Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 MnSi
MnSi O
O
Kawamata, Masahiro*; Pang, X.*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Masuda, Hidetoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Hanasaki, Noriaki*; Onose, Yoshinori*; Nambu, Yusuke*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ishii, Yui*; Yamamoto, Arisa*; Sato, Naoki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ohara, Koji*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Mori, Takao*; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134111_1 - 134111_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mattan, K.*; Ono, Toshio*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Nambu, Yusuke*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 105(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_8, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
Nambu, Yusuke*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(8), p.081002_1 - 081002_15, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.49(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Chen, Y.*; Sato, Masahiro*; Tang, Y.*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Masaki*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.5199_1 - 5199_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Takahashi, Hidefumi*; Aono, Kai*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Nomoto, Takuya*; Sakano, Masato*; Ishizaka, Kyoko*; Arita, Ryotaro*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*
Physical Review B, 102(17), p.174425_1 - 174425_6, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:65.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The competing magnetic ground states of the itinerant magnet EuCuSb, which has a hexagonal layered structure, were studied via magnetization, resistivity, and neutron-diffraction measurements on single-crystal samples. EuCuSb has a three-dimensional semimetallic band structure as confirmed by band calculation and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy, consistent with the nearly isotropic metallic conductivity in the paramagnetic state. However, below the antiferromagnetic transition temperature of 
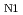 (8.5 K), the resistivity, especially along the hexagonal axis, increases significantly. This implies the emergence of anisotropic magnetic ordering coupled to the conducting electrons. Neutron-diffraction measurements show that the Eu spins, which order ferromagnetically within each layer, are collinearly modulated (up-up-down-down) along the hexagonal axis below
(8.5 K), the resistivity, especially along the hexagonal axis, increases significantly. This implies the emergence of anisotropic magnetic ordering coupled to the conducting electrons. Neutron-diffraction measurements show that the Eu spins, which order ferromagnetically within each layer, are collinearly modulated (up-up-down-down) along the hexagonal axis below 
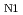 , followed by the partial emergence of helical spin modulation below
, followed by the partial emergence of helical spin modulation below 
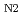 (6 K). Based on the observation of anomalous magnetoresistance with hysteretic behavior, we discuss the competing nature of the ground state inherent in a frustrated Heisenberg-like spin system with a centrosymmetric structure.
(6 K). Based on the observation of anomalous magnetoresistance with hysteretic behavior, we discuss the competing nature of the ground state inherent in a frustrated Heisenberg-like spin system with a centrosymmetric structure.
Nambu, Yusuke*; Barker, J.*; Okino, Yuki*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Enderle, M.*; Weber, T.*; Winn, B.*; Graves-Brook, M.*; Tranquada, J. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 125(2), p.027201_1 - 027201_6, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:94.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
 Cs
Cs Fe
Fe Se
Se
Hawai, Takafumi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Du, F.*; Hirata, Yasuyuki*; Avdeev, M.*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya; Sekine, Yurina; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Ma, J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 91(18), p.184416_1 - 184416_11, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:55.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the iron-based ladder compounds (Ba, Cs)Fe Se
Se , whose parent compounds, BaFe
, whose parent compounds, BaFe Se
Se and CsFe
and CsFe Se
Se , have different space groups, formal valences of Fe and magnetic structures. Electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, X-ray diffraction and powder neutron diffraction measurements were conducted to obtain the temperature and composition phase diagram of this system. Block magnetism seen in BaFe
, have different space groups, formal valences of Fe and magnetic structures. Electrical resistivity, specific heat, magnetic susceptibility, X-ray diffraction and powder neutron diffraction measurements were conducted to obtain the temperature and composition phase diagram of this system. Block magnetism seen in BaFe Se
Se is drastically suppressed with Cs doping. In contrast, stripe magnetism observed in CsFe
is drastically suppressed with Cs doping. In contrast, stripe magnetism observed in CsFe Se
Se more resilient to Ba doping. Novel magnetic structure appears in intermediate compositions, which is similar to the stripe magnetism of CsFe
more resilient to Ba doping. Novel magnetic structure appears in intermediate compositions, which is similar to the stripe magnetism of CsFe Se
Se but with different inter-ladder spin configuration. Intermediate compounds show insulating behavior, nevertheless finite T-linear contribution in specific heat was obtained at low temperature.
but with different inter-ladder spin configuration. Intermediate compounds show insulating behavior, nevertheless finite T-linear contribution in specific heat was obtained at low temperature.
 Se
Se
Nambu, Yusuke*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Du, F.*; Avdeev, M.*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Munakata, Koji*; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Chi, S.*; Ueda, Yutaka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 85(6), p.064413_1 - 064413_5, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:91.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetism in the insulating BaFe Se
Se was examined through susceptibility, specific heat, resistivity and neutron diffraction measurements. After formation of a short-range magnetic correlation, a long-range ordering was observed below
was examined through susceptibility, specific heat, resistivity and neutron diffraction measurements. After formation of a short-range magnetic correlation, a long-range ordering was observed below 
 255 K. The transition is obscured by bulk properties. Magnetic moments are arranged to form a Fe
255 K. The transition is obscured by bulk properties. Magnetic moments are arranged to form a Fe ferromagnetic unit, and each Fe
ferromagnetic unit, and each Fe stacks antiferromagnetically. This block magnetism is of the third type among magnetic structures of ferrous materials. The magnetic ordering drives unusually large distortion via magnetoelastic coupling.
stacks antiferromagnetically. This block magnetism is of the third type among magnetic structures of ferrous materials. The magnetic ordering drives unusually large distortion via magnetoelastic coupling.
 Ga
Ga O
O showing thermal Hall effect
showing thermal Hall effectMori, Michiyasu; Fujita, Masaki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Urlich, C.*; Sushkov, O. P.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Ga
Ga O
O having thermal Hall effect
having thermal Hall effectFujita, Masaki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Urlich, C.*; Sushkov, O. P.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Xu, P. G.; Ojima, Mayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Nambu, Shoichi*; Inoue, Junya*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Harjo, S.; Akita, Koichi
no journal, ,