Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nankawa, Takuya
Shikizai Kyokai-Shi, 98(1), p.2 - 6, 2025/01
The use of lacquer in Japan has a very long history dating back to the Jomon period. Lacquer painting is known for its beautiful colors and superior resistance to chemicals and seawater compared to today's petroleum products. Despite these excellent properties, it is very difficult to measure the structure of lacquer films, which cause the excellent physical properties and few people have investigated about it. In this study, we focused on the interactions between urushiol in raw lacquer and black lacquer and by using quantum beams, and we analyzed the nano-structure in raw lacquer and black lacquer, which is responsible for the color difference.
Takahara, Yuta*; Beni, Yusuke*; Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Fukazawa, Tomoko*
ACS Omega (Internet), 9(45), p.45554 - 45563, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:37.20(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nankawa, Takuya
Kagaku, 79(8), p.48 - 52, 2024/08
Lacquer is a natural paint with excellent water and chemical resistance. It has long been known that adding a very small amount of iron into raw lacquer produces a very beautiful black color called Shikoku. However, the structure and reactions of lacquer are still largely unknown, and the reason of black color is also unclear. In this study, we analyzed the structure of raw lacquer and black lacquer films by using different kind of quantum beams. As a result, black lacquer has a completely different nanostructure from raw lacquer, and that the color changes depending on the difference in the structure. This result is the first successful analysis of the structure of the lacquer film, which had been a mystery for many years. This commentary describes this research and also explains how this research has been proceeded.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 23(2), p.50 - 63, 2024/06
Selective separation of radioactive ions is essential for reducing or cleaning radioactive wastes. Among the radioisotopes to be removed,  Sr poses a major threat to human health and the environment. However, removal of
Sr poses a major threat to human health and the environment. However, removal of  Sr from environmental wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating
Sr from environmental wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating  Sr
Sr from Ca
from Ca . Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Samarium (Sm) to Thulium (Tm) for application to selective removal of
. Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Samarium (Sm) to Thulium (Tm) for application to selective removal of  Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. The LOFs had ion exchangeable anionic pores, in which the size of the pores changed in a stepwise manner depending on the host Ln species. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr
Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. The LOFs had ion exchangeable anionic pores, in which the size of the pores changed in a stepwise manner depending on the host Ln species. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius (0.2
selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius (0.2  ) between Sr
) between Sr and Ca
and Ca . The Sr
. The Sr selectivity was higher than that of conventional adsorbents. The pore size tuning of the LOFs by selecting the constituent Ln species yielded a highly ion-selective adsorbent material. This novel strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
selectivity was higher than that of conventional adsorbents. The pore size tuning of the LOFs by selecting the constituent Ln species yielded a highly ion-selective adsorbent material. This novel strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Shibayama, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Nanoscale, 16(19), p.9400 - 9405, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.71(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A tough carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMF)/ zirconium (Zr) hydrogel was obtained by freeze cross-linking method. The hydrogel was prepared by adding HCl solution containing Zr to frozen CMF and thawing it. The hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for fluoride. This simple gelation method provides useful insight for developing hydrogel-metal complexes.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Oba, Yojiro*; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shibayama, Yuki; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Carbohydrate Polymers, 327, p.121538_1 - 121538_11, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.68(Chemistry, Applied)We describe non-toxic, tough nanocellulose (NC) hydrogels formed from chemically unmodified NC by cellulose crystalline transformation and subsequent freeze cross-linking reaction. Using low-concentration NaOH and freezing together induced the crystalline transformation of NC from cellulose I to II via freeze concentration. After the crystalline transformation, cross-linking between the NC and CA in the freeze concentration layer (FCL) provided a strong NC network structure, forming NC hydrogels with high mechanical strength. The freeze-cross-linked NC hydrogel easily retained powder adsorbents in its inner space by mixing the NC-NaOH sol and the powder, and the hydrogel showed high removal efficiency for heavy metals. The results highlight the versatility of chemically unmodified celluloses in developing functional materials, suggest possible practical applications.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Matsumura, Daiju; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takata, Shinichi; Kamiya, Yoshimi*; Honda, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 40(11), p.5725 - 5730, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The chemical reaction between Fe and lacquer has been used to create the black color lacquer since ancient times. Here, the chemical state of Fe ions in black lacquer was investigated by using X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), and Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Fe(II) or Fe(III) was added to the lacquer paste to prepare black lacquer films by air drying, heating, or UV irradiation. The XANES spectral features of all the film samples were similar, meaning that the Fe ions in the samples existed in the trivalent state regardless of the oxidation state of the initially added Fe. The corresponding Fourier transforms of the EXAFS spectra around the Fe K-edge were used to investigate Fe sites in the lacquer films. The spectra of all the film samples were similar shapes, but the peak intensities decreased in the order air dried  heated
heated  UV irradiated films. This result indicates that heating and UV irradiation made the coordination structure of Fe in the lacquer non-uniform, and that heating caused the greatest non-uniformity. The complementary use of XANES, XAFS, and FT-IR spectroscopy is highly effective for non-destructive analysis of black lacquer in precious cultural artifacts.
