Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirayama, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Morishima, Makoto*; Uematsu, Mikio*; Sato, Osamu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(11), p.1339 - 1361, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:20.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)Progress in calculation methods for radiation shielding are reviewed based on basis of the activities of research committees related to radiation shielding fields established in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan. A technological roadmap for the field of radiation shielding, progress and prospects for specific shielding calculation methods such as the Monte Carlo, discrete ordinate Sn transport, and simplified methods, and shielding experiments used to validate calculation methods are presented in this paper.
Kameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Shimada, Asako; Katayama, Atsushi; Nakashima, Mikio*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(3), p.216 - 225, 2011/09
Analytical methods have been developed for simple and rapid determination of radioactive nuclides, which are selected as important nuclides for safety assessment of disposal of wastes generated from research facilities. We advanced the development of a high-efficiency non-destructive measurement technique for  -ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
-ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
 trapping
trappingIshimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Matsue, Hideaki; Oki, Yoshiyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 69(2), p.506 - 510, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.28(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In order to establish a simple and rapid analytical method for  C in solidified products made from non-metallic low-level radioactive solid wastes by melting treatment, a radiochemical analysis in combination with alkaline fusion as a sample decomposition method was examined. A simulated solidified product containing
C in solidified products made from non-metallic low-level radioactive solid wastes by melting treatment, a radiochemical analysis in combination with alkaline fusion as a sample decomposition method was examined. A simulated solidified product containing  C, which was prepared by using nuclear reaction
C, which was prepared by using nuclear reaction  N(n, p)
N(n, p) C with thermal neutron irradiation, was analyzed by the present method to compare with a conventional radiochemical analysis using oxidizing combustion. The reproducible and quantitative recovery of
C with thermal neutron irradiation, was analyzed by the present method to compare with a conventional radiochemical analysis using oxidizing combustion. The reproducible and quantitative recovery of  C from the simulated solidified product indicates that the present method is superior and more efficient for
C from the simulated solidified product indicates that the present method is superior and more efficient for  C analysis in solidified products than the conventional method using oxidizing combustion.
C analysis in solidified products than the conventional method using oxidizing combustion.
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 286(3), p.765 - 770, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.28(Chemistry, Analytical)Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.117 - 123, 2010/10
Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka; Katayama, Atsushi; Sakai, Akihiro; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Nakashima, Mikio; Kihara, Shinji; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-023, 84 Pages, 2010/03
In order to establish the practical evaluation methods such as scaling factor method to determine the radioactivity concentrations of the important nuclides for safety assessment of disposal of radioactive wastes, we analyzed low-level radioactive liquid waste (56 samples), which is generated from various research facilities at Nuclear Science Research Institute from FY1998 to FY2007 and accumulated the radioactivity concentrations data (563 data) of the 17 important nuclides. We investigated the correlation of the radioactivity concentrations of the important nuclides with the "Key nuclides ( Co or
Co or  Cs)". In present paper, the radioactivity concentrations data of the 17 important nuclides and the results of the correlation of the radioactivity concentrations are summarized for the data to establish the practical evaluation methods to determine the radioactivity concentrations in asphalt-solidified or cement-solidified products.
Cs)". In present paper, the radioactivity concentrations data of the 17 important nuclides and the results of the correlation of the radioactivity concentrations are summarized for the data to establish the practical evaluation methods to determine the radioactivity concentrations in asphalt-solidified or cement-solidified products.
 Tc in radioactive waste using Tc extraction disk and imaging plates
Tc in radioactive waste using Tc extraction disk and imaging platesKameo, Yutaka; Katayama, Atsushi; Hoshi, Akiko; Haraga, Tomoko; Nakashima, Mikio
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 68(1), p.139 - 143, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.3(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)A simple method was developed for determination of  Tc in low-level radioactive waste: Technetium-99 retained by a solid phase extraction disk was directly measured with imaging plates system. It was found that more than 97% of Tc were retained by the disk from a solution of pH 2 to 12, whereas depth profile of Tc in the disk, which greatly influences the counting efficiency, depended on solution pH. The present method was successfully applied to actual radioactive liquid waste samples arising from nuclear research facilities.
Tc in low-level radioactive waste: Technetium-99 retained by a solid phase extraction disk was directly measured with imaging plates system. It was found that more than 97% of Tc were retained by the disk from a solution of pH 2 to 12, whereas depth profile of Tc in the disk, which greatly influences the counting efficiency, depended on solution pH. The present method was successfully applied to actual radioactive liquid waste samples arising from nuclear research facilities.
