Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Shibata, Keiichi; Ichihara, Akira; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.09002_1 - 09002_6, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:99.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 2(11), p.1800067_1 - 1800067_8, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.47(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Osamu; Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Ichihara, Akira; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02005_1 - 02005_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Ferroelectrics, 512(1), p.92 - 99, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamanaka, Satoru*; Kim, J.*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Yamada, Noboru*; et al.
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 1(3-4), p.1600020_1 - 1600020_6, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Sato, Toshinori; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Eiichi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Fujita, Tomoo*; Tanai, Kenji; Nakayama, Masashi; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-025, 313 Pages, 2017/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. This report summarizes the results of the Phase II investigations carried out from April 2005 to June 2014 to a depth of 350m. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase II goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to made to be addressed in the Phase II investigations Efforts are made to summarize as many lessons learnt from the Phase II investigations and other technical achievements as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations.
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Noguchi, Akira*; Nakayama, Masashi; Sugita, Yutaka; Suto, Shunkichi; Tanai, Kenji; Fujita, Tomoo; Sato, Haruo*
JAEA-Technology 2016-011, 20 Pages, 2016/07
Cementitious materials are expected to be used for the construction of an underground repository for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Ordinary Portland Cement(OPC) would conventionally be used in the fields of civil engineering and architecture, however, OPC has the potential to generate a highly alkaline plume (pH 12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
Kim, Y.*; Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Ogawa, Takashi*; Serizawa, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Baba, Masaaki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; et al.
Advanced Energy Materials, 5(13), p.1401942_1 - 1401942_6, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:60.17(Chemistry, Physical)An innovative electro-thermodynamic cycle based on temporal temperature variations using pyroelectric effect has been presented. Practical energy is successfully generated in both 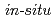 synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements under controlled conditions and
synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements under controlled conditions and 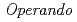 real engine dynamometer experiments. The main generating origin is revealed as a combination of a crystal structure change and dipole change phenomenon corresponds to the temperature variation. In particular, the electric field induced 180
real engine dynamometer experiments. The main generating origin is revealed as a combination of a crystal structure change and dipole change phenomenon corresponds to the temperature variation. In particular, the electric field induced 180 domain switching extremely improves generating power, and the true energy breakeven with temperature variation is firstly achieved.
domain switching extremely improves generating power, and the true energy breakeven with temperature variation is firstly achieved.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.269 - 275, 2013/10
Following the release of radionuclides into the environment as a result of the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had to develop an immediate and effective method of reducing the dose rate received by students in school facilities. A demonstration of a reducing method was carried out by JAEA at a junior high school ground and kindergarten yard in the center of Fukushima-city. Dose rates of the released radionuclides are largely controlled by the ground level contamination and accumulation of mainly cesium-137 ( Cs) and cesium-134 (
Cs) and cesium-134 ( Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5
Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5  Sv/h to 0.15
Sv/h to 0.15  Sv/h.
Sv/h.
Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka; Noguchi, Akira
JAEA-Research 2010-055, 25 Pages, 2011/02
In Japan, any high level radioactive waste repository is to be constructed at over 300 m depth below surface. Tunnel support is used for safety during the construction and operation, and shotcrete and concrete lining are used as the tunnel support. Concrete is a composite material comprised of aggregate, cement and various additives. Low alkaline cement has been developed for the long term stability of the barrier systems whose performance could be negatively affected by highly alkaline conditions arising due to cement used in a repository. JAEA has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC, containing over 60wt% of SF and FA. JAEA are presently constructing an URL at Horonobe for research and development in the geosciences and repository engineering technology. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete material in construction of part of the 140 m deep gallery in Horonobe URL. The objective of this experiment was to assess the performance of HFSC shotcrete in terms of mechanics, workability, durability, and so on. HFSC used in this experiment is composed of 40wt% OPC, 20wt% SF, and 40wt% FA. This composition was determined based on mechanical testing of various mixes of the above components. Because of the low OPC content, the strength of HFSC tends to be lower than that of OPC in normal concrete. The total length of tunnel using HFSC shotcrete is about 73 m and about 500 m of HFSC was used. This experimental construction confirmed the workability of HFSC shotcrete. Although several in-situ experiments using low alkaline cement as shotcrete have been performed at a small scale, this application of HFSC at the Horonobe URL is the first full scale application of low alkaline cement in the construction of a URL in the world. In this report, we present detailed results of the in-situ construction test.
of HFSC was used. This experimental construction confirmed the workability of HFSC shotcrete. Although several in-situ experiments using low alkaline cement as shotcrete have been performed at a small scale, this application of HFSC at the Horonobe URL is the first full scale application of low alkaline cement in the construction of a URL in the world. In this report, we present detailed results of the in-situ construction test.
