Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otsuka, Satoshi; Shizukawa, Yuta; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Yano, Yasuhide; Onizawa, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Onuma, Masato*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.288 - 298, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:76.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has been developing 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) tempered martensitic steel(TMS) as a candidate material for the fuel cladding tubes of sodium-cooled fast reactors(SFRs). The reliable prediction of in-reactor creep-rupture strength is critical for implementing the 9Cr-ODS TMS cladding tube in the SFR. This study investigated the quantitative correlation between the creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700
C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Kurino, Koichi*; Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Toyama, Takeshi*; Onuma, Masato*; Nakashima, Hideharu*
Tetsu To Hagane, 109(3), p.189 - 200, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel, a candidate material for fast reactor fuel cladding, has low thermal expansion, good thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to irradiation damage and high temperature strength. The origin of the excellent high-temperature strength lies in the dispersion of fine oxides. In this study, creep tests at 700 or 750 C, which are close to the operating temperatures of fast reactors, and high-temperature tensile tests at 900 to 1350
C, which are close to the operating temperatures of fast reactors, and high-temperature tensile tests at 900 to 1350  C, which simulate accident conditions, were conducted on 9Cr ODS ferritic steels, M11 and MP23, and 12Cr ODS ferritic steel, F14, to confirm the growth behavior of oxides. In the M11 and F14 creep test samples, there was little oxide growth or decrease in number density from the initial state, indicating that dispersion strengthening by oxides was effective during deformation. After creep deformation of F14, the development of dislocation substructures such as dislocation walls and subgrain boundaries was hardly observed, and mobile dislocations were homogeneously distributed in the grains. The dislocation density increased with increasing stress during the creep test. In the high-temperature ring tensile tests of MP23 and F14, the strength of both steels decreased at higher temperatures. In MP23, elongation decreased with increasing test temperature from 900 to 1100
C, which simulate accident conditions, were conducted on 9Cr ODS ferritic steels, M11 and MP23, and 12Cr ODS ferritic steel, F14, to confirm the growth behavior of oxides. In the M11 and F14 creep test samples, there was little oxide growth or decrease in number density from the initial state, indicating that dispersion strengthening by oxides was effective during deformation. After creep deformation of F14, the development of dislocation substructures such as dislocation walls and subgrain boundaries was hardly observed, and mobile dislocations were homogeneously distributed in the grains. The dislocation density increased with increasing stress during the creep test. In the high-temperature ring tensile tests of MP23 and F14, the strength of both steels decreased at higher temperatures. In MP23, elongation decreased with increasing test temperature from 900 to 1100  C, but increased at 1200
C, but increased at 1200  C, decreased drastically at 1250
C, decreased drastically at 1250  C, and increased again at 1300
C, and increased again at 1300  C. In F14, elongation decreased with increasing temperature. It was inferred that the formation of the
C. In F14, elongation decreased with increasing temperature. It was inferred that the formation of the  -ferrite phase was responsible for this complex change in mechanical properties of MP23 from 1200 to 1300
-ferrite phase was responsible for this complex change in mechanical properties of MP23 from 1200 to 1300  C.
C.
Sato, Satoshi*; Konno, Chikara; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Shionaga, Ryosuke*; Nose, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Yuji*; Hashimoto, Hirohide*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(4), p.410 - 417, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to enhance the neutron shielding performance, we developed concrete with boron of more than 10 wt%. We performed a neutron shielding experiment using the mockup of the newly developed boron-loaded concrete and DT neutrons at FNS in JAEA, and measured the reaction rates of the  Nb(n,2n)
Nb(n,2n)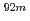 Nb and
Nb and  Au(n,
Au(n, )
)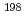 Au reactions in the mockup. The calculations were conducted by using MCNP-5.14 and FENDL-2.1. The calculation results agreed well with the measured ones, and we confirmed that the accuracy was very good on the atomic composition data of the boron-loaded concrete and their nuclear data. In addition, we calculated effective dose rates and reaction rates of the
Au reactions in the mockup. The calculations were conducted by using MCNP-5.14 and FENDL-2.1. The calculation results agreed well with the measured ones, and we confirmed that the accuracy was very good on the atomic composition data of the boron-loaded concrete and their nuclear data. In addition, we calculated effective dose rates and reaction rates of the  Co(n,
Co(n, )
) Co and
Co and  Eu(n,
Eu(n, )
) Eu reactions in the boron-loaded concrete and other concretes. It is concluded that the boron-loaded concrete has much better shielding performance for DT neutrons than other concretes.
