Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ,
,  ') reaction of
') reaction of  U on the target thickness
U on the target thicknessNegm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Zen, H.*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Hori, Toshitada*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.811 - 820, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)The dependence of the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) yield on the target thickness was studied. To this end, an NRF experiment was performed on  U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)
U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)  -ray beam at the High Intensity
-ray beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source facility at Duke University.
-ray Source facility at Duke University.
 -ray source at JAEA 150-MeV microtron
-ray source at JAEA 150-MeV microtronHajima, Ryoichi; Ferdows, M.; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.1943 - 1945, 2014/07
 (Ce) detectors near 2 MeV
(Ce) detectors near 2 MeVOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Bakr, M.*; Zen, H.*; Hori, Toshitada*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.102 - 107, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)The performance of LaBr (Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident
(Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident  -rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B
-rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B C target to excite the
C target to excite the  B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr
B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr (Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
(Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
 U measured with high-resolution LaBr
U measured with high-resolution LaBr (Ce) scintillation detectors
(Ce) scintillation detectorsOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Zen, H.*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_4, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.20(Physics, Applied)A nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) experiment was performed on a  U target with quasi-monochromatic
U target with quasi-monochromatic  -rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr
-rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr (Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr
(Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr (Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr
(Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr (Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
(Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Minato, Futoshi; Daito, Izuru*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
no journal, ,
Nuclear electric or magnetic dipole transitions can be studied by nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). The NRF process takes place via only the electromagnetic (EM) interaction. Since the EM interaction is well-known, the information on the nuclear dipole excitation can be obtained in a nuclear model-independent way. We used a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam produced by inverse Compton scattering of laser light with high energy electrons at the NewSUBARU electron storage ring facility of Hyogo University. A natural Cr target with a 1-cm diameter and a 3-cm length was irradiated by photon beams with the maximum energies of 8.2, 8.8, 9.4, 10, 11, and 12 MeV. Scattering photons were measured by three high purity Ge detectors with relative efficiencies of 100 to 140%. Two of the Ge detectors were horizontally or vertically placed at the scattering angle of 90 . The polarization of the photon beams was fixed to the horizontal plane.
. The polarization of the photon beams was fixed to the horizontal plane.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Zen, H.*; Omer, M.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi
no journal, ,
Recently, a nondestructive measurement method of shielded fissional isotopes such as  U or
U or  Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy
Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy  -ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered
-ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered  -rays from NRF with LCS
-rays from NRF with LCS  -ray beams using the LaBr
-ray beams using the LaBr (Ce) detectors. The LaBr
(Ce) detectors. The LaBr (Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope
(Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope 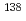 La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as
La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as 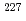 Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of
Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of  -rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of
-rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of  U using the LCS
U using the LCS  -rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF
-rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF  -rays plus the Compton scattered
-rays plus the Compton scattered  -ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr
-ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr (Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr
(Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr (Ce).
(Ce).
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Minato, Futoshi; Daito, Izuru*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
no journal, ,
Mono-energetic and linearly polarized (LCS)  -rays can be generated by Compton scattering of laser light with high energy electrons. In nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF), spins of the excited states and their transition probabilities can be extracted in a model independent way. In addition, by using high polarization of LCS
-rays can be generated by Compton scattering of laser light with high energy electrons. In nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF), spins of the excited states and their transition probabilities can be extracted in a model independent way. In addition, by using high polarization of LCS  -rays, it is possible to precisely determine multipolarity (E1 or M1) of the NRF
-rays, it is possible to precisely determine multipolarity (E1 or M1) of the NRF  -rays, i.e., parities of the excited states. We have performed NRF measurements at the NewSUBARU electron ring facility of University of Hyogo. LCS
-rays, i.e., parities of the excited states. We have performed NRF measurements at the NewSUBARU electron ring facility of University of Hyogo. LCS  -rays with maximum energies of 8.2, 8.8, 9.4, 10, 11, and 12 MeV were used to irradiate a natural Cr target. From results of the measurements we have determined the parities of the excited states below the neutron separation energy of about 12 MeV. In this paper, we will report the results of the measurements and the comparison of the dipole strength distribution with the RPA calculation.
-rays with maximum energies of 8.2, 8.8, 9.4, 10, 11, and 12 MeV were used to irradiate a natural Cr target. From results of the measurements we have determined the parities of the excited states below the neutron separation energy of about 12 MeV. In this paper, we will report the results of the measurements and the comparison of the dipole strength distribution with the RPA calculation.
 -rays
-raysHajima, Ryoichi; Kando, Masaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Negm, H.*; Hori, Toshitada*; Fujimoto, Shinya*; Sakai, Fumio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English