Kameo, Yutaka; Shimada, Asako; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Katayama, Atsushi; Hoshi, Akiko; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2009-051, 81 Pages, 2009/10
Simple and rapid determination methods were developed for an evaluation of important nuclides, U, and Th in wastes generated from research facilities at Nuclear Science Research Institute and Oarai Research and Development Center. The present methods were assumed to apply to solidified products made from miscellaneous wastes by plasma melting at the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities. In order to reduce costs of radiochemical analysis and to establish a routine analytical system, counting efficiency of non-destructive  -ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
-ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
 Ni and
Ni and  Ni in low-level radioactive wastes arising from nuclear research facilities
Ni in low-level radioactive wastes arising from nuclear research facilitiesKameo, Yutaka; Haraga, Tomoko; Katayama, Atsushi; Hoshi, Akiko; Nakashima, Mikio
Radioisotopes, 58(5), p.153 - 160, 2009/05
A routine analytical method was developed for the determination of  Ni and
Ni and  Ni in low-level radioactive wastes arising from nuclear research facilities. A separation scheme of
Ni in low-level radioactive wastes arising from nuclear research facilities. A separation scheme of  Ni and
Ni and  Ni in waste samples was optimized by considering concentration of interference radionuclides and chemical composition of the waste samples. Concentrations of
Ni in waste samples was optimized by considering concentration of interference radionuclides and chemical composition of the waste samples. Concentrations of  Ni and
Ni and  Ni in actual radioactive wastes such as pipes and liquid waste could be well determined by the present analytical method. In the determination, the time required for the chemical separation was five to seven days per ten samples. It was concluded that the present method could be applied to a routine determination of
Ni in actual radioactive wastes such as pipes and liquid waste could be well determined by the present analytical method. In the determination, the time required for the chemical separation was five to seven days per ten samples. It was concluded that the present method could be applied to a routine determination of  Ni and
Ni and  Ni in low-level radioactive wastes. In the present experiment, radioactivity ratio of
Ni in low-level radioactive wastes. In the present experiment, radioactivity ratio of  Ni/
Ni/ Ni in pipe samples, which were taken from a nuclear research reactor, was estimated by a computer code (ORIGEN2). Radioactivity ratio of
Ni in pipe samples, which were taken from a nuclear research reactor, was estimated by a computer code (ORIGEN2). Radioactivity ratio of  Ni/
Ni/ Ni, obtained by the computer calculation, was ranged from 98 to 109 and that obtained by the present analytical method was 118
Ni, obtained by the computer calculation, was ranged from 98 to 109 and that obtained by the present analytical method was 118  6.
6.
Fujiwara, Asako; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio
Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(18), p.4125 - 4127, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:31.95(Biochemical Research Methods)Dependence of Th recovery on HF concentration in nitric acid solutions (1 5 mol/dm
5 mol/dm ) containing 1
) containing 1 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm of Th and various concentrations of HF was studied using a commercially available UTEVA resin column (for uranium and tetravalent actinide). Thorium recovery decreased with an increase in the HF concentration in the sample solutions. The concentration of HF at which Th recovery started to decrease was about 1
of Th and various concentrations of HF was studied using a commercially available UTEVA resin column (for uranium and tetravalent actinide). Thorium recovery decreased with an increase in the HF concentration in the sample solutions. The concentration of HF at which Th recovery started to decrease was about 1 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm in 1 mol/dm
in 1 mol/dm HNO
HNO solution, about 1
solution, about 1 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm in 3 mol/dm
in 3 mol/dm HNO
HNO solution, and about 1
solution, and about 1 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm in 5 mol/dm
in 5 mol/dm HNO
HNO solution. When Al(NO
solution. When Al(NO )
) (0.2 mol/dm
(0.2 mol/dm ) or Fe(NO
) or Fe(NO )
) (0.6 mol/dm
(0.6 mol/dm ) was added as a masking agent for F
) was added as a masking agent for F into the Th solution containing 1
into the Th solution containing 1 10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm HF and 1 mol/dm
HF and 1 mol/dm HNO
HNO , the Th recovery improved from 1.4
, the Th recovery improved from 1.4 0.3% to 95
0.3% to 95 5% or 93
5% or 93 3%. Effective extraction of Th on UTEVA resin was achieved by selecting the concentration of HNO
3%. Effective extraction of Th on UTEVA resin was achieved by selecting the concentration of HNO and/or adding masking agents such as Al(NO
and/or adding masking agents such as Al(NO )
) according to the concentration of HF in the sample solution.
according to the concentration of HF in the sample solution.
