Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Nagae, Yuji; Nagai, Eiichi*; Yasumatsu, Tomohiro*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Ogino, Shoya*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Proceedings of 11th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research Conference (ERMSAR 2024) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2024/05
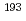 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adductsKaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(17), p.12740 - 12752, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.88(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In the present study, density functional theory (DFT) calculation was applied to Vaska's complexes of formula 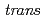 -[IrCl(CO)(PPh
-[IrCl(CO)(PPh )
) ], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H
], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H , i.e.,
, i.e., 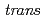 -[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh
-[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh )
) ], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding
], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding 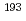 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and 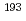 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl
ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl and negative for the complex with YZ = H
and negative for the complex with YZ = H . This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
. This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
Fukasawa, Yuto*; Kaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 329(1), p.77 - 84, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Density functional theory calculations were applied to understand the selectivity between Am and Eu
and Eu ions with the crown ethers type ligands. 18C6 is predicted to form the most stable complex with Eu
ions with the crown ethers type ligands. 18C6 is predicted to form the most stable complex with Eu and show the higher stability for Am
and show the higher stability for Am over Eu
over Eu , being consistent with previously reported Am
, being consistent with previously reported Am /Eu
/Eu selectivity. We modeled N- and S-donor complexes by using framework of 18C6 complex and analyzed the complexation Gibbs energies, indicating that 18C6 with N-donor atoms is suitable for both complexation and higher Am
selectivity. We modeled N- and S-donor complexes by using framework of 18C6 complex and analyzed the complexation Gibbs energies, indicating that 18C6 with N-donor atoms is suitable for both complexation and higher Am stability over Eu
stability over Eu due to the stronger covalent interaction.
due to the stronger covalent interaction.
 O)
O) ]
] with nitrate ions by using density functional theory calculation
with nitrate ions by using density functional theory calculationKato, Akane*; Kaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
RSC Advances (Internet), 10(41), p.24434 - 24443, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Complexation reactions of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes in HNO solution were investigated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations in order to predict the stability of Ru species in high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) solution. Equilibrium structure of [Ru(NO)(NO
solution were investigated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations in order to predict the stability of Ru species in high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) solution. Equilibrium structure of [Ru(NO)(NO )
) (H
(H O)
O) ] obtained by DFT calculations reproduced the experimental Ru-ligands bond lengths and IR frequencies reported previously. Comparison of the Gibbs energies among the geometrical isomers revealed that the complexation reactions of the ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes with NO
] obtained by DFT calculations reproduced the experimental Ru-ligands bond lengths and IR frequencies reported previously. Comparison of the Gibbs energies among the geometrical isomers revealed that the complexation reactions of the ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes with NO
 proceed via the NO
proceed via the NO
 coordination to the equatorial plane toward the Ru-NO axis. We also estimated Gibbs energy differences on the stepwise complexation reactions to succeed in reproducing the fraction of Ru-NO species in 6 M HNO
coordination to the equatorial plane toward the Ru-NO axis. We also estimated Gibbs energy differences on the stepwise complexation reactions to succeed in reproducing the fraction of Ru-NO species in 6 M HNO solution, such as in HLLW, by considering the association energy between the Ru-NO species and the substituting ligands. Electron density analyses of the complexes indicated that the strength of the Ru-ligands coordination bonds depends on the stability of the Ru species and the Ru complex without NO
solution, such as in HLLW, by considering the association energy between the Ru-NO species and the substituting ligands. Electron density analyses of the complexes indicated that the strength of the Ru-ligands coordination bonds depends on the stability of the Ru species and the Ru complex without NO
 at the axial position is more stable than that wit NO
at the axial position is more stable than that wit NO
 , which might attribute to the difference in the trans influence between H
, which might attribute to the difference in the trans influence between H O and NO
O and NO
 . Finally, we demonstrated the complexation kinetics in the reactions
. Finally, we demonstrated the complexation kinetics in the reactions 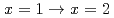 . The present study is expected to enable us to model the precise complexation reactions of platinum-group metals in HNO
. The present study is expected to enable us to model the precise complexation reactions of platinum-group metals in HNO solution.
solution.
 Ru M
Ru M ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes
ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexesKaneko, Masashi; Kato, Akane*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(20), p.14024 - 14033, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.50(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We applied density functional theory calculations to ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes, which are known to exist in high-level radioactive waste, to give a theoretical correlation between  Ru M
Ru M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters (
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters ( and
and 
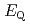 ) and ligand field strength (
) and ligand field strength (
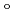 ) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L
) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L ] (L = Br
] (L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN ), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO
), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO )L
)L ] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the
] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the  and
and 
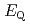 values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br
values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN . Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
. Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
 ) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C
) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C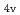 symmetry and showed the increase of
symmetry and showed the increase of 
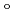 values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of
values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of  -donor and
-donor and  -acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the
-acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the  values.
values.
