Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formationFujiwara, Satoru*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Matsumoto, Tomoharu*; Narita, Tetsuhiro*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Molecular Biology, 431(17), p.3229 - 3245, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:49.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) -synuclein (
-synuclein ( Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.
Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.  Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of
Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of  Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of
Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of  Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of
Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of  Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 10, p.367 - 373, 2012/07
To apply organic thin films as new devices, it is important to immobilize organic molecules on oxide surfaces. In this study, we investigated the formation of organic self-assembled monolayer on the oxide surface. Decyl phosphonic acid (DPA) molecules were used as the adsorbed molecule on the surface. The DPA film was prepared by immersing the sapphire substrate in DPA ethanol solution. The sample was measured by XPS using synchrotron soft X-ray. For the P 1s XPS spectra of the DPA powder and the DPA film on the sapphire surface, a single peak was observed and the binding energies of the two samples were almost the same. And we measured the sample by the total reflection (TR) XPS, which is highly surface sensitive method. Compared with the normal XPS, the intensity of the C 1s peak in TR-XPS was enhanced. As a result, it was elucidated that the phosphonic acid of the DPA molecule was located at the lower side, while the alkyl chain was located at the upper side on the surface.
Baba, Yuji; Narita, Ayumi; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Entani, Shiro; Sakai, Seiji
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 10, p.69 - 73, 2012/04
We report on the first results for the geometrical determination of adsorbed atoms on an oxide by a soft-X-ray sanding wave method. The samples investigated were alkyl phosphonic acid (C10) adsorbed on a sapphire surface, which is one of the candidate systems for organic self-assembled monolayer (SAM) on oxides. The surface was irradiated by synchrotron soft X-rays from the surface normal. The intensity of photoelectrons was plotted as a function of the photon energy. We observed clear profiles of the photoelectron intensity due to the standing wave from the substrate. Compared with the simulation using the crystal parameters, it was found that the phosphorus atoms are located at 0.11 nm from the surface, while the constant height was not observed for carbon atoms. The results are in consistent with the results by XPS and NEXAFS; the molecules form SAM on the sapphire surface with phosphonic acids and alkyl chains are located at the upper side.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Applied Surface Science, 258(6), p.2034 - 2037, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.46(Chemistry, Physical)In order to apply the organic thin films to electric and optical devices, the immobilization of organic molecules on inorganic substrate is essential. Considering optical devices, it is important to immobilize organic molecules on oxide surfaces, because many of oxides have insulating and transparent properties. In this study, we have investigated the chemical states of the interface between organic molecules with silicon alkoxide and sapphire surfaces by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and near edge absorption fine structure (NEXAFS). Octadecyl-triethoxy-silane (ODTS) molecules which are terminated by silicon alkoxide were adsorbed on sapphire surfaces. On the basis of the Si 1s XPS spectra for monolayer, it is supposed that the chemical bond between silicon alkoxide and the surface is formed. For Si K-edge NEXAFS spectra, the polarization dependence was observed, which suggests that the Si-O bond in ODTS was located perpendicular to the surface.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Photon Factory Activity Report 2011, Part B, P. 94, 2012/00
Immobilization of organic molecules on oxide surface has been investigated using phosphonic acid as an anchor. The molecule investigated was decyl-phosphonic acid (DPA). The DPA film was formed by immersing the sapphire substrate in DPA ethanol solution. The results for X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) showed that the alkyl chain of the DPA molecules is located at the upper side, while the phosphonic acid is the lower side on the surface. The XPS and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) results indicated that the DPA film became homogeneous monolayer by heating at 250 C. It is concluded that the phosphonic acid is an excellent anchor that immobilizes the organic molecules on an oxide surface.
C. It is concluded that the phosphonic acid is an excellent anchor that immobilizes the organic molecules on an oxide surface.
Baba, Yuji; Narita, Ayumi; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Entani, Shiro; Sakai, Seiji
Photon Factory Activity Report 2011, Part B, P. 201, 2012/00
no abstracts in English
Mannan, M. A.*; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Narita, Ayumi; Nagano, Masamitsu*; Noguchi, Hideyuki*
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 181(2-3), p.242 - 248, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.03(Spectroscopy)The ordering and molecular orientation of polydimethylsilane (PDMS) films grown on indium tin oxide (ITO) surface has been assigned. The orientation of the samples as well as that of the annealed sample was studied by Si K-edge near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using linearly polarized synchrotron radiation. The Si K-edge NEXAFS spectra for the thick film have at least four resonance peaks of which two peaks are found to be strongly polarization dependent. On the basis of the polarization dependences of the peak intensities, it is revealed that the backbones of the PDMS films are perpendicularly oriented on the ITO surface. The angle between surface and the Si-Si bonds for multilayered film calculated from the helical structure of PDMS molecule was found to be 41.5  which was almost coincided with the experimentally obtained angle of 40
which was almost coincided with the experimentally obtained angle of 40  . It was concluded that PDMS molecules are highly self-ordered on ITO surface.
. It was concluded that PDMS molecules are highly self-ordered on ITO surface.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Narita, Ayumi; Deng, J.*
Surface and Interface Analysis, 42(6-7), p.863 - 868, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:1.68(Chemistry, Physical)Metal phthalocyanines (Pc) have attracted growing attention due to potential application as organic semiconductors or light emitters. Recently it has been pointed out that orientation of Pc molecules is one of key properties that improve the career mobility. We studied orientation property of Si-phthalocyanine thin films using synchrotron radiation. We report on following topics: (1) Orientation analysis using polarized X-rays, (2) Effect of metal substrates and annealing on orientation, (3) Analysis aided by molecular orbital method, and (4) New method to observe chemical-bond directions in nanometer scale using combined techniques of polarized X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy and photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM).