Katayama, Atsushi; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio
Shitsuryo Bunseki, 56(5), p.229 - 234, 2008/10
A new technique is described for minor isotope analysis by using a rotating electric field and an imaging detector. The rotating electric field is generated by cylindrically arranged six plane electrodes with multi-phase sinusoidal wave voltage. When ion packets that are discriminated by time-of-flight enter the rotating electric field, these are circularly deflected and make a spiral image on fluorescent screen of detector. This spiral image represents m/z values data as position of ions and abundance of ions as brightness. For minor isotopes analysis, the micro channel plate detector is used under gate control operation to remove from influence of high intensity of major isotopes.
Hoshi, Akiko; Watanabe, Koichi; Fujiwara, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takebe, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(3), p.177 - 185, 2008/09
The simple and rapid separation method was developed for actinides in the low-level radioactive waste. Extraction chromatographic columns were used for the separation of U, Np, Pu, Am, and Cm in the solution of the simulated solidified product and the simulated waste solution. In the investigation of separation procedure, it was tried to construct the scheme with the relatively non-corrosive reagents aiming to apply to the routine analysis of the radioactive waste. Recoveries and decontamination factors of actinides in the solution of simulated waste were high enough to determine of actinides in radioactive waste by alpha-spectrometry, mass spectroscopy. The time required of the separation operation was 2-3 hours. The chromatographic method was applied to analysis of actinide in actual waste solution, high recoveries and decontamination factors were obtained, which indicated that the extraction chromatographic separation method would be adopted as a simple and rapid separation method of actinide in waste.
 -ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)
-ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)Ishimori, Kenichiro; Oki, Keiichi; Takaizumi, Hirohide; Kameo, Yutaka; Oki, Yoshiyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2007-065, 20 Pages, 2008/01
In order to prepare a reference material which is used for radiochemical analysis of solidified products made from non-metallic miscellaneous low level radioactive solid wastes by melting in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the preparation method of the reference material was investigated. Under the optimum melting conditions obtained in this report, the reference material containing  Np,
Np,  Am and
Am and  Cm as
Cm as  -ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188
-ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188 0.001 Bq/g for
0.001 Bq/g for  Np, 0.368
Np, 0.368 0.004 Bq/g for
0.004 Bq/g for  Am, 0.402
Am, 0.402 0.010 Bq/g for
0.010 Bq/g for  Cm.
Cm.
Katayama, Atsushi; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Dai-10-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.234 - 237, 2008/00
The determination of  I by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) has generally been used measurement targets from AgI precipitation. For more sensitive determination of
I by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) has generally been used measurement targets from AgI precipitation. For more sensitive determination of  I, it is necessary to reduce the quantity of iodine carrier for precipitation. But, more than 1mg is the amount of carrier stable iodine needed at present to make a reliable sample treatment and AMS determination. In this study, we examined the basics of procedures of the direct measurement target that used adsorption reaction of the molecular iodine to the metal silver surface in substitution for precipitation. Using this procedure, we have prepared measurement targets with a carrier from 1 to 0.2 mg iodine.
I, it is necessary to reduce the quantity of iodine carrier for precipitation. But, more than 1mg is the amount of carrier stable iodine needed at present to make a reliable sample treatment and AMS determination. In this study, we examined the basics of procedures of the direct measurement target that used adsorption reaction of the molecular iodine to the metal silver surface in substitution for precipitation. Using this procedure, we have prepared measurement targets with a carrier from 1 to 0.2 mg iodine.
