Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.295 - 307, 2021/10
Kirihara, Yoichi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sanami, Toshiya*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Takemoto, Akinori*; Yamaguchi, Masashi*; Asano, Yoshihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.444 - 456, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:63.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(3), p.119 - 126, 2014/09
A method of deducing the I-131 concentration in a radioactive plume from the time history of peak count rates determined from pulse height spectra obtained from an NaI(Tl)scintillation detector employed as a detector of a monitoring post was presented. The concentrations of I-131 in the plumes were estimated from the count rates using the calculated response of the NaI(Tl) detector with egs5 for a model of a plume uniformly containing I-131. This method was applied to the data from the monitoring posts at Nuclear Science Research Institutes of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The estimated time history variation of I-131 concentrations in plumes was in fair agreement with those measured directly by an air sampling method. The difference was less than a factor of 4 for plumes that arrived on March 15 and March 21, indicating relatively high I-131 concentrations among the plumes studied in this work.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(2), p.264 - 271, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.18(Biology)Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site is basic information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. To estimate RBE, lineal energy,  , can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of
, can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of  distributions,
distributions, 
 (
( ), for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He, 290 MeV/u C, 490 MeV/u Si and 500 MeV/u Ar. Data of
), for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He, 290 MeV/u C, 490 MeV/u Si and 500 MeV/u Ar. Data of 
 (
( ) were also obtained in the wide range of LET. The dose-means of
) were also obtained in the wide range of LET. The dose-means of  ,
, 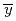
 , were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated
, were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated 
 (
( ) and
) and 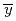
 agree fairly well with those measured. The values of
agree fairly well with those measured. The values of 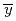
 are larger than those of LET less than
are larger than those of LET less than  10 keV/
10 keV/ m because of the discrete energy deposition by delta rays, while the relation is reversed above 10 keV/
m because of the discrete energy deposition by delta rays, while the relation is reversed above 10 keV/ m. The results indicate that care should be taken in the difference between
m. The results indicate that care should be taken in the difference between 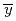
 and LET when the values of RBE of energetic heavy ions are estimated.
and LET when the values of RBE of energetic heavy ions are estimated.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
KEK Proceedings 2011-8, p.100 - 108, 2011/12
Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site is basic information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. To estimate RBE, lineal energy, y, can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of y distributions, 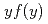 , for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He and 490 MeV/u Si ion beams. Data of
, for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He and 490 MeV/u Si ion beams. Data of 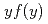 and the dose-means of
and the dose-means of  ,
, 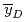 , were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated
, were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated 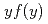 and
and 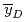 agree fairly well with those measured, as well as the already reported result of 290 MeV/u carbon beam.
agree fairly well with those measured, as well as the already reported result of 290 MeV/u carbon beam.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-136, p.219 - 220, 2011/11
Measurements of lineal energy distribution were employed using 160 MeV proton and 490 MeV/u Si. The calculated 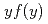 by PHITS and
by PHITS and 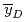 agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of
agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of 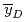 was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
 carbon beam
carbon beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.450 - 454, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.88(Environmental Sciences)A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter, wall-less TEPC, has been designed and used for the measurement of the y distributions for energetic heavy ions in order to verify a biological dose calculation model incorporated in the PHITS code. It is found that the dose-mean value of y obtained by the wall-less TEPC is 50 - 60% of the LET of the argon ions in water, since the delta-rays with relatively low y can be measured.