 ssbauer isomer shifts using second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian
ssbauer isomer shifts using second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess HamiltonianKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Hyperfine Interactions, 239(1), p.20_1 - 20_10, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:81.35(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We optimized a mixing ratio of exchange energy between pure DFT and exact Hartree-Fock using TPSS exchange-correlation functional to estimate the accurate coordination bonds in f-block complexes by numerically benchmarking with the experimental data of M ssbauer isomer shifts for
ssbauer isomer shifts for  Eu and
Eu and  Np nuclides. Second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian with segmented all-electron relativistically contracted basis set was employed to calculate the electron densities at Eu and Np nuclei, i.e. contact densities, for each five complexes for Eu(III) and Np(IV) systems. We compared the root mean square deviation values of their isomer shifts between experiment and calculation by changing the mixing ratio of Hartree-Fock exchange parameter from 0 to 100 % at intervals of 10 %. As the result, it was indicated that the mixing ratio of 30 and 60 % for Eu and Np benchmark systems, respectively, gives the smallest deviation values. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the covalency in the metal-ligand bonds for both Eu and Np complexes decreases with increasing the Hartree-Fock exchange admixture.
Np nuclides. Second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian with segmented all-electron relativistically contracted basis set was employed to calculate the electron densities at Eu and Np nuclei, i.e. contact densities, for each five complexes for Eu(III) and Np(IV) systems. We compared the root mean square deviation values of their isomer shifts between experiment and calculation by changing the mixing ratio of Hartree-Fock exchange parameter from 0 to 100 % at intervals of 10 %. As the result, it was indicated that the mixing ratio of 30 and 60 % for Eu and Np benchmark systems, respectively, gives the smallest deviation values. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the covalency in the metal-ligand bonds for both Eu and Np complexes decreases with increasing the Hartree-Fock exchange admixture.
Nakashima, Satoru*; Kaneko, Masashi; Yoshinami, Keisuke*; Iwai, Saki*; Dote, Haruka*
Hyperfine Interactions, 239(1), p.39_1 - 39_15, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.70(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)The present study reveals the on/off of spin-crossover (SCO) phenomenon in assembled Fe(II) complexes bridged by bis(pyridyl) type ligand. Whether SCO phenomenon occurs or not in assembled Fe(II) complexes bridged by bis(pyridyl) type ligand is determined by local structure around iron atom. SCO phenomenon occurs when the coordinating pyridines facing to each other across the iron atom are propeller type, while the phenomenon does not occur when they are parallel type or distorted propeller type. DFT calculation explained that, in the shortening of Fe-pyridine bonds when changing from high-spin state to low-spin state, the pyridines of propeller type can approach the iron atom with smaller steric hindrance than those of parallel and distorted propeller type complexes. The local structure is controlled by introducing methyl substituent and introducing  -system, changing SCO phenomenon. And the transition temperature of SCO is also controlled in assembled complexes bridged by 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane by mixing anionic ligand.
-system, changing SCO phenomenon. And the transition temperature of SCO is also controlled in assembled complexes bridged by 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane by mixing anionic ligand.
Kimura, Taiki*; Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 47(42), p.14924 - 14931, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:44.23(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We demonstrated density functional calculations of Eu(III) and Am(III) complexes with pnictogen-donor (X) ligands, CH )
) X-CH
X-CH -CH
-CH -X(CH
-X(CH )
) (X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.
(X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.

 /
/ values by benchmark study of the M
values by benchmark study of the M ssbauer Isomer shifts for Ru, Os complexes using relativistic DFT calculations
ssbauer Isomer shifts for Ru, Os complexes using relativistic DFT calculationsKaneko, Masashi; Yasuhara, Hiroki*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.36_1 - 36_9, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:76.04(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We aim to evaluate the validity of density functional calculations to the bonding property for Ru and Os complexes. We performed the benchmarking of theoretical computational method with  Ru,
Ru, 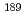 Os M
Os M ssbauer isomer shifts. As the result, the computational values of the electron densities at nucleus position correlated with the experimental M
ssbauer isomer shifts. As the result, the computational values of the electron densities at nucleus position correlated with the experimental M ssbauer isomer shifts.
ssbauer isomer shifts.
 ssbauer isomer shifts with density functional calculations
ssbauer isomer shifts with density functional calculationsKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Radioisotopes, 66(8), p.289 - 300, 2017/08
Scalar-relativistic density functional calculations applied to some trivalent europium complexes. Five Eu(III) complexes whose  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts vary from -1.8 to 0.5 mm/s are referred by previously reported results. Geometrical optimizations of their complexes reproduces the experimental coordination structures. Single-point calculations are applied to their optimized geometries at three density functionals, namely, BP86, B3LYP, and B2PLYP, to obtain their electron densities at Eu nucleus. A comparison of the linearity between the electron densities and the corresponding
ssbauer isomer shifts vary from -1.8 to 0.5 mm/s are referred by previously reported results. Geometrical optimizations of their complexes reproduces the experimental coordination structures. Single-point calculations are applied to their optimized geometries at three density functionals, namely, BP86, B3LYP, and B2PLYP, to obtain their electron densities at Eu nucleus. A comparison of the linearity between the electron densities and the corresponding  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts reveals that B2PLYP functional shows the best linearity. Electron population and bond analyses indicate that d- and f-orbital electrons of Eu ion in the complexes are found to be correlated to the experimental
ssbauer isomer shifts reveals that B2PLYP functional shows the best linearity. Electron population and bond analyses indicate that d- and f-orbital electrons of Eu ion in the complexes are found to be correlated to the experimental  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts. This indicates that the d- and f-orbital electrons are involved in the covalent interaction of the coordination bond between the Eu ion and the ligands.