 I in radioactive wastes by accelerator mass spectrometry
I in radioactive wastes by accelerator mass spectrometryKatayama, Atsushi; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio
Radioisotopes, 56(12), p.787 - 793, 2007/12
Determination of the concentration of  I in radioactive wastes is important according to waste management and environmental concern. In the present work, accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was applied to measurement of
I in radioactive wastes is important according to waste management and environmental concern. In the present work, accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was applied to measurement of  I/
I/ I ratio to determine
I ratio to determine  I concentration in radioactive waste. Solid-phase extraction disks (Anion-SR) for chemical separation of iodine from radioactive waste samples were used to prepare AMS targets. This method made it possible to swiftly separate iodide ions from sample solutions, compared with a conventional liquid-liquid extraction method. Considering contamination of a sample with
I concentration in radioactive waste. Solid-phase extraction disks (Anion-SR) for chemical separation of iodine from radioactive waste samples were used to prepare AMS targets. This method made it possible to swiftly separate iodide ions from sample solutions, compared with a conventional liquid-liquid extraction method. Considering contamination of a sample with  I from a work site environment, we derived the suitable amount of the
I from a work site environment, we derived the suitable amount of the  I carrier to keep the background value of the
I carrier to keep the background value of the  I/
I/ I ratio as low as possible. The present method was successfully applied to laboratory standards and liquid waste samples arising from nuclear facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
I ratio as low as possible. The present method was successfully applied to laboratory standards and liquid waste samples arising from nuclear facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
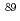 Sr and
Sr and  Sr in radioactive waste using Sr extraction disk and beta-ray spectrometer
Sr in radioactive waste using Sr extraction disk and beta-ray spectrometerKameo, Yutaka; Katayama, Atsushi; Fujiwara, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Nakashima, Mikio
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 274(1), p.71 - 78, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.32(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Katayama, Atsushi; Nakashima, Mikio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(1), p.58 - 64, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Nakashio, Nobuyuki; Kameo, Yutaka; Hoshi, Akiko; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Review 2007-005, 35 Pages, 2007/02
The Nuclear Science Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency constructed the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVRF) in February 2003 for treatment of low-level radioactive miscellaneous solid waste (LLW). The waste volume reduction is carried out by a high-compaction process or melting processes in the AVRF. In advance of operating the melting process in the AVRF, melting tests of simulated LLW with RI tracers ( Co,
Co,  Cs and
Cs and  Eu) have been conducted by using the plasma melter in pilot scale. Viscosity of molten waste, chemical composition and physical properties of solidified products and distribution of the tracers in each product were investigated in various melting conditions. In this review, experimental results of the melting tests were discussed in order to contribute to actual treatment of LLW in the AVRF.
Eu) have been conducted by using the plasma melter in pilot scale. Viscosity of molten waste, chemical composition and physical properties of solidified products and distribution of the tracers in each product were investigated in various melting conditions. In this review, experimental results of the melting tests were discussed in order to contribute to actual treatment of LLW in the AVRF.
Fujiwara, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Hoshi, Akiko; Haraga, Tomoko; Nakashima, Mikio
Journal of Chromatography A, 1140(1-2), p.163 - 167, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:56.06(Biochemical Research Methods)Extraction chromatography with UTEVA resin was applied to separation of Th and U from control solutions prepared from a multi-element control solution and from sample solutions of solidified simulated waste. Thorium and U in control solutions with 1 to 5 M HNO were extracted with UTEVA resin and recovered with a solution containing 0.1 M HNO
were extracted with UTEVA resin and recovered with a solution containing 0.1 M HNO and 0.05 M oxalic acid to be separated from the other metallic elements. Extraction behavior of U in the sample solutions was similar to that in the control solutions, but extraction of Th was dependent on the concentration of HNO
and 0.05 M oxalic acid to be separated from the other metallic elements. Extraction behavior of U in the sample solutions was similar to that in the control solutions, but extraction of Th was dependent on the concentration of HNO . Thorium was extracted from 5 M HNO
. Thorium was extracted from 5 M HNO sample solutions but not from 1 M HNO
sample solutions but not from 1 M HNO sample solutions. We conjecture that thorium fluoride formation interferes with extraction of Th. Addition of Al(NO
sample solutions. We conjecture that thorium fluoride formation interferes with extraction of Th. Addition of Al(NO )
) and Fe(NO
and Fe(NO )
) , which have a higher stability constant with fluoride ion than Th does with it improved extractability of Th from 1 M HNO
, which have a higher stability constant with fluoride ion than Th does with it improved extractability of Th from 1 M HNO sample solution.
sample solution.
Dung, L. T. K.*; Imai, Tomoki*; Tomioka, Osamu; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Meguro, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 22(11), p.1425 - 1430, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:23.21(Chemistry, Analytical)Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) method using supercritical CO fluid containing a complex of HNO
fluid containing a complex of HNO -tri-
-tri- -butyl phosphate (TBP) as an extractant was applied to extract uranium from a several uranyl phosphate compounds and simulated uranium ores. Extraction method consisting of a static and a dynamic extraction processes was established and experimental condition such as pressure, temperature, and extraction time were optimized. It was found that uranium could be efficiently extracted from both of the uranyl phosphates and simulated ores by the SFE method and then it was demonstrated that SFE was useful as a pretreatment method for uranium analysis in ores.
-butyl phosphate (TBP) as an extractant was applied to extract uranium from a several uranyl phosphate compounds and simulated uranium ores. Extraction method consisting of a static and a dynamic extraction processes was established and experimental condition such as pressure, temperature, and extraction time were optimized. It was found that uranium could be efficiently extracted from both of the uranyl phosphates and simulated ores by the SFE method and then it was demonstrated that SFE was useful as a pretreatment method for uranium analysis in ores.