Eu reactions in the boron-loaded concrete and other concretes. It is concluded that the boron-loaded concrete has much better shielding performance for DT neutrons than other concretes.
Ozu, Akira; Komeda, Masao; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Nakashima, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(12), p.700 - 704, 2017/12
, 59(12), p.700 - 704, 2017/12
no abstracts in English
Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.41 - 46, 2016/09
Neutron- and proton-induced cross-section data are required in a wide energy range beyond 20 MeV, for the design of accelerator applications. New evaluations are performed with recent knowledge in the optical and pre-equilibrium model calculations. We also evaluated cross-sections for p+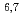 Li and p+
Li and p+ Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Ozu, Akira; Komeda, Masao; Kureta, Masatoshi; Zaima, Naoki; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Nakashima, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(2), p.115 - 127, 2016/06
A non-destructive assay system using the fast neutron direct interrogation method has been developed to put its method into practical use for the determination of uranium ( U) mass contained in actual uranium-contaminated waste drums. The method is capable of measuring the fissile mass in a drum by counting the number of fission neutrons resulting from nuclear fission reactions between the fissile materials contained in a drum and thermal neutrons generated by 14 MeV fast neutrons irradiated from outside the drum. The performance test employing simulated metal waste drums demonstrated that a natural uranium mass of as low as 10 g could be detected within an error of
U) mass contained in actual uranium-contaminated waste drums. The method is capable of measuring the fissile mass in a drum by counting the number of fission neutrons resulting from nuclear fission reactions between the fissile materials contained in a drum and thermal neutrons generated by 14 MeV fast neutrons irradiated from outside the drum. The performance test employing simulated metal waste drums demonstrated that a natural uranium mass of as low as 10 g could be detected within an error of  20% regardless of the distribution of uranium samples in the drum. A demonstration test employing actual waste drums could determine the uranium mass by using a newly developed correction method for deriving the fissile mass in a drum. It has been proved by the experimental validation tests that the assay system equipped with the correction method is very useful for the accountancy of the waste drums.
20% regardless of the distribution of uranium samples in the drum. A demonstration test employing actual waste drums could determine the uranium mass by using a newly developed correction method for deriving the fissile mass in a drum. It has been proved by the experimental validation tests that the assay system equipped with the correction method is very useful for the accountancy of the waste drums.
 nanocubes by solvothermal synthesis
nanocubes by solvothermal synthesisYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Nakashima, Koichi*; Nagata, Hajime*; Wada, Satoshi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 54(10S), p.10NC01_1 - 10NC01_6, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.5(Physics, Applied)The atomic-scale structure of KNbO nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO
nanopowder synthesized by solvothermal method has been studied using high-energy X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and the atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) technique. It was found that the local structure of KNbO nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO
nanoparticles deviates from the average structure. The local structure was found to be rhombohedral structure though the average structure was tetragonal structure. The rhombohedral distortion of NbO octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
octahedra was maintained in the annealed sample.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:94.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:83.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Otsuka, Yoshimasa
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2014/07
We have researched and developed the FNDI method for a long time through experiments in NUCEF in JAEA Tokai. Referred from the pilot machine, we designed a demonstrator, called as JAWAS-N, for applying to non-destructive assay tools for uranium waste drums in JAEA Ningyo. In this paper, we present the modeling and the simulations concerning JAWAS-N's characteristics, and discuss for practical use compared analytical results with obtained some experimental data.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Satoshi; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.879 - 882, 2014/04
PHITS is a general purpose 3-dimensional Monte-Carlo particle transport simulation code developed under collaboration of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Research Organization for Information Science and Technology (RIST), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) and a couple of other institutes in Japan and Sweden. General features of the PHITS code together with details of the established model will be presented at the meeting.
