoshi; Yonekawa, Minoru; Nakano, Junichi; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Nakajima, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part1), p.331 - 334, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) caused by simultaneous effects of neutron irradiation and high temperature water environments has been pointed out as one of the major concerns of in-core structural materials not only for the light water reactors (LWRs) but also for the water-cooled fusion reactor. It is necessary to evaluate precisely stress condition under irradiation environment, because stress is one of key factors on IASCC. Stress relaxation of tensile type specimens under fast neutron irradiation at 288 C has been studied for type 316L stainless steel in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). This paper describes the in-pile and out-of-pile stress-relaxation test results of tensile type specimens for type 316L stainless steel as compared with the literature data by Foster, which were mainly obtained by bent beam specimens. Moreover these experimental results were compared with the analytical ones by using Nakagawa's model.
C has been studied for type 316L stainless steel in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). This paper describes the in-pile and out-of-pile stress-relaxation test results of tensile type specimens for type 316L stainless steel as compared with the literature data by Foster, which were mainly obtained by bent beam specimens. Moreover these experimental results were compared with the analytical ones by using Nakagawa's model.
Tsuji, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Nakano, Junichi; Miwa, Yukio
JAERI-Conf 2001-008, p.187 - 203, 2001/07
no abstracts in English