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Narita, Ayumi; Deng, J.
Surface Science, 603(16), p.2612 - 2618, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.98(Chemistry, Physical)The morphology, electronic structure and ordering for micropatterns of silicon phthalocyanine thin films on gold have been investigated at nanometer scale by photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) excited by polarized soft X-rays from synchrotron light source. The incident angle dependences of the X-ray absorption fine structure (XANES) spectra at the silicon K-edge revealed that the molecules of 5-layered films are lying nearly flat on the surface. Clear image of the micropattern was observed by PEEM at room temperature, while the surface diffusion was observed upon heating. On the basis of the photon-energy dependences of the brightnesses in the PEEM images, it was found that the molecules diffusing to the fresh gold surface rather stand-up at 240 C. The observed changes in the molecular orientations at nanometer domains are discussed on the basis of the strengths of the molecular-molecular and molecular-surface interactions.
C. The observed changes in the molecular orientations at nanometer domains are discussed on the basis of the strengths of the molecular-molecular and molecular-surface interactions.
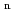 H
H (n
(n 2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiation
2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiationNarita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(8), p.489 - 494, 2008/08
The formation of molecular ions and neutral molecules from adsorbed CH , CD
, CD and N
and N following 1 keV He
following 1 keV He ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
 ) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C
) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C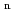 H
H
 ) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C
) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C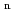 H
H ) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He
) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He
energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He ions and adsorbed molecules.
ions and adsorbed molecules.
Honda, Mitsunori; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Narita, Ayumi
Proceedings of 25th European Conference on Surface Science (ECOSS-25), p.644 - 645, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
 at nanometer scale by photoelectron emission microscopy combined with synchrotron radiation
at nanometer scale by photoelectron emission microscopy combined with synchrotron radiationBaba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Deng, J.; Narita, Ayumi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 100, p.012015_1 - 012015_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.80(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Chemical-state-selective mapping of micro-patterns for silicon compounds has been demonstrated using photoelectron emission microscopy excited by soft X-rays from synchrotron light source. The samples investigated were micro-patterns of silicon oxides, silicon nitrides, and organic silicon compounds. By scanning the X-ray energy around the Si  -edge, we succeeded in observing the sub-micron images depending on the valence states. When we annealed the sample, the lateral diffusion was observed from 700
-edge, we succeeded in observing the sub-micron images depending on the valence states. When we annealed the sample, the lateral diffusion was observed from 700 C. During the annealing, however, no intermediate valence states were observed at the Si-SiO
C. During the annealing, however, no intermediate valence states were observed at the Si-SiO interfaces. It was elucidated that the diffusion of oxygen induced the sudden changes of the Si valence states from Si
interfaces. It was elucidated that the diffusion of oxygen induced the sudden changes of the Si valence states from Si to Si
to Si without any intermediate valence states. The results for the chemical-state-selective mappings and lateral diffusions are also presented for organic silicon compounds.
without any intermediate valence states. The results for the chemical-state-selective mappings and lateral diffusions are also presented for organic silicon compounds.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Narita, Ayumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Narita, Ayumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Baba, Yuji; Hirao, Norie*; Narita, Ayumi; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Photon or electron irradiation breaks chemical bond and induces desorption of fragment. However, formation of chemical bond from adsorbed light molecules, such as methane, by high energy radiation has scarcely been reported. This process is important in space, because organic molecules can be formed through these reactions. In this report, we have investigated formation of molecular ions and neutral molecules with covalent bond from frozen methane by He+ ion irradiation. It was found that acetylene ion(C2H2+), and ethylene ion(C2H4+) with covalent bond were formed by He+ ion irradiation. These results were compared with Monte-Carlo simulation for energy-loss processes of He+ ions in solid methane. As a result, it was elucidated that molecular ions are formed inside of frozen methane by high-density excitation due to nuclear collision. On the other hand, neutral molecules are formed by rapid evaporation due to temperature increase along the nuclear track.
 interface by PEEM using synchrotron radiation
interface by PEEM using synchrotron radiationHirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Narita, Ayumi
no journal, ,
The electrical properties of Si-based semiconductor devices such as SOI depend on the valence state of silicon at the Si-SiO interface. In order to observe valence states of a solid surface at nanometer scale, we have developed a photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) system combined with synchrotron soft X-ray. The samples investigated were micropattern of Si and SiO
interface. In order to observe valence states of a solid surface at nanometer scale, we have developed a photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) system combined with synchrotron soft X-ray. The samples investigated were micropattern of Si and SiO prepared by ion implantation. We have observed the chemical state at the Si-SiO
prepared by ion implantation. We have observed the chemical state at the Si-SiO interface and the lateral diffusion of the valence states, during the annealing. Compared to the previously reported longitudinal diffusion, two differences are found in the present lateral diffusion, i.e., (1) the diffusion temperature is lower than that of longitudinal diffusion by 300
interface and the lateral diffusion of the valence states, during the annealing. Compared to the previously reported longitudinal diffusion, two differences are found in the present lateral diffusion, i.e., (1) the diffusion temperature is lower than that of longitudinal diffusion by 300 C, and (2) the intermediate valence states are absent at the Si-SiO
C, and (2) the intermediate valence states are absent at the Si-SiO interface. These differences are interpreted by the volatile property of SiO molecules, i.e., SiO released from surface during the diffusion.
interface. These differences are interpreted by the volatile property of SiO molecules, i.e., SiO released from surface during the diffusion.