 C beam
C beamTsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 55(17), p.5089 - 5101, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.44(Engineering, Biomedical)The frequency distribution of the lineal energy of 290 MeV/u carbon beam was measured using a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) in a cylindrical volume with simulated diameter 0.72  m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
m in verifying the accuracy of a dose calculation model. The measured lineal energy distribution as well as its dose-mean value agreed fairly well with the corresponding data from microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code within the experimental uncertainty. It is found that a wall-less TEPC is needed to measure the precise energy deposition spectra of the delta rays produced secondarily by energetic heavy ion beams. The measured data also indicate that more than 11% of the energy escaped from the path of the trajectory of the carbon beam.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-134 (CD-ROM), p.227 - 228, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
KEK Proceedings 2009-12, p.36 - 44, 2010/01
Knowledge of energy deposition at micrometer dimensions along heavy ion tracks is essential to understand the biological effects of radiation. Wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (wall-less TEPC) was produced for the purpose of measurement of lineal energy distribution including secondary-produced high-energy electrons, delta-rays. The measurement using the wall-less TEPC was performed at Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator at NIRS, Japan. It is found that lineal energy distributions could be measured for primary carbon beam with energy of 400MeV per nucleon and delta-rays. Detail of the experiment, energy calibration and estimation of delta-rays production will be presented.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sasaki, Shinichi*
KEK Proceedings 2009-6, p.90 - 95, 2009/11
Deposit energy distributions of secondary high-energy electrons, delta-rays, have been calculated in a wall/wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter, TEPC, using Monte Carlo simulation code EGS5. It is found that wall-less TEPCs are indispensable for lineal energy distribution in tissue equivalent gas irradiated by energetic heavy ion beams.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
NIRS-M-226, HIMAC-132, p.264 - 265, 2009/06
A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter was designed and applied to measuring deposit energy distribution of heavy ion beams, including the contribution of delta-rays produced along heavy ion tracks. Lineal energy distributions were obtained for 400 MeV/u carbon and 490 MeV/u silicon beams.
Asano, Yoshihiro; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Tanaka, Shunichi; Namito, Yoshihito*; Ban, Shuichi*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Nariyama, Nobuteru*
IRPA9: 1996 International Congress on Radiation Protection, Proceedings, p.4_253 - 4_255, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Namito, Yoshihito*; Ban, Shuichi*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Nariyama, Nobuteru*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Asano, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Shunichi
Physical Review A, 51(4), p.3036 - 3043, 1995/04
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:91.00(Optics)no abstracts in English
; Tanaka, Shunichi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Namito, Yoshihito*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Ban, Shuichi*;
Health Physics, 68(2), p.253 - 260, 1995/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.82(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Asano, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Shunichi; Ban, Shuichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Hirayama, Hideo*;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 365, p.553 - 558, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.87(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
; Tanaka, Shunichi; Yoshizawa, Michio; Hirayama, Hideo*; Ban, Shuichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 310, p.696 - 702, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:79.84(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Mori, Seiji*; ; Kawai, Masayoshi*; ; Sakurai, Kiyoshi; Shin, Kazuo*; Sekimoto, Hiroshi*; Oyama, Yukio; et al.
JAERI-M 87-203, 230 Pages, 1987/12
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
no journal, ,
Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site is basic information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. To estimate RBE, lineal energy, y, can be an appropriate physical index. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been designed and used for the measurement of y distributions, yf(y), for 160 MeV H, 150 MeV/u He, 290 MeV/u C, 490 MeV/u Si and 500 MeV/u Ar. Data of yf(y) were also obtained in the wide range of LET. The dose-means of y, yD, were compared with those calculated by the microdosimetric function of PHITS. It is found that the calculated yf(y) and yD agree fairly well with those measured. The values of yD are larger than those of LET less than 10 keV/um because of the discrete energy deposition by delta rays, while the relation is reversed above 10 keV/um. The results indicate that care should be taken in the difference between yD and LET when the values of RBE of energetic heavy ions are estimated.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Ban, Shuichi*; Takada, Masashi*
no journal, ,
Knowledge of energy deposition at micrometer dimensions along heavy ion tracks is essential to understand the biological effects of radiation. Wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter (TEPC) was produced for the purpose of measurement of lineal energy distribution of delta-rays. The measurement using the TEPC was performed at Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator at NIRS, Japan. It is found that lineal energy distributions could be measured for primary carbon beam with energy of 400MeV per nucleon and delta-rays. Detail of the experiment, energy calibration and estimation of delta-rays production will be presented.