Tokunaga, Tomonori*; Watanabe, Hideo*; Yoshida, Naoaki*; Nagasaka, Takuya*; Kasada, Ryuta*; Lee, Y.-J.*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Tokitani, Masayuki*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Hinoki, Tatsuya*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 442(1-3), p.S287 - S291, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:63.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hashimoto, Shintaro; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; et al.
Igaku Butsuri, 33(2), p.88 - 95, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Zaima, Naoki; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Takase, Misao; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Kureta, Masatoshi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(9), p.913 - 923, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:564 Percentile:99.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)An upgraded version of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS 2.52, was developed and released to public. The new version has been greatly improved from the previous released version, PHITS 2.24, in terms of not only the code itself but also the contents of its package such as attached data libraries. Owing to these improvements, PHITS became a more powerful tool for particle transport simulation applicable to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research.
Hirayama, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sanami, Toshiya*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Osamu*; Takagi, Shunji*; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; Iwai, Satoshi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 55(2), p.83 - 96, 2013/02
, 55(2), p.83 - 96, 2013/02
Since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, units of radiation doses such as Sv have been frequently reported by newspapers. However, it is not exactly understood even by experts on nuclear engineering that there are two different concepts which are the protection quantity such as the effective dose related to a radiation health risk and the practical quantity such as ambient dose equivalents related to measurements. In this special issue, Radiological Protection Quantity, and Operational Quantity and Radiological Protection Quantity, explain the radiation protection dose system including the protection and practical quantities established by ICRP and ICRU. Relation between Dosimeters used at Fukushima etc. and Radiological Protection Quantity describes a method and its problems to measure radiations from Cs on surface and underground using survey meters and personal dosimeters, and convert the measured values to effective doses.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
RIST News, (54), p.14 - 24, 2013/01
Features of the latest version of the PHITS code (version 2.52) is described.
Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Kado, Kazumi; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-33-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2012/10
We developed uranium mass assay systems for 200-litter wastes drums applied passive neutron measurements by NDA method and applied for the actual wastes drums stored in URCP. The neutron measurement methodology of  U(
U( ,n) reaction using
,n) reaction using  He proportional counters delivered superior performance, however also included some problems that the neutron penetration rates are depend upon matrices or density of wastes drums, so it was difficult to determine uranium mass against "unknown objects". For the purpose of solving problems active neutron measurements appears promising, we are now challenging to improve our equipments, which are composed of neutron generator, polyethylene moderators and
He proportional counters delivered superior performance, however also included some problems that the neutron penetration rates are depend upon matrices or density of wastes drums, so it was difficult to determine uranium mass against "unknown objects". For the purpose of solving problems active neutron measurements appears promising, we are now challenging to improve our equipments, which are composed of neutron generator, polyethylene moderators and  He proportional counters. The uranium mass are determined by counting secondary neutrons generated from nuclear fissions. Our preliminary simulations suggest good performances with higher sensitivities and accuracies. It is extremely expected to contribute in the fields of safeguards works.
He proportional counters. The uranium mass are determined by counting secondary neutrons generated from nuclear fissions. Our preliminary simulations suggest good performances with higher sensitivities and accuracies. It is extremely expected to contribute in the fields of safeguards works.
Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Kado, Kazumi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-33-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Ito, Masayasu; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Nagata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Naka, Michihiro; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yamaura, Takayuki; Ide, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-031, 123 Pages, 2012/01
The number of research reactors in the world is decreasing because of their aging. However, the planning to introduce the nuclear power plants is increasing in Asian countries. In these Asian countries, the key issue is the human resource development for operation and management of nuclear power plants after constructed them, and also the necessity of research reactor, which is used for lifetime extension of LWRs, progress of the science and technology, expansion of industry use, human resources training and so on, is increasing. From above backgrounds, the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center began to discuss basic concept of a multipurpose low-power research reactor for education and training, etc. This design study is expected to contribute not only to design tool improvement and human resources development in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center but also to maintain and upgrade the technology on research reactors in nuclear power-related companies. This report treats the activities of the working group from July 2010 to June 2011 on the multipurpose low-power research reactor in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center and nuclear power-related companies.