UV irradiated films. This result indicates that heating and UV irradiation made the coordination structure of Fe in the lacquer non-uniform, and that heating caused the greatest non-uniformity. The complementary use of XANES, XAFS, and FT-IR spectroscopy is highly effective for non-destructive analysis of black lacquer in precious cultural artifacts.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 96(10), p.1150 - 1155, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.62(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The phase separation of ice crystals and solutes and bound water that occurs during freezing can be used as a reaction field to control a hierarchical structure of hydrogels. Here, we present a study of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogels formed using the solid-quasi liquid phase separation. CMCF hydrogels were formed simply by adding citric acid to frozen CMCF and thawing the mixture. It was found that rearrangement of CMCF structures via hydrogen bonding proceeds in the freeze concentration layer before the ice crystals melt. Under freeze concentration, CMCF and bound water are confined at high concentrations. The crosslinking reaction in such a unique space contributed to the formation of CMCF hydrogel with high mechanical strength. We discuss the gelation behavior and properties of freeze crosslinked CMCF hydrogels and their applications.
Miura, Daisuke*; Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Oba, Yojiro; Hiroi, Kosuke; Ozawa, Tatsuhiko
Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications (Internet), 4, p.100251_1 - 100251_9, 2022/12
The reaction mechanism of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel formed by freeze-crosslinking was investigated. We succeeded in observing the hierarchical structural changes during the freeze-crosslinking reaction. Freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels exhibited a characteristic hierarchical alignment structure from the angstrom to micrometer scale that differed from normal cross-linked CMCF hydrogels produced by a conventional method without freezing. It was shown that the characteristic hierarchical structure contributes the excellent mechanical properties of freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 95(5), p.825 - 829, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.12(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Advances in hazardous metal ion removal are essential for wastewater clean-up to tackle the global water shortage crisis. Here, we report a Pb-selective adsorbent using a Tb oxalate framework (TOF) synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal method. The TOF has a two-dimensional sheet structure, in which the interlayer space functions as an ion exchangeable site. Sorption tests using a mixed-ion solution containing Pb , Cd
, Cd , Mn
, Mn , Co
, Co , Ni
, Ni , Cu
, Cu , Na
, Na , K
, K , Mg
, Mg , and Ca
, and Ca showed that the TOF has high selectivity for Pb
showed that the TOF has high selectivity for Pb among other metal ions. The saturated adsorption capacity of the TOF for Pb
among other metal ions. The saturated adsorption capacity of the TOF for Pb was 276 mg g
was 276 mg g , which is higher than that of conventional adsorbents. Furthermore, the TOF exhibited reversible Pb
, which is higher than that of conventional adsorbents. Furthermore, the TOF exhibited reversible Pb adsorption/desorption and could be used for at least three cycles. The results showed that TOF has excellent potential as an adsorbent for removing Pb
adsorption/desorption and could be used for at least three cycles. The results showed that TOF has excellent potential as an adsorbent for removing Pb , and because of its reusability, it is also a promising material for wastewater clean-up.
