Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
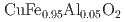
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) triangular skyrmion lattice state in the cubic chiral helimagnet EuPtSi
triangular skyrmion lattice state in the cubic chiral helimagnet EuPtSiMatsumura, Takeshi*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; Nakao, Hironori*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Physical Review B, 109(17), p.174437_1 - 174437_8, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Pt
Pt Ga
Ga studied by resonant X-ray and neutron scattering
studied by resonant X-ray and neutron scatteringTabata, Chihiro; Kon, Fusako*; Ota, Kyugo*; Hibino, Ruo*; Matsumoto, Yuji*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Nakao, Hironori*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kaneko, Koji
Physical Review B, 109(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)

 Sn
Sn (
( = Rh and Ir)
= Rh and Ir)Shimoda, Ami*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 38, p.011091_1 - 011091_6, 2023/05
 PdSi
PdSi
Hirschberger, M.*; Nakajima, Taro*; Kriener, M.*; Kurumaji, Takashi*; Spitz, L.*; Gao, S.*; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Yamasaki, Yuichi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(22), p.220401_1 - 220401_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:90.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)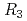 Ir
Ir Sn
Sn (
( : La and Ce) investigated using neutron and X-ray diffraction
: La and Ce) investigated using neutron and X-ray diffractionNakazato, Seiya*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Hashimoto, Daisuke*; Shiozawa, Mami*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011128_1 - 011128_6, 2020/03
 magnetic order in trillium lattice antiferromagnet EuPtSi studied by resonant X-ray scattering
magnetic order in trillium lattice antiferromagnet EuPtSi studied by resonant X-ray scatteringTabata, Chihiro*; Matsumura, Takeshi*; Nakao, Hironori*; Michimura, Shinji*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Inami, Toshiya*; Kaneko, Koji; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 88(9), p.093704_1 - 093704_5, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:89.11(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kubota, Masato; Sakurai, Takeaki*; Miyadera, Tetsuhiko*; Nakao, Hironori*; Sugita, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yuji*
Journal of Applied Physics, 120(16), p.165501_1 - 165501_5, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We performed soft X-ray resonant scattering experiments on P3HT:PCBM blend thin films to reveal the domain structure and electronic state, where P3HT and PCBM mean regioregular poly (3-hexylthiophene) and [6,6]-phenyl-C61-buteric acid methyl ester, respectively. We measured two films, where chloroform (CF sample) and 1,2-dichlorobenzene (DCB sample) are used as solvents in the fabrication process. There is negligible X-ray incident angle dependence of the X-ray absorption spectra at the S  -absorption edge in the CF sample, whereas the DCB sample exhibits clear incident angle dependence. We obtained the wave-number resolved spectra at
-absorption edge in the CF sample, whereas the DCB sample exhibits clear incident angle dependence. We obtained the wave-number resolved spectra at 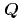 = (1, 0, 0) for P3HT molecules in both samples. The packing growth of P3HT molecules is revealed to be much more developed in the DCB sample than the CF sample. In addition, the electronic structure at local sulfur element sites clearly changes for both of the samples.
= (1, 0, 0) for P3HT molecules in both samples. The packing growth of P3HT molecules is revealed to be much more developed in the DCB sample than the CF sample. In addition, the electronic structure at local sulfur element sites clearly changes for both of the samples.
Torigoe, Shuhei*; Ishimoto, Yutaro*; Aoishi, Yuhei*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yoshii, Kenji; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Nishihata, Yasuo; Kodama, Katsuaki; Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(8), p.085109_1 - 085109_5, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) )
) (SrMnO
(SrMnO )
) superlattice revealed by resonant soft X-ray scattering
superlattice revealed by resonant soft X-ray scatteringKubota, Masato; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Hironori*; Okamoto, Jun*; Yamasaki, Yuichi*; Sawa, Akihito*; Murakami, Yoichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(5S1), p.05FH07_1 - 05FH07_5, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.21(Physics, Applied) high-spin state with a large orbital angular momentum in La
high-spin state with a large orbital angular momentum in La Ca
Ca CoO
CoO
Okamoto, Jun*; Nakao, Hironori*; Yamasaki, Yuichi*; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Tanaka, Arata*; Kubota, Masato; Horigane, Kazumasa*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(4), p.044705_1 - 044705_6, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)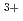 in LaCo
in LaCo Rh
Rh O
O investigated by structural phenomena
investigated by structural phenomenaAsai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kobayashi, Wataru*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Kumai, Reiji*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(11), p.114606_1 - 114606_6, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co
have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O
ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O octahedron of LaCo
octahedron of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh
are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO
substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co
from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co
ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh
ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh ions.
ions.
Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Fujioka, Jun*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Takahashi, Yoichiro*; Shimano, Ryo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 407(11), p.1685 - 1688, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.57(Physics, Condensed Matter) and TbVO
and TbVO under high pressure
under high pressureBizen, Daisuke*; Nakao, Hironori*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Fujioka, Jun*; Yasue, Toshio*; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(2), p.024715_1 - 024715_6, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic phase diagrams for  VO
VO (
( = Y, Tb) were determined by low temperature and high pressure neutron-diffraction techniques. We found that the magnetic ground state in TbVO
= Y, Tb) were determined by low temperature and high pressure neutron-diffraction techniques. We found that the magnetic ground state in TbVO changes from
changes from 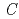 -type spin ordering (
-type spin ordering (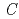 -SO) to
-SO) to  -type spin ordering (
-type spin ordering ( -SO) on application of pressure. The transition of the magnetic ground state also indicates that the ground state of the orbital ordering changes from
-SO) on application of pressure. The transition of the magnetic ground state also indicates that the ground state of the orbital ordering changes from  -type orbital ordering (
-type orbital ordering ( -OO) to
-OO) to 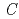 -type orbital ordering (
-type orbital ordering (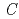 -OO). In YVO
-OO). In YVO , the
, the  -SO and
-SO and 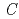 -OO phases set in simultaneously up to 6.2 GPa, and the disorder-[
-OO phases set in simultaneously up to 6.2 GPa, and the disorder-[ -SO,
-SO, 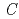 -OO] phase transition appears above 6 GPa. This is the first observation of a simultaneous spin and orbital order-disorder phase transition in perovskite-type transition-metal oxides
-OO] phase transition appears above 6 GPa. This is the first observation of a simultaneous spin and orbital order-disorder phase transition in perovskite-type transition-metal oxides  MO
MO . The [
. The [ -SO,
-SO, 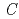 -OO] phase is strongly stabilized with increasing pressure, and both the covalency effect and the superexchange interaction play roles in this stabilization.
-OO] phase is strongly stabilized with increasing pressure, and both the covalency effect and the superexchange interaction play roles in this stabilization.
Owada, Kenji; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 320, p.012086_1 - 012086_5, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have performed an X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy measurement of 91 Pb(Zn
Pb(Zn Nb
Nb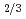 )O
)O -9
-9 PbTiO
PbTiO and found a slow structural fluctuation in time near
and found a slow structural fluctuation in time near  . The slow fluctuation consists of long-term and short-term fluctuations. We have derived the short-term fluctuation from the intensity fluctuations and found out the relaxation time to be an order of 10s. It is suggested that the slow fluctuation is owing to the competition between macroscopic tetragonal symmetry and the microscopic orthorhombic symmetry. The competition should be a main reason for the low-frequency dielectric permittivity.
. The slow fluctuation consists of long-term and short-term fluctuations. We have derived the short-term fluctuation from the intensity fluctuations and found out the relaxation time to be an order of 10s. It is suggested that the slow fluctuation is owing to the competition between macroscopic tetragonal symmetry and the microscopic orthorhombic symmetry. The competition should be a main reason for the low-frequency dielectric permittivity.

 in Pb(Zn
in Pb(Zn Nb
Nb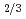 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO PbTiO
PbTiO
Owada, Kenji; Mizuki, Junichiro; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Hirota, Kazuma*
Physical Review B, 83(22), p.224115_1 - 224115_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Complementary use of coherent X-ray diffraction (CXD), X-ray diffuse scattering, conventional X-ray diffraction techniques and dielectric measurements has enabled us to investigate Pb(Zn Nb
Nb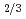 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
 S
S
Nakao, Hironori*; Owada, Kenji; Shimomura, Susumu*; Ochiai, Akira*; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Mimura, Hidekazu*; Yamauchi, Kazuto*; Murakami, Yoichi*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1234, p.935 - 938, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.61(Physics, Applied)Owada, Kenji; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Mimura, Hidekazu*; Yamauchi, Kazuto*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 49(2), p.020216_1 - 020216_3, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.42(Physics, Applied) C
C
Matsumura, Takeshi*; Inami, Toshiya; Kosaka, Masashi*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Inukai, Takaki*; Ochiai, Akira*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Katano, Susumu*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(10), p.103601_1 - 103601_4, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
O ; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloom
; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloomOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Noda, Yukio*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Isobe, Masahiko*; et al.
Hoshako, 21(2), p.87 - 96, 2008/03
Devil's flower has been found in a temperature-pressure phase diagram of NaV O
O , which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV
, which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV O
O . The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
. The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.