Nakayama, Masashi; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Noguchi, Akira; Miura, Norihiko*; Noda, Masaru*; Iriya, Keishiro*; Hitomi, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2009-036, 49 Pages, 2009/11
In Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (Horonobe URL) Project, construction practicality test with HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silica-fume Cement) is planned in a part of the gallery. It is necessary to validate that HFSC has performance under the actual construction, before HFSC is placed in the gallery. The main tasks in 2008 are follows; (1) suggestion of mix design for liner concrete of shaft in Horonobe URL, (2) investigation of long term pH changes in order to use for modeling, and (3) an experiment for interaction between HFSC and ground water around Horonobe URL. (1) 4 types of mix proportion are designed for ordinary concrete and high strength concrete which contains polypropylene fiber or not. As early age strength, 5N/mm is required because of concrete formwork. HFSC424 with low water binder ratio can fulfill this requirement in combination with super plasticizer. (2) pH and components of solid and liquid phase which were made in 2003, and stored in water were analyzed. And cement paste of shotcrete which are made in 2006 were also analyzed. In this pH of shotcrete is lower than other in situ concrete since accelerating agent may act as decreasing factor of pH. (3) An experiment which investigates dissolution of HFSC cement hydrates to ground water around Horonobe URL. According to the experiment, dissolving depth of HFSC is 4 times small comparing to Ordinary Portland Cement hydrates after 30th water exchange.
is required because of concrete formwork. HFSC424 with low water binder ratio can fulfill this requirement in combination with super plasticizer. (2) pH and components of solid and liquid phase which were made in 2003, and stored in water were analyzed. And cement paste of shotcrete which are made in 2006 were also analyzed. In this pH of shotcrete is lower than other in situ concrete since accelerating agent may act as decreasing factor of pH. (3) An experiment which investigates dissolution of HFSC cement hydrates to ground water around Horonobe URL. According to the experiment, dissolving depth of HFSC is 4 times small comparing to Ordinary Portland Cement hydrates after 30th water exchange.
 hybrid Monte Carlo and
hybrid Monte Carlo and  path integral hybrid Monte Carlo simulations by using an auxiliary potential energy surface
path integral hybrid Monte Carlo simulations by using an auxiliary potential energy surfaceNakayama, Akira*; Taketsugu, Tetsuya*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemistry Letters, 38(10), p.976 - 977, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.38(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Efficiency of the ab initio hybrid Monte Carlo and  path integral hybrid Monte Carlo methods is enhanced by employing an auxiliary potential energy surface that is used to update the system configuration via molecular dynamics scheme. As a simple illustration of this method, a dual-level approach is introduced where potential energy gradients are evaluated by computationally less expensive ab initio electronic structure methods.
path integral hybrid Monte Carlo methods is enhanced by employing an auxiliary potential energy surface that is used to update the system configuration via molecular dynamics scheme. As a simple illustration of this method, a dual-level approach is introduced where potential energy gradients are evaluated by computationally less expensive ab initio electronic structure methods.
Iida, Yoshihisa; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Tanaka, Tadao; Kitamura, Akira; Nakayama, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Workshop on Mobile Fission and Activation Products in Nuclear Waste Disposal, p.135 - 145, 2009/00
We performed dissolution experiments of iron-selenium compounds from both undersaturation and oversaturation directions to determine the solubility limiting solid of selenium in the presence of iron under anoxic conditions. The solid products was identified to be iron diselenide but the concentration of selenium was 9 orders of magnitude higher than the value calculated from the existing thermodynamic data of FeSe , therefore FeSe
, therefore FeSe was not considered to be the solubility limiting solid. The pH and Eh dependencies of the concentration of selenium were best interpreted as the dissolution reaction of Se(cr), but the concentration of selenium was still 3 orders of magnitude higher than the value calculated from the existing thermodynamic data of Se(cr). Because any selenium compounds other than FeSe
was not considered to be the solubility limiting solid. The pH and Eh dependencies of the concentration of selenium were best interpreted as the dissolution reaction of Se(cr), but the concentration of selenium was still 3 orders of magnitude higher than the value calculated from the existing thermodynamic data of Se(cr). Because any selenium compounds other than FeSe was not detected by XRD and the concentration of selenium was higher than the solubility of Se(cr), the solubility limiting solid was considered to be amorphous selenium.
was not detected by XRD and the concentration of selenium was higher than the solubility of Se(cr), the solubility limiting solid was considered to be amorphous selenium.