, and because of its reusability, it is also a promising material for wastewater clean-up.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina
Isotope News, (778), p.34 - 35, 2021/12
A high-performance adsorbent was synthesized by reaction of waste bone and sodium hydrogen carbonate. Since waste bones are inexpensive and well-supplied materials, it has the potential to be used for a wide range of decontamination and removal of harmful metals.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Takeguchi, Masaki*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kozai, Naofumi; Morooka, Satoshi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), p.105114_1 - 105114_12, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:44.55(Engineering, Environmental)Remediating toxic ion contamination is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. This study aimed to provide a powerful strategy for effectively utilizing bone waste from the food production and preparation industries for removal of toxic ions. Here, we show that immersing pig bone in NaHCO solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr
solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr , Cd
, Cd , Pb
, Pb , and Cu
, and Cu . The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
. The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya
Chem-Station (Internet), 1 Pages, 2021/03
We will explain the experimental results and the background of the research that developed a highly efficient toxic metal adsorbent using wastebone as a raw material.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yunoki, Shunji*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Teppei*
ACS Applied Polymer Materials (Internet), 2(12), p.5482 - 5491, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:94.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We developed a cross-linking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a new type of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel with high compressive strength ( 80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
Kuwahara, Akira; Aiba, Yasuaki*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Nankawa, Takuya; Matsui, Makoto*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 33(7), p.1150 - 1153, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.07(Chemistry, Analytical)Although high-temperature plasma sources have been used for direct isotope analysis of solid samples, the spectral resolution of diode laser absorption spectroscopy in high-temperature plasma is limited by the Doppler broadening of atomic absorption lines. Thus, a decrease in translational temperature is necessary to enhance the spectral resolution and distinguish isotope shifts due to mass number. In this study, a supersonic plasma wind tunnel, also called an arc-jet plasma wind tunnel, was used to enhance spectral resolution drastically, and a demonstration was carried out using natural stable xenon isotopes. As a result, the temperature was found to be about 180 K and the spectral resolution was about one order of magnitude higher than that of the conventional high-temperature source. Additionally, the method proposed herein was verified by using two xenon isotopes.
Kuwahara, Akira; Aiba, Yasuaki*; Nankawa, Takuya; Matsui, Makoto*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 33(5), p.893 - 896, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.82(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 adsorption
adsorption  lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water molecules
lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water moleculesIshizaki, Manabu*; Akiba, Sae*; Otani, Asako*; Hoshi, Yuji*; Ono, Kenta*; Matsuba, Mayu*; Togashi, Takanari*; Kanaizuka, Katsuhiko*; Sakamoto, Masatomi*; Takahashi, Akira*; et al.
Dalton Transactions, 42(45), p.16049 - 16055, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:195 Percentile:99.56(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have revealed the fundamental mechanism of specific Cs adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs
adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe
adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe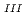
 [Fe
[Fe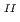 (CN)
(CN) ]3
]3 xH
xH O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH
O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH )0.70Fe
)0.70Fe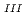 1.10[Fe
1.10[Fe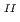 (CN)
(CN) ]
] 1.7H
1.7H O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs
O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe
adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe and 3[Fe
and 3[Fe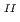 (CN)
(CN) ]
]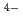 , showed much more efficient Cs
, showed much more efficient Cs adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Nankawa, Takuya; Onuki, Toshihiko
Chemistry Letters, 42(8), p.888 - 890, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.61(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Chen, R.*; Tanaka, Hisashi*; Kawamoto, Toru*; Asai, Miyuki*; Fukushima, Chikako*; Na, H.*; Kurihara, Masato*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Arisaka, Makoto; Nankawa, Takuya
Electrochimica Acta, 87, p.119 - 125, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:94.44(Electrochemistry)A novel electrochemical adsorption system using a nanoparticle film of copper (II) hexacyanoferrate (III) was proposed for selectively removing cesium from wastewater. This system can be used for cesium separation without extra chemical reagents or any filtration treatment. Cesium uptake and elution can be simply controlled by switching the applied potentials between anodes and cathodes. Data from batch kinetic studies well fitted the intraparticle diffusion equation, reflecting a two-step process: a steepest ascent portion followed by a plateau extending to the equilibrium. The effective cesium removal with a high distribution coefficient (

 5
5 10
10 mL/g) can be adopted in a large pH range from 0.3 to 9.2, and in the presence of several diverse coexisting alkaline cations, suggesting it can be taken as a promising technology for actual nuclear wastewater treatment.
mL/g) can be adopted in a large pH range from 0.3 to 9.2, and in the presence of several diverse coexisting alkaline cations, suggesting it can be taken as a promising technology for actual nuclear wastewater treatment.