Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nanjo, Kotaro; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nanjo, Kotaro; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1407 - 1416, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ise, Kotaro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Nanjo, Isao*; Asano, Takahiro*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Geomicrobiology Journal, 34(6), p.489 - 499, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.45(Environmental Sciences)We investigated the change in bacterial community structure after drilling boreholes, 09-V250-M02 and 09-V250-M03 in the 250 m depth research gallery of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL). In 09-V250-M02,  -Proteobacteria was predominantly detected in the clone library analyses of the groundwater samples conducted immediately after drilling the borehole. All these
-Proteobacteria was predominantly detected in the clone library analyses of the groundwater samples conducted immediately after drilling the borehole. All these  -Proteobacteria clones are closely related to
-Proteobacteria clones are closely related to 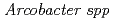 . which is known as sulfide oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacteria. After four years, the microbial structure was drastically changed and most detected OTUs were uncultured species such as candidate division OP9 and Chloroflexi relatives which are frequently detected in deep-sea sediments.
. which is known as sulfide oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacteria. After four years, the microbial structure was drastically changed and most detected OTUs were uncultured species such as candidate division OP9 and Chloroflexi relatives which are frequently detected in deep-sea sediments.
Ise, Kotaro; Nanjo, Isao; Amamiya, Hiroki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Asano, Takahiro*; Kageyama, Koji*; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amano, Yuki; Sasaki, Yoshito; Nanjo, Isao*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Mizuno, Takashi; Ise, Kotaro; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
Continuous monitoring of groundwater chemistry of the boreholes during the facility construction indicated that the salinity around 140 m have not changed from the beggining to date. Water pressures within the area several tens to hundreds meter from the shafts also went down in process of time. Regarding the chemical disturbance in the area, the redox potencial of the groundwaters in the monitoring boreholes showed reducing condition nevertheless the gallery is in oxidized condition. However, microbial community structure changed considerably from the beggining to date. These results indicate that microbial redox reaction could contribute to maintain of reducing conditions in the groundwater system, despite of hydrochemical disturbance caused by facility construction.