Kitamura, Akira; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Sato, Haruo; Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Research 2008-004, 39 Pages, 2008/03
Distribution coefficient of cesium onto bentonite and sedimentary rocks was determined in saline groundwaters. Distribution coefficient of cesium onto the solid phases was also determined in sodium chloride and potassium chloride solutions in order to elucidate sorption behavior of cesium. It was expected that the sorption behavior of cesium was regarded as ion exchange reactions with sorption sites of the solid phases from the results of dependencies of distribution coefficient on pH and ionic strength. It was found that only potassium ion was competed with cesium for the sorption onto sedimentary rocks, while both sodium and potassium ions was competed with cesium for the sorption onto bentonite. It was also found that sorption behavior of cesium onto sedimentary rocks was well described using a model on the sorption of cesium onto illite. The present study was performed in Tokai Works, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (one of the predecessors of JAEA) in FY 2002-2003.
 path integral ring polymer molecular dynamics; Vibrational spectra of molecules
path integral ring polymer molecular dynamics; Vibrational spectra of moleculesShiga, Motoyuki; Nakayama, Akira*
Chemical Physics Letters, 451(4-6), p.175 - 181, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:87.18(Chemistry, Physical)The path integral ring polymer molecular dynamics method is combined with "on-the-fly"  electronic structure calculations and applied to vibrational spectra of small molecules, LiH and H
electronic structure calculations and applied to vibrational spectra of small molecules, LiH and H O, at the room temperature. The results are compared with those of the numerically exact solution and
O, at the room temperature. The results are compared with those of the numerically exact solution and  path integral centroid molecular dynamics calculation. The peak positions in the calculated spectra are found to be reasonable, showing the red shift due to potential anharmonicity. This unification enables the investigation of real-time quantum dynamics of chemically complex molecular systems on the
path integral centroid molecular dynamics calculation. The peak positions in the calculated spectra are found to be reasonable, showing the red shift due to potential anharmonicity. This unification enables the investigation of real-time quantum dynamics of chemically complex molecular systems on the  Born-Oppenheimer potential energy surface.
Born-Oppenheimer potential energy surface.
Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.
Nakayama, Okatsu; Ogawa, Hiroshi*; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Kenji; Tobita, Akira; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-15) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/04
Water experiment using an 1/10th scaled upper plenum model was carried out to investigate thermal stratification after a scram in a compact reactor, which has high velocity local flow in the upper plenum. The experiments showed that the rising speed of the stratification interface was dependent on Richardson number and the temperature gradient of the stratification interface was also influenced by the temperature difference and fluctuation. Furthermore, the temperature gradient could be reduced greatly by changing position of structure in the upper plenum.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ezure, Toshiki; Nakayama, Okatsu; Tobita, Akira; Ito, Masami*; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2006-005, 45 Pages, 2006/03
An innovative sodium cooled fast reactor has been investigated in a frame work of the FBR feasibility study. One of the thermal hydraulic issues in this design is gas entrainment at free surface in the reactor vessel. Dipped plates (D/P) are set below the free surface in order to prevent the gas entrainment. We performed an 1/10th scaled model water experiment for the upper plenum of reactor vessel and flow optimization was done to reduce flow velocity near the free surface. However, previous studies showed that the gas entrainment depends on model scale. Then an 1/1.8th scaled model was also planned to confirm the phenomena in an enough large model. As a test section, 90 degree sector and region between the free surface and the D/P was modeled by 1/1.8th scale. Boundary conditions at D/P gaps and radial cross sections of sector ends were obtained by the 1/10th scaled full sector model. The gas entrainment was not observed in the model under the velocity condition of reactor full power operation at water levels higher than 3% of the normal height from the D/P in the case of double D/Ps geometry (current design). As for the case of single D/P geometry, it was found by the visualization and the velocity measurement that the gas entrainment occurred as the circumferential velocity increased at the water level higher than 50% of the normal height condition. It is shown that the gas entrainment in the reactor vessel will be eliminated in the current design approach.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Tobita, Akira; Kobayashi, Jun; Nakayama, Oukatsu; Ito, Masami*; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2004-067, 48 Pages, 2004/05
An innovative sodium cooled fast reactor has been investigated in a frame work of the FBR feasibility study. A compact reactor vessel is designed to reduce the construction cost, where sodium flow velocity increases. One of the thermal hydraulic issues in this design is gas entrainment at free surface in the reactor vessel. Dipped plates (D/P) are set below the free surface in order to prevent the gas entrainment.We performed an 1/10th scaled model water experiment for the upper plenum of reactor vessel and flow optimization was done to reduce flow velocity near the free surface. However, previous studies showed that the gas entrainment depends on model scale. Then an 1/1.8th scaled model was also planned to confirm the phenomena in an enough large model. As a test section, 90 degree sector and region between the free surface and the D/P was modeled by 1/1.8th scale. Boundary conditions at D/P gaps and radial cross sections of sector ends were obtained by the 1/10th scaled full sector model. The gas entrainment was not observed in the model under the velocity condition of reactor full power operation at water levels higher than 4% of the normal height from the D/P. It is shown that the gas entrainment will be eliminated in the reactor vessel according to the current design approach.