ssbauer isomer shifts. This indicates that the d- and f-orbital electrons are involved in the covalent interaction of the coordination bond between the Eu ion and the ligands.
Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 17, p.9 - 15, 2017/03
Density functional calculations were applied to the complexation of Eu(III) and Am(III) ions with phosphinic acid (O-donor) and dihiophosphinic acid (S-donor) from the viewpoint of the bonding nature of valence orbitals in metal ion. Two and four conformers for S-donor and O-donor complexes, respectively were optimized. Their stabilization energies by complex formation toward [M(H O)
O) ]
] were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
Nakashima, Satoru*; Kaneko, Masashi
Advances in Chemistry Research, Vol.36, p.171 - 195, 2017/01
Spin-crossover (SCO) phenomena of the assembled coordination polymers are introduced. When the bridging ligand is flexible like 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane, 1,3-bis(4-pyridyl)propane, a variety of assembled structure can be obtained, depending on the conformer of the ligand and the guest molecules. Guest-dependent SCO phenomena of the assembled iron complexes are shown. Density functional theory is applied to know the cause of guest-dependent SCO phenomena. The validity of an iron mono-nucleus model is evaluated for the coordination polymers. It is shown that SCO occurs or not depends on the local structure around iron ion.
Uyama, Masao*; Hitomi, Takashi*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Research 2015-010, 67 Pages, 2015/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting a research project on (Grouting Technology Development for the Radioactive Waste Repository) funded by Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), Japan. As a part of the project, various investigations were carried out in the -200m Refuge Niche where pre-excavation grouting was performed and the distribution of the injected grouting material, also the effectiveness of grouting penetration for reduction of groundwater inflow were confirmed As the continuation of these investigations, chemical influences of grouting material on the rock mass were determined through (Laboratory testing of rock core samples from pre-excavation grouting area at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory). Specifically, core samples were obtained by check boring at where infiltration solidification of the grouting material was expected, and X-ray florescent analysis and Transmission Electron Microscope observation were performed focused on the contact parts of the grouting material and rock mass in fractures. As a result, the chemical influences of grouting material on the rock mass were identified.
Isayama, Akihiko; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Furukawa, Masaru*; Matsunaga, Go; Yamazaki, Kozo*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; Tamura, Naoki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(6), p.374 - 377, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Osakabe, Masaki*; Shinohara, Koji; Toi, Kazuo*; Todo, Yasushi*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(12), p.839 - 842, 2009/12
no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yoshida, Maiko; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tamura, Naoki*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Aiba, Nobuyuki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(12), p.952 - 955, 2008/12
no abstracts in English
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Tomioka, Osamu; Imai, Tomoki*; Fujimoto, Shigeyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio; Yoshida, Zenko; Honda, Tadashi*; Koya, Fumio*; Kitamura, Nobu*; Wada, Ryutaro*; et al.
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposium 2004 (WM '04) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/03
Supercritical CO fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO
fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO fluid containing a complex of HNO
fluid containing a complex of HNO - tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
- tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
Watanabe, Takeshi*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Yamamoto, Ichiro*; Tomioka, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Mikio; Wada, Ryutaro*; Nagase, Yoshiyuki*; Fukuzato, Ryuichi*
Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environment Applications (Super Green 2003), p.363 - 366, 2004/00
Recovery of salts by supercritical fluid leaching (SFL) method using carbon dioxide was experimentally studied. It was confirmed that LiCl was recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide and methanol, and KCl and SrCl were recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and crown ether. The influence of crown ether for KCl and SrCl
were recovered with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and crown ether. The influence of crown ether for KCl and SrCl extraction were found to increase in the order of 15-crown-5 (15C5)
extraction were found to increase in the order of 15-crown-5 (15C5)  18-crown-6 (18C6)
18-crown-6 (18C6)  dicychlohexyl-18-crown-6 (DC18C6). It is expected that other salts can be recovered selectively with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and suitable crown ether.
dicychlohexyl-18-crown-6 (DC18C6). It is expected that other salts can be recovered selectively with a mixed fluid of carbon dioxide, methanol and suitable crown ether.
Nagano, Tetsushi; Isobe, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Ashizaki, Midori*
Applied Spectroscopy, 56(5), p.651 - 657, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.41(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Nagano, Tetsushi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Nakayama, Shinichi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 47(6), p.748 - 754